IVD of Hepatitis A Virus
Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is the causative agent of hepatitis A and belongs to the genus hepatovirus in the family Picornaviridae. Transmitted through the fecal-oral route, HAV invades the human body through the mouth and intestines and is eventually located in the liver, the main target organ, causing liver damage. Detection of HAV antibodies in serum or plasma is the main means of diagnosing HAV infection. Its specific indicators include anti-HAV IgM antibodies, IgG antibodies, or anti-HAV total antibodies.
Main Steps of IVD for Hepatitis A Virus
- Serological testing, including antigen and antibody testing. ELISA was used to detect anti-HAV IgM and anti-HAV IgG in patient serum.
- Isolation of HAV using cell culture methods.
- The isolated virus is identified by detecting cytopathic effects, virus antigen structure, virus biological characteristics, etc.
- Use molecular biology techniques, such as gene chips and RT-PCR to detect the genetic sequence of the virus to determine the genotype and subtype of the virus.
- HAV exists in the patient's blood, stool, and liver cytoplasm. IVD can quickly determine whether the patient is infected with HAV by testing the antigens and antibodies in the patient's serum.
Creative BioMart provides high-quality recombinant HAV proteins used for IVD, including ELISA, lateral flow assays, western blots, and other immunoassays.
Highlights of Our Products
- High sensitivity, high specificity, and high purity.
- It is widely used and suitable for downstream immunological experiments.
- Easy to store and transport, conducive to large-scale production and use of vaccines.
- Outstanding success rate and fast development speed.
Our Outstanding Advantages
- IVD proteins can be used to test for a variety of diseases and conditions, making them valuable tools for diagnosing and monitoring health.
- Guarantee high performance, high reliability, and high consistency of protein quality, leading the industry.
- A complete IVD protein platform can provide customized services to meet different scientific research needs.
- High-quality service, high-level experiments, and reliable analysis.
In addition, Creative BioMart also offers a series of viral proteins and protein-related services to provide customers with high-quality, low-cost active recombinant proteins to meet different needs and assist in preclinical drug development.
Case Study
Case 1: Pintó RM, Pérez-Rodríguez FJ, Costafreda MI, Chavarria-Miró G, Guix S, Ribes E, Bosch A. Pathogenicity and virulence of hepatitis A virus. Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1174-1185. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1910442. PMID: 33843464; PMCID: PMC8043188.
Hepatitis A is an acute infection of the liver, which is mostly asymptomatic in children and increases the severity with age. Although in most patients the infection resolves completely, in a few of them it may follow a prolonged or relapsed course or even a fulminant form. The reason for these different outcomes is unknown, but it is generally accepted that host factors such as the immunological status, age and the occurrence of underlaying hepatic diseases are the main determinants of the severity. However, it cannot be ruled out that some virus traits may also contribute to the severe clinical outcomes. In this review, we will analyze which genetic determinants of the virus may determine virulence, in the context of a paradigmatic virus in terms of its genomic, molecular, replicative, and evolutionary features.
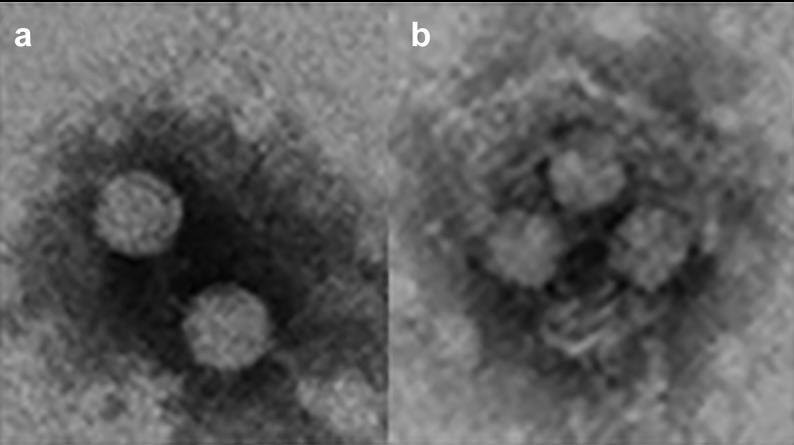 Fig1. HAV exists in a dual phenotype. (a) Naked virions are shed in the feces of infected patients and are responsible for the fecal host-to-host transmission (b). Quasi-enveloped virions are present in the blood and are responsible for the cell-to cell transmission and occasionally parenteral host-to-host transmission. These images were obtained in our lab from supernatants of HuH7 cells infected with the HM175-43 c strain of HAV.
