IFNB1
-
Official Full Name
interferon, beta 1, fibroblast -
Overview
Has antiviral, antibacterial and anticancer activities. -
Synonyms
IFNB1;interferon, beta 1, fibroblast;IFB;IFF;IFNB;interferon beta;IFN-beta;fibroblast interferon
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rabbit
- Mouse
- Pig
- Rhesus macaque
- Equine
- Cattle
- Dog
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Horse
- HEK293
- Yeast
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Pseudomonas Fluorescens
- Human
- Human Cells
- CHO
- Fibroblast
- Fc
- Non
- mFc
- His
- GST
- Avi
Background
What is IFNB1 protein?
IFNB1 gene (interferon beta 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9p21. This gene encodes a cytokine that belongs to the interferon family of signaling proteins, which are released as part of the innate immune response to pathogens. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the type I class of interferons, which are important for defense against viral infections. Following secretion in response to a pathogen, type I interferons bind a homologous receptor complex and induce transcription of genes such as those encoding inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The IFNB1 protein is consisted of 187 amino acids and IFNB1 molecular weight is approximately 22.3 kDa.
What is the function of IFNB1 protein?
IFNB1 protein is a cytokine that plays a key role in the innate immune response. It activates the Jak-STAT signaling pathway by binding to the high-affinity IFNAR2 and low-affinity IFNAR1 heterodimer receptors, thereby promoting transcriptional activation or inhibition of interferon-regulated genes such as antiviral proteins, cell proliferation and differentiation regulators, and immunomodulators. In addition, IFNB1 also plays a role in regulating B-cell development, myeloid cell generation, and tumor necrosis factor production. In the nervous system, IFNB1 protects dopaminergic neurons and maintains neurohomeostasis by promoting neuronal autophagy and α-synuclein clearance. In terms of tumor control, IFNB1 is more potent than interferon alpha and is able to induce apoptotic and anti-proliferative pathways needed to control tumor cell growth.
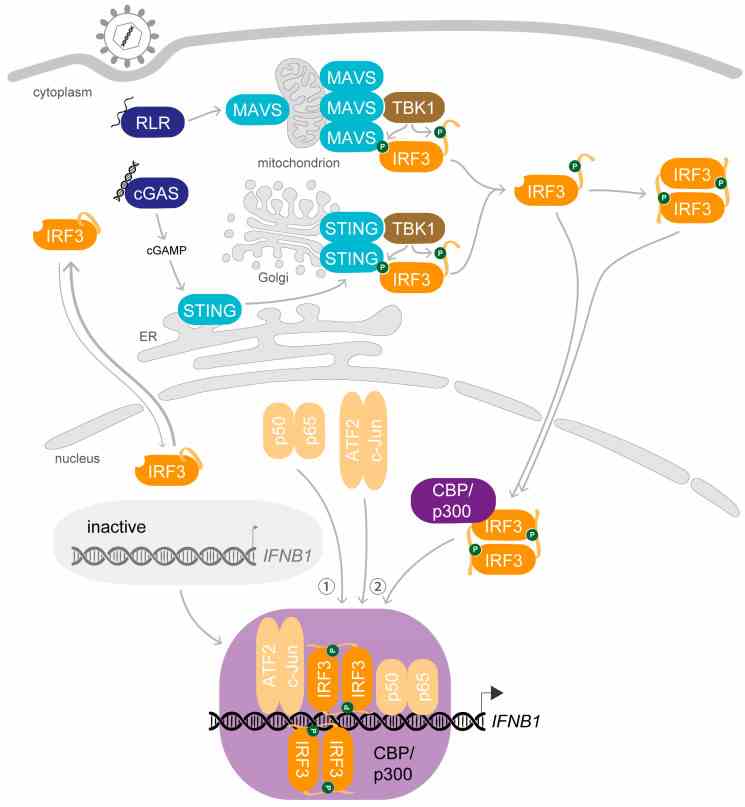
Fig1. IRF3 activation induces transcription of IFNB1 upon viral infection. (Hella Schwanke, 2020)
IFNB1 related signaling pathway
IFNB1 (interferon β-1) is a multifunctional cytokine that primarily plays a role in immune response. By binding to its receptors IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, it activates the downstream JAK-STAT signaling pathway, thereby regulating the expression of multiple genes. IFNB1 binds to the receptor, causing a conformational change that allows JAK1 and TYK2 kinases to approach and phosphorylate the receptor, and the phosphorylated receptor-JAK complex recruits and activates STAT1, STAT2, and STAT3 STAT family members. In addition, IFNB1 can induce the expression of multiple antiviral genes, inhibit the growth and proliferation of tumor cells, and induce the apoptosis of tumor cells. IFNB1 can regulate the differentiation and function of immune cells, such as promoting the differentiation of Th1 cells, inhibiting the differentiation of Th2 cells, and enhancing the activity of NK cells. IFNB1 can induce the production of other types of interferons (such as IFNA, IFNG, etc.) to further enhance the immune response.
