CD40LG
-
Official Full Name
CD40 ligand -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is expressed on the surface of T cells. It regulates B cell function by engaging CD40 on the B cell surface. A defect in this gene results in an inability to undergo immunoglobulin class switch and is associated with hyper-IgM syndrome. -
Synonyms
CD40LG;CD40 ligand;IGM;IMD3;TRAP;gp39;CD154;CD40L;HIGM1;T-BAM;TNFSF5;hCD40L;CD40-L;CD40 antigen ligand;T-cell antigen Gp39;T-B cell-activating molecule;TNF-related activation protein;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily member 5;tu
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Dog
- Monkey
- Rhesus macaque
- Pig
- Canine
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Cynomolgus
- Zebrafish
- Cattle
- Human/Rhesus macaque
- Cercocebus atys (Sooty mangabey) (Cercocebus torquatus atys)
- Felis catus
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Yeast
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- Non
- Flag
- mFc
- GST
- S
- mIgG2a
Background
What is CD40LG protein?
CD40LG gene (CD40 ligand) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq26. CD40LG, also known as CD40 ligand or CD154, is a protein expressed on the surface of activated T cells. It plays a crucial role in the immune system by binding to CD40 on B cells, which triggers a series of signals that instruct B cells to start producing various types of antibodies, such as IgG, IgA, and IgE. This interaction is essential for class-switch recombination in B cells and for T cell differentiation and interaction with other immune cells. The CD40LG protein is consisted of 261 amino acids and CD40LG molecular weight is approximately 29.3 kDa.
What is the function of CD40LG protein?
CD40LG is a key immune system protein expressed on activated T cells. It engages with CD40 on B cells, initiating signals that drive B cell differentiation and antibody production, including IgG, IgA, and IgE. This interaction is vital for immune response regulation, T cell activation, and the immune system's ability to mount effective humoral immunity. CD40LG also plays a role in the pathogenesis of certain autoimmune diseases and is a prognostic marker in some cancers, influencing tumor immunity and patient outcomes.
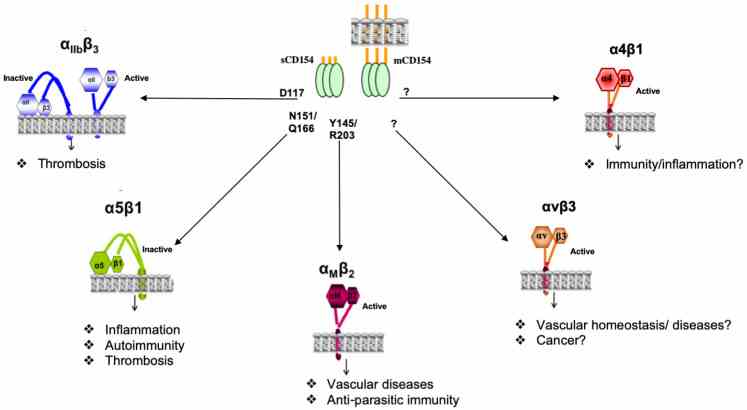
Fig1. Model representing the interaction of CD154 with integrins. (Ghada S Hassan, 2022)
CD40LG related signaling pathway
CD40LG engages the CD40 receptor primarily found on B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. This interaction initiates a signaling cascade that is crucial for T cell activation, B cell proliferation, and differentiation, class-switch recombination, and the production of antibodies. In the context of diseases, CD40LG is implicated in conditions such as X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome when mutated, and it plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease by promoting a pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Moreover, CD40LG is involved in atherosclerosis, where it modulates immune responses and contributes to plaque stability or progression depending on the cellular context.
CD40LG related diseases
CD40LG is a protein involved in the immune system's response, particularly in T cell activation. It is a key component in the interaction between T cells and B cells, leading to B cell activation, proliferation, and antibody production. CD40LG is associated with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome when defective and plays a significant role in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Furthermore, CD40LG has been identified as a prognostic marker in breast cancer, where its expression level in the tumor microenvironment correlates with patient survival, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target.