Fig1. HAV exists in a dual phenotype. (a) Naked virions are shed in the feces of infected patients and are responsible for the fecal host-to-host transmission (b). Quasi-enveloped virions are present in the blood and are responsible for the cell-to cell transmission and occasionally parenteral host-to-host transmission. These images were obtained in our lab from supernatants of HuH7 cells infected with the HM175-43 c strain of HAV.Case 2: Nainan OV, Xia G, Vaughan G, Margolis HS. Diagnosis of hepatitis a virus infection: a molecular approach. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;19(1):63-79. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.63-79.2006. PMID: 16418523; PMCID: PMC1360271.
Recent advances in methods to identify and characterize nucleic acid markers of viral infections have provided the foundation for the field of molecular epidemiology and increased our knowledge of the molecular biology and epidemiology of HAV. Although HAV is primarily shed in feces, there is a strong viremic phase during infection which has allowed easy access to virus isolates and the use of molecular markers to determine their genetic relatedness. In addition, these new diagnostic methods have provided tools for the rapid detection of food-borne HAV transmission and identification of the potential source of the food contamination.
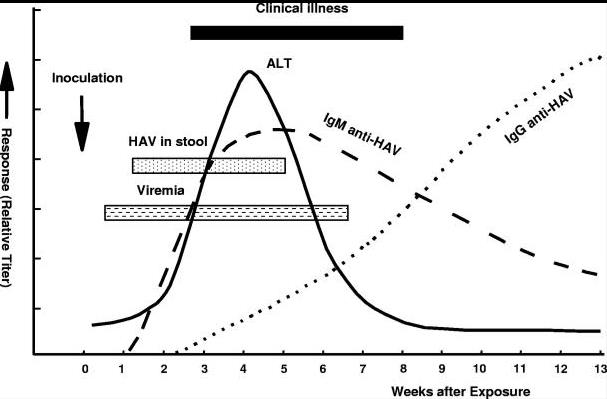 Fig1. Virologic, immunologic and biochemical events during the course of experimental hepatitis A virus infection in chimpanzees inoculated intravenously with human HAV, strain HLD2. ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
Fig1. Virologic, immunologic and biochemical events during the course of experimental hepatitis A virus infection in chimpanzees inoculated intravenously with human HAV, strain HLD2. ALT, alanine aminotransferase.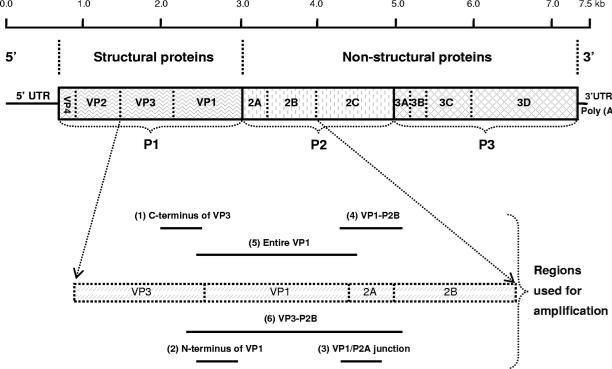 Fig2. Schematic representation of the HAV genome organization, translation products, and regions used for amplification. The area encoding the polyprotein is represented by solid box and the proposed cleavage sites by vertical lines. Regions commonly used for PCR amplifications are as follows: region 1, C terminus of VP3 region (nt 2,020 to nt 2,226); region 2, N terminus of VP1 region (nt 2,172 to nt 2,415); region 3, VP1/P2A junction region (nt 2,984 to nt 3,217); region 4, VP1-P2B region (nt 2,896 to nt 3,289); region 5, entire VP1 region (nt 2,172 to nt 3,125); and region 6, VP3-P2B region (nt 2,133 to nt 3,289). Nucleotide position numbering is according to the HM175 sequence.