IFNB1 related diseases
IFNB1 is a key cytokine that has been implicated in a variety of diseases, including antiviral response, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), some types of cancer, and possibly the development of inflammatory diseases. It is activated by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), triggering signaling pathways that enhance cell resistance to viral infection and affect tumor immune surveillance. In addition, IFNB1 expression is associated with a variety of immunomodulatory processes, including cellular responses to viruses, B-cell proliferation, and defense responses to other organisms. Its abnormal expression or function may be associated with type I interferon disease, a group of diseases caused by mutations in specific genes that cause a multisystem inflammatory response throughout the body.
Bioapplications of IFNB1
IFNB1 plays a key role in a variety of biological applications. It mainly activates downstream signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT by binding to specific cell surface receptors, thereby promoting the expression of antiviral proteins, inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, and regulating immune response. Clinically, IFNB1 is widely used to treat multiple sclerosis, certain types of cancer, and certain viral infections. In addition, it is also used to study immune response and predictive markers in tumor immunotherapy, helping to predict a patient's response to immunotherapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Olena Kourko, 2023
In prostate cancer patients, NK cells show changes that correlate with better outcomes. For late-stage patients, NK cell-based immunotherapies are a potential treatment after traditional options fail. Researchers investigated how to enhance NK cell anti-cancer activity. This study found that combining IL-27 with poly(I:C) in advanced prostate cancer cell lines stimulated IFN-β secretion, key for activating NK cells to kill cancer cells. PC3 cells were more vulnerable to NK cell killing, linked to higher IFN-β levels. This treatment also increased NK cell granzyme B and TRAIL expression, partially mediating the killing of PC3 cells. Our findings offer insights into enhancing NK cell cytotoxicity against prostate cancer.
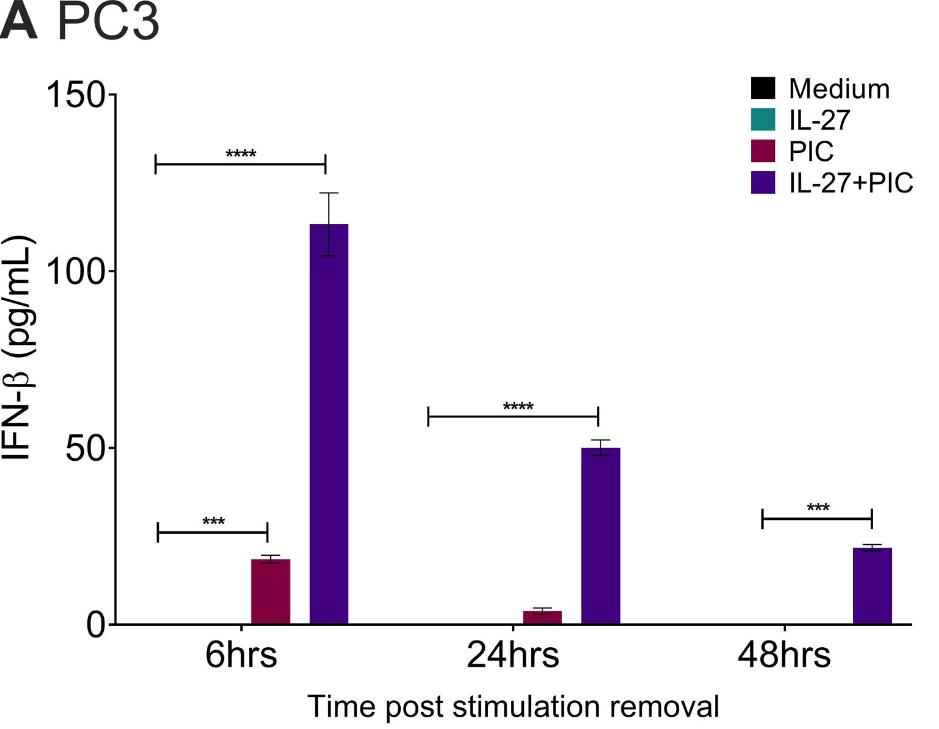
Fig1. IL-27 enhances poly(I:C)-mediated expression of IFN-β of PC3 cells.