Bioapplications of CD40LG
In the context of bioapplications, CD40LG is a promising target for immunotherapy, particularly in cancer treatment. It is being explored as a means to enhance anti-tumor immune responses by activating dendritic cells and T cells, and by increasing the immunogenicity of tumor cells. Moreover, the interaction between CD40 and CD40LG is associated with better responses to immune checkpoint blockade therapy in certain cancers, suggesting that CD40LG expression levels could serve as a predictive biomarker for treatment outcomes. Furthermore, CD40LG has been implicated in autoimmune diseases, and targeting the CD40-CD40LG pathway is being investigated as a potential therapeutic strategy to modulate humoral immunity and beyond.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kathrine Pedersen, 2024
The binding of CD40 ligand (CD40L) on activated T cells to the CD40 receptor on B cells provides essential co-stimulatory signals for B cell activation. Dysregulation of the CD40L:CD40 axis is linked to various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Soluble CD40L (sCD40L) in plasma has been associated with conditions ranging from cardiovascular diseases to cancers, making it a potential disease biomarker. To utilize sCD40L as a biomarker, accurate measurement in blood samples is crucial. Researchers developed a sandwich-type time-resolved immunofluorometric assay for quantifying sCD40L in plasma and serum. This involved generating 29 monoclonal anti-CD40L antibodies and selecting the best capture and detection antibody combinations. They tested various factors, including sample type, freeze-thaw cycles, sampling times, and centrifugation effects.
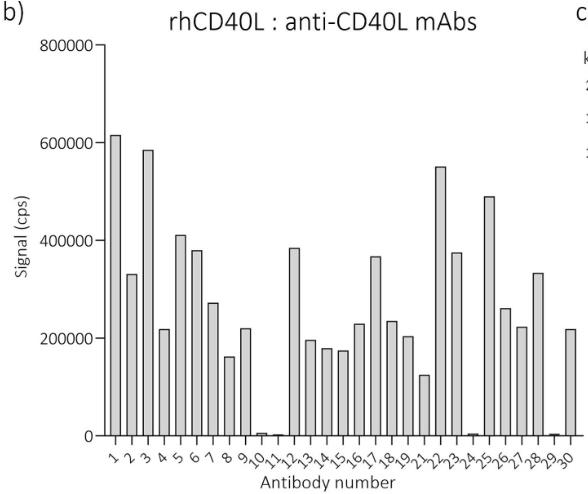
Fig1. Test of the binding of anti-human CD40L mAbs to rhCD40L coated microtiter wells.
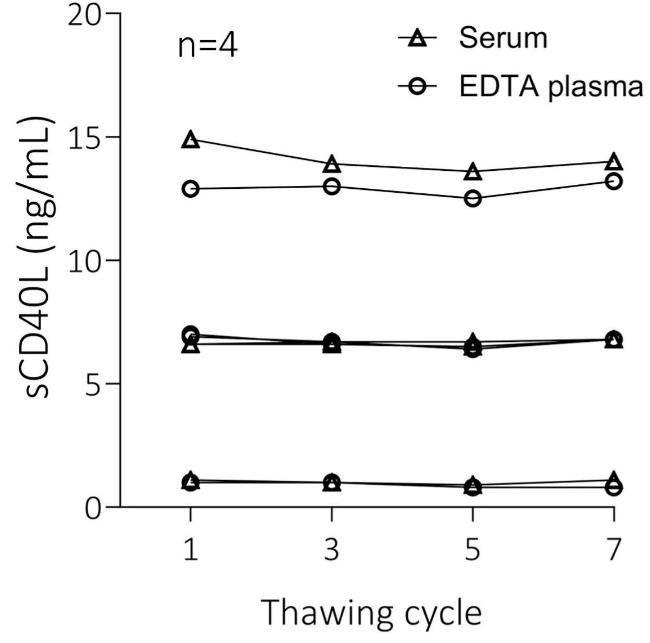
Fig2. The levels of sCD40L were measured by the CD40L assay in plasma and serum samples.