Fig2. Schematic representation of the HAV genome organization, translation products, and regions used for amplification. The area encoding the polyprotein is represented by solid box and the proposed cleavage sites by vertical lines. Regions commonly used for PCR amplifications are as follows: region 1, C terminus of VP3 region (nt 2,020 to nt 2,226); region 2, N terminus of VP1 region (nt 2,172 to nt 2,415); region 3, VP1/P2A junction region (nt 2,984 to nt 3,217); region 4, VP1-P2B region (nt 2,896 to nt 3,289); region 5, entire VP1 region (nt 2,172 to nt 3,125); and region 6, VP3-P2B region (nt 2,133 to nt 3,289). Nucleotide position numbering is according to the HM175 sequence.Case 3: Sasaki-Tanaka R, Shibata T, Moriyama M, Kogure H, Hirai-Yuki A, Okamoto H, Kanda T. Masitinib Inhibits Hepatitis A Virus Replication. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 3;24(11):9708. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119708. PMID: 37298659; PMCID: PMC10253910.
The hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection causes acute hepatitis. HAV also induces acute liver failure or acute-on-chronic liver failure; however, no potent anti-HAV drugs are currently available in clinical situations. For anti-HAV drug screening, more convenient and useful models that mimic HAV replication are needed. In the present study, the researchers established HuhT7-HAV/Luc cells, which are HuhT7 cells stably expressing the HAV HM175-18f genotype IB subgenomic replicon RNA harboring the firefly luciferase gene. Then, they investigated whether 1134 US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs exhibited in vitro anti-HAV activity.
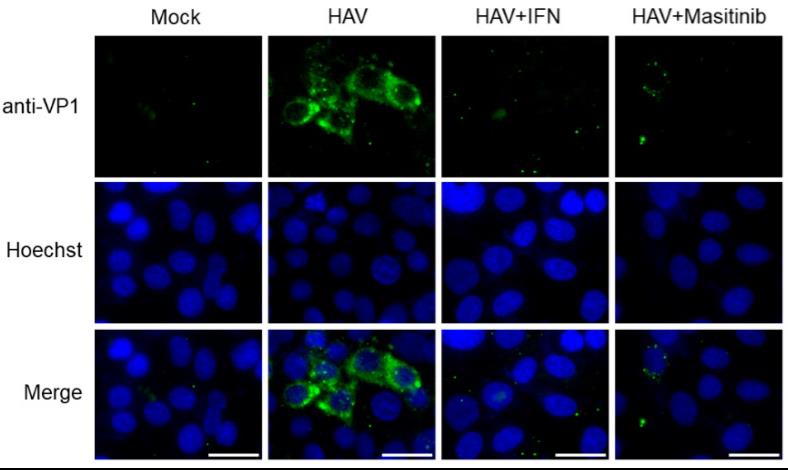 Fig1. Immunofluorescence analysis of hepatitis A virus (HAV) HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells. Antibodies against HAV VP1 are shown in green, and nuclei stained with Hoechst are shown in blue [17,21]. Positive immunofluorescence staining observed for HAV VP1 in HAV-infected cells but not in the uninfected cells (Mock) [21]. HAV HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells treated with 10 µM masitinib reduced HAV VP1 staining. HAV HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells treated with 0.1 μg/mL interferon-α-2a (IFN) stained with HAV VP1 as the control. Scale bar: 25 μm.
Fig1. Immunofluorescence analysis of hepatitis A virus (HAV) HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells. Antibodies against HAV VP1 are shown in green, and nuclei stained with Hoechst are shown in blue [17,21]. Positive immunofluorescence staining observed for HAV VP1 in HAV-infected cells but not in the uninfected cells (Mock) [21]. HAV HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells treated with 10 µM masitinib reduced HAV VP1 staining. HAV HM175-18f genotype IB-infected Huh7 cells treated with 0.1 μg/mL interferon-α-2a (IFN) stained with HAV VP1 as the control. Scale bar: 25 μm.Reference
- Wang X, Ren J, Gao Q, et al. (2015). Hepatitis A virus and the origins of picornaviruses[J]. Nature. 517(7532): 85-88.