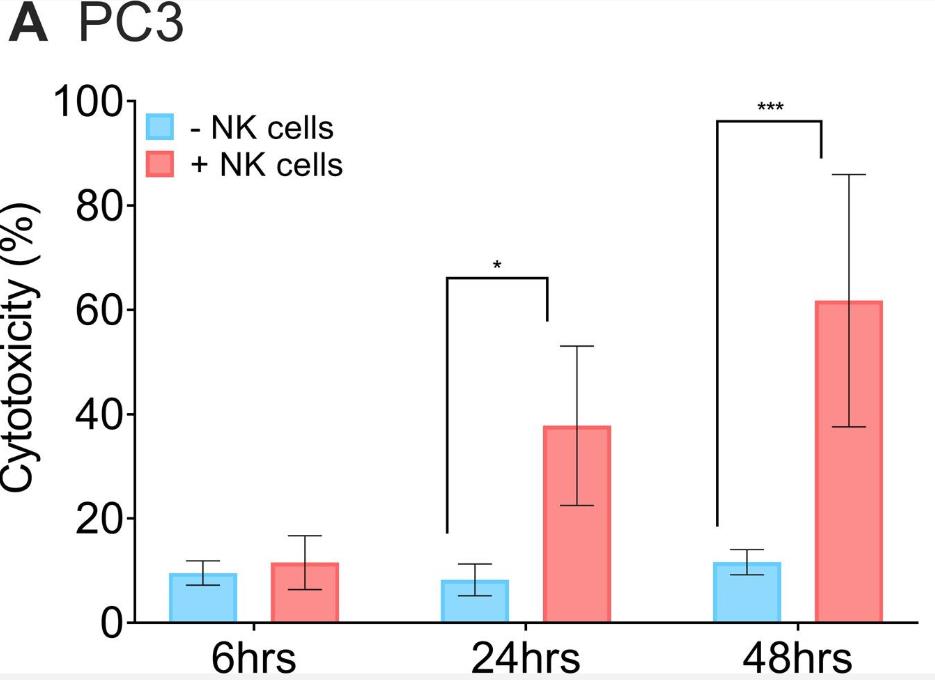
Fig2. NK cells are cytotoxic toward PC3 cells after addition of rIFNβ.
Case Study 2: Mateusz Gawrysiak, 2024
Human rhinovirus 16 (HRV16) can trigger inflammation and antiviral responses in lung endothelial cells (ECs), potentially disrupting their barrier. However, the mechanisms that restrict HRV16 in lung ECs are not well understood. Researchers infected human lung vascular ECs (HMVEC-L) with HRV16 and measured IFN-β, OAS-1, and PKR expression using various techniques. HRV16 induced IFN-β production, which activated OAS-1 and PKR, key for antiviral defense. Blocking IFN-β reduced these defenses and increased HRV16 replication. Silencing OAS-1 with siRNA also increased viral copies. The results suggest that lung ECs can mount an IFN-β-dependent antiviral response involving OAS-1 and PKR to limit HRV16 infection.
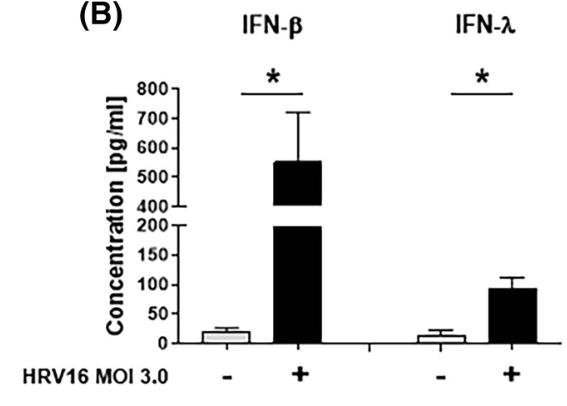
Fig3. IFN-β and IFN-λ release.
