Ctla4
-
Official Full Name
Ctla4 cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 -
Overview
CD152 is a 33 kD member of the immunoglobulin superfamily also known as CTLA-4 or Ly-56. It is expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes. CD152 is similar to CD28 in amino acid sequence, structure, and genomic organization and these two receptors share common B7 family counter-receptors (B7-1, B7-2). Whereas CD28 delivers a costimulatory signal in T cell activation, CTLA-4 negatively regulates cellmediated immune responses. CD152 is thought to play a role in the induction and maintenance of immunological tolerance, as well as the development of protective immunity and thymocyte regulation. -
Synonyms
CD;GSE;GRD4;ICOS;CD152;CTLA-4;IDDM12;CELIAC3;cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4;CD152 isoform;celiac disease 3;cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4;cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4;cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated serine esterase-4;cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4 short spliced form;ligand and transmembrane spliced cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4;Ipilimumab;Yervoy;477202-00-9;Ticilimumab (= tremelimumab);745013-59-6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Monkey
- Rat
- Mouse
- Dog
- Bovine
- Cynomolgus
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus
- Canine
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Guinea pig
- Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
- Mus musculus
- Insect Cell
- HEK293
- Human Cell
- Yeast
- NS1
- CHO
- HEK293 cells
- Mammalian Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- Mammalian cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- Hamster
- E.coli expression system
- His
- Fc
- His&Fc
- mFc&Avi
- His&Avi
- Non
- Twin Strep
- Fc&Avi
- His&Flag&StrepII
- GST
- His&Flag
- mIgG2a
- His&T7
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- N-His and C-His
- His&Myc&SUMO
- C-rFc
- N-Twin-Strep&C-His-Avi
- N-Twin-Strep
- Strep
- His&GST
- His&SUMO
- APC
Background

Fig1. CTLA-4 expressing cells. (Parviz Azimnasab-Sorkhabi, 2023)
What is CTLA4 protein?
CTLA4 gene (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q33. This gene is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and encodes a protein which transmits an inhibitory signal to T cells. The protein contains a V domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. The membrane-bound isoform functions as a homodimer interconnected by a disulfide bond, while the soluble isoform functions as a monomer. The CTLA4 protein is consisted of 223 amino acids and CTLA4 molecular weight is approximately 24.7 kDa.
What is the function of CTLA4 protein?
CTLA4 competitively inhibits CD28 ligand binding through high affinity binding to B7 molecules (CD80 and CD86), thereby transmitting inhibitory signals to T cells and reducing T cell activation and proliferation. CTLA4 can act as a competitive ligand through its extracellular domain to prevent the transmission of CD28 signals and thus inhibit T cell activation. CTLA4 is expressed in Treg cells, contributing to their inhibitory function and maintaining immune tolerance. The cytoplasmic tail of CTLA4 contains a YVKM motif that binds PI3K, PP2A, and SHP-2, as well as a proline-rich motif that binds SH3, which is involved in intracellular signaling. CTLA4 has been shown to interact with a variety of proteins, such as AP2M1, CD80, CD86 and SHP-2, and is involved in the regulation of immune responses.
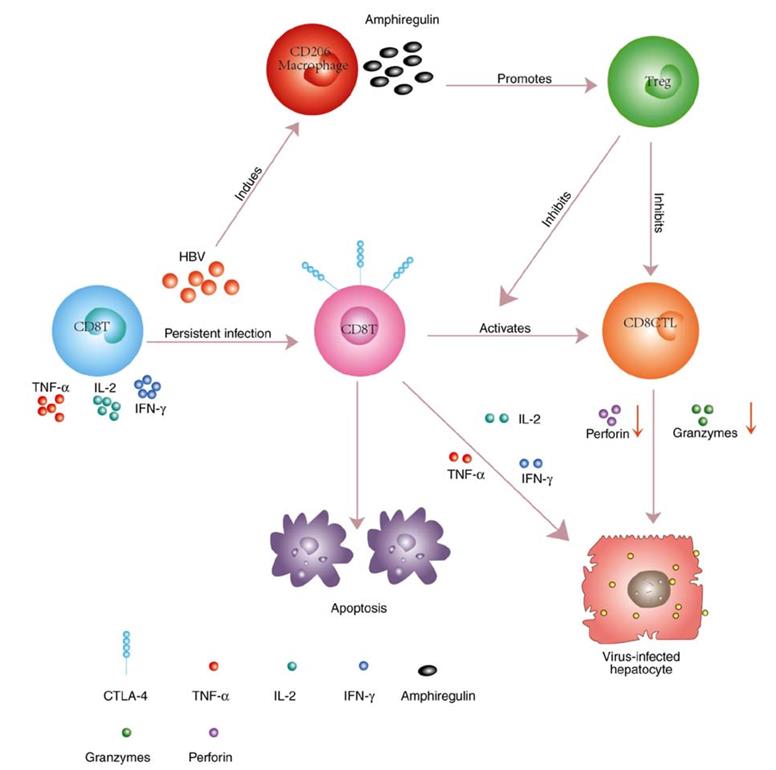
Fig2. Persistent HBV infection results in the upregulation of CTLA-4 and Bim on hepatic CD8+ T cells. (Hui Cao, 2018)
CTLA4 Related Signaling Pathway
In the co-stimulatory signaling pathway, CTLA4 shares the B7 molecule (CD80 and CD86) ligand with CD28. Unlike CD28, CTLA4 induces T cell nonresponsiveness after binding to the B7 molecule, thereby inhibiting T cell overactivation. The cytoplasmic tail of CTLA4 contains moieties that can bind PI3K, PTEN, SHP-2 and PP2A and participate in intracellular signaling processes. These molecules are involved in the regulation of T cell proliferation, survival and differentiation. CTLA4 is a highly endocytotic receptor, which can regulate its expression level on the cell surface through endocytosis, thus affecting the activation state of T cells.
CTLA4 Related Diseases
Mutations in the CTLA4 gene are associated with autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, Graves' disease, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), thyroid-associated orbital disease, and primary biliary cirrhosis. CTLA4 haploidy deficiency leads to CTLA4 deficiency or CHAI disease (CTLA4 haploidy deficiency with autoimmune infiltration), which is a rare genetic disorder of the immune system that can lead to immune system disorders and may lead to lymphocyte proliferation, autoimmunity, hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent infections, and possibly a slightly increased risk of lymphoma. It is also associated with solid tumors such as melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Bioapplications of CTLA4
CTLA4 inhibitors, such as ipilimumab (Yervoy), enhance the immune system's attack on tumors by blocking the binding of CTLA4 to its ligand and are important drugs in tumor immunotherapy. Biologic drugs based on CTLA4, such as Orencia (abatacept) and Nulojix (belatacept), have been developed to treat autoimmune diseases, and there are multiple CTLA4-related drugs in clinical trials. CTLA4 acts as an immune checkpoint molecule that, by binding to its ligand B7 molecule, transmits inhibitory signals to T cells and attenuates excessive immune responses, and is therefore a potential target for the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases. The expression level and functional status of CTLA4 can be used as biomarkers for certain diseases, such as autoimmune diseases and tumors, and contribute to the diagnosis and prognosis assessment of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Adish Zhansaya, 2022
The use of chimeric proteins that selectively interact with various immune cell receptors to treat oncology patients has increased. One effective way to obtain recombinant proteins is to use the E. coli expression system. However, in eukaryotic protein production in E. coli, several difficulties arise that can be solved by fusing the target protein with thioredoxin. Thioredoxin can enhance solubility, but its large size can lead to an erroneous assessment of protein solubility, folding, and activity. The present study examined the ligand-binding activity of PD-L1, and CTLA-4 receptors fused with thioredoxin. The de novo synthesized genes of the extracellular domains of the PD-L1 and CTLA-4 were cloned into the pET28 and pET32 expression plasmids and used to transform E. coli BL21 cells. Purified recombinant proteins were characterized by western blotting, LC-MS/MS spectrometry, and ELISA. This study revealed that the fusion of thioredoxin with recombinant proteins through linkers slightly affected the activity of the extracellular domains of CTLA-4 and PD-L1.
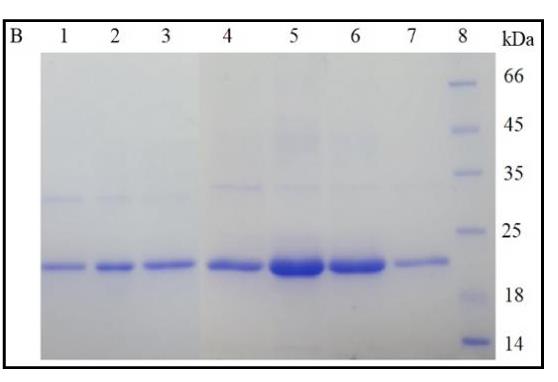
Fig1. SDS-PAGE of purified rCTLA-4.