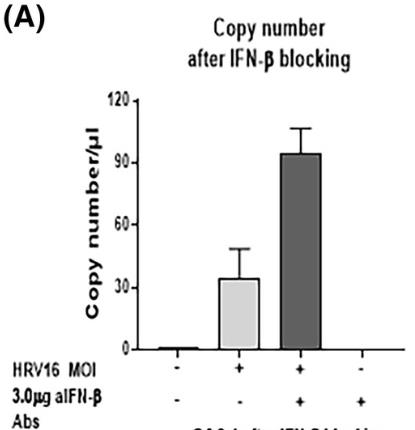
Fig4. The data shows the results after IFN-β blocking for HRV16 copy number.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (IFNB1-243H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (IFNB1-155H)
Involved Pathway
IFNB1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways IFNB1 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Osteoclast differentiation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with IFNB1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Osteoclast differentiation | TNFRSF11B,SOCS1,FCGR3A,TAB2,PIK3CG,LILRA1,FHL2,BTK,NFATC1,PIK3R1 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | INHBA,IL4,PRP2,CLCF1,CCR9,TNFSF13B,IFNA6,CCR8,TNFRSF17,PF4 |
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | IFNA7,FCGR3,RAC2,PTK2B,PLCG2,IFNAR2,RAET1E,IFNA4,KIR2DS5,TNFRSF10A |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | PIK3CD,RIPK1,IFNA10,IL12B,IL1B,IFNAR2,IFNB,CASP8,MAP2K1,STAT1B |
| Influenza A | STAT2,IL12B,HLA-DQA1,IFNA13,RSAD2,MAPK11,MAPK13,CPSF4,BLB2,EIF2AK3 |
| Tuberculosis | CARD9,ATP6V0B,FCGR2A,MAPK1,MAPK3,PIK3C3,TNF,BCL10,ITGB2,CAP18 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | POLR3B,IFI202B,NFKBIAB,AIM2,ZBP1,IFNPHI3,MAVS,IKBKB,IFNA6,POLR2EB |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | IKBKE,RNF125,MAP3K1,TNF,PL10,IFNA14,IFNA17,TRAF3,IL12A,MAPK8B |
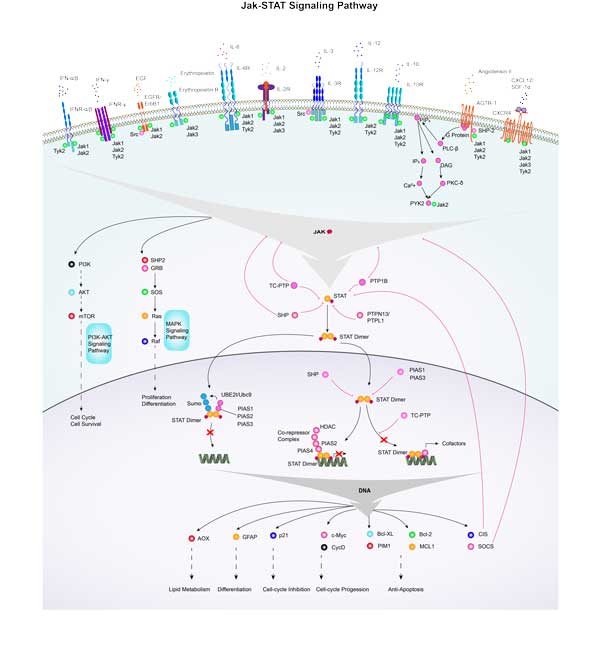
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | SOCS6B,SOCS9,CSH,MCL1A,IL9,IL12B,PIK3R3,AOX3,IL2RA,EP300 |
Protein Function
IFNB1 has several biochemical functions, for example, chloramphenicol O-acetyltransferase activity,cytokine activity,type I interferon receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by IFNB1 itself. We selected most functions IFNB1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with IFNB1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| type I interferon receptor binding | IFNPHI2,IFNPHI3,IFNA4,Ifna15,IFNA6,Gm13290,IFNK,GM13279,IFNA2,IFNA3 |
| cytokine activity | CCL4,SPAW,THPO,GM13288,FAM3D,MSTNB,IFNA10,IFNA13,WNT7A,LEFTY2 |
Interacting Protein
IFNB1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with IFNB1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of IFNB1.
IFNB1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References