Fig2. ELISA to assess the binding of recombinant CTLA-4 proteins to recombinant B7-1Fc proteins.
Case Study 2: Jaclyn Stromp Peraino, 2013
Researchers have recently expressed and purified the recombinant soluble porcine CTLA-4 both with and without N-glycosylation in yeast Pichia pastoris for in vivo use in preclinical swine model. In this study researchers have linked each of the glycosylated and non-N-glycosylated soluble porcine CTLA-4 proteins to the truncated diphtheria toxin DT390 through genetic engineering yielding three versions of the porcine CTLA-4 fusion toxins. Protein synthesis inhibition analysis demonstrated that while all three fusion toxins are capable of inhibiting protein synthesis in vitro, the non-N-glycosylated porcine CTLA-4 isoforms function most efficiently. Binding analysis using flow cytometry of the porcine CTLA-4 fusion toxins to LCL13271 cells also demonstrated that the non-N-glycosylated porcine CTLA-4 isoforms bind to these cells with higher affinity compared to the glycosylated fusion toxin. The monovalent non-N-glycosylated porcine CTLA-4 fusion toxin was tested in vivo. This recombinant protein may therefore provide a novel approach for in vivo depletion of porcine antigen presenting cells (APCs) for studies investigating the induction of transplantation tolerance, autoimmune disease and cancer treatment.

Fig3. SDS Gel Analysis of the Three Porcine CTLA-4 Fusion Toxins.

Fig4. In vitro Protein Synthesis Inhibition Analysis of the Three Porcine CTLA-4 Fusion Toxins.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
Ctla4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Ctla4 participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Autoimmune thyroid disease,CTLA4 inhibitory signaling, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Ctla4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes | EGR4,IRF4,DGKA,BATF3,JUNB,EGR2,EGR3,CSF2,CDK4,EGR1 |
| Immune System | ASB14,HAVCR2,TXN,BST2,TREX1,SIGLEC10,RNF14,BTR12,NCKAP1,BTR16 |
| Costimulation by the CD28 family | BTLA,THEM4,HLA-DQB2,MAP3K8,CSK,PDPK1A,MAPKAP1 |
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | CD99,CLDN11B,CD40,HLA-DRB4,LRRC4B,CD274,CLDN17,CADM3,Siglec1,HLA-B |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | ATP6V0C,TNFRSF11A,ATP6V1G1,CXCL1,TNF,CCL3,IL17A,LTB,Ccl12,GM-CSF |
| Adaptive Immune System | DNM2,LTN1,ARIH2,CLEC2H,ERAP1,DYNLL2,CD300E,SIGLEC7,RASGRP1,KLRB1A |
| Autoimmune thyroid disease | IL10,IFN-a,OSTN,CGA |
Protein Function
Ctla4 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Ctla4 itself. We selected most functions Ctla4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Ctla4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | PIP5K1B,HILPDA,DTX1,AKR1A1,C2orf50,TRIM24,KHDRBS3,SNRPB,MST1R,HIPK1 |
Interacting Protein
Ctla4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Ctla4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Ctla4.
CD86;PIK3R1;CD80;FYN;STAT5A;STAT5B;RAPGEF1;RAB8A;TRIM25;LAX1
Resources
Research Area
Cancer Drug TargetsITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules
B7/CD28 Family
T Cell Markers
CD Antigen (Helper T Cells)
Co-stimulatory Molecules
Thymus-Dependent B Cell Activation
Dendritic Cell Co-stimulatory Molecules
Immune Checkpoints
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Venditti, O; De Lisi, D; et al. Ipilimumab and immune-mediated adverse events: a case report of anti-CTLA4 induced ileitis. BMC CANCER 15:-(2015).
- Garin, EH; Reiser, J; et al. Case series: CTLA4-IgG1 therapy in minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY 30:469-477(2015).

.jpg)
.jpg)