Case Study 2: Ming Yuan, 2021
Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) plays a role in chronic inflammation and coronary artery disease (CAD) by regulating adipokines and cytokines. The CD40L/CD40 pathway, known for its involvement in inflammation, has an unclear role in adipokine production within EAT. This study aimed to investigate this role. Higher CD40 expression in EAT from CAD patients compared to non-CAD individuals. Experiments with CD40 manipulation in isolated EAT adipocytes showed that silencing CD40 reduced the rCD40L-induced increase in inflammatory markers, while CD40 overexpression had the opposite effect. Additionally, rCD40L increased MLL1 expression, which was blocked by CD40 depletion and enhanced by CD40 overexpression. Chromatin analysis indicated that CD40 affected histone modifications at the promoters of inflammatory genes. Significantly, MLL1 silencing counteracted the effects of CD40 on adipokine and cytokine secretion, suggesting that CD40 may promote inflammation in EAT through MLL1 regulation.
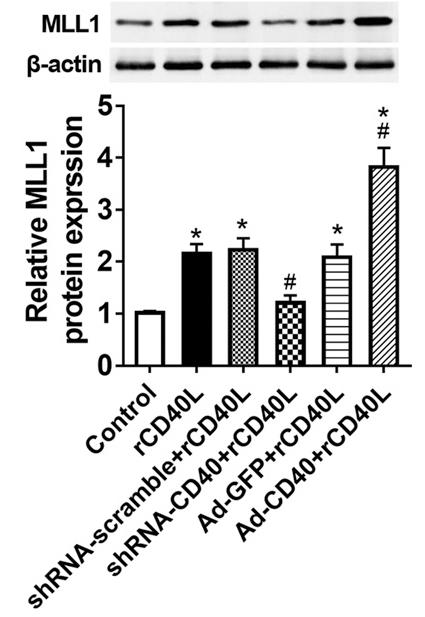
Fig3. Western blot was used to estimate MLL1 protein level.
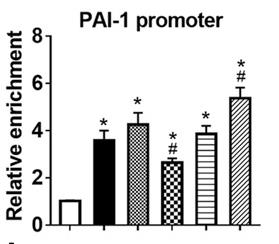
Fig4. ChIP-qPCR was used to detect the enrichment of H3K4me3 at the PAI-1.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
CD40LG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD40LG participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD40LG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Malaria | SELE,TLR9,TLR4,TGFB1,GYPA,IL1B,TGFB3,SDC1,CCL2,HBB |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | H2AFJ,ACTN2,TROVE2,HIST1H2BM,FCGR2A,HIST1H2AJ,HIST2H2AC,C1QA,HIST1H2BH,HIST1H2BB |
| ne thyroid disease | H2-Q10,TG,IFNA14,HLA-DOA,Il2,HLA-DMA,FASLG,IFNA8,H2-AA,HLA-DMB |
| nodeficiency | CD4,RAG1,RFX5,TAP2,LCK,ZAP70,PTPRC,ORAI1,IKBKG,Cd79a |
| Autoi | IFNA5,IFNA12,FAS,HLA-DPA1,CD40,IFNA4,FASLG,GZMB,Fasl,IFNA13 |
| Allograft rejection | CD40,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DOA,IL12B,HLA-G,HLA-C,MICA,H2-AB1,IL5,IL4 |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | PAK7,FYN,MAP3K7,PIK3R1,MAPK11,GRAPA,PPP3CC,PIK3CB,ZAP70,MAPK3 |
| Intestinal i | HLA-DPB1,ITGB7,BMA1,HLA-DMB,IL15,CD86,HLA-DRA,IL15RA,HLA-DQA1,BLA |
| Asthma | HLA-DRB5,IL4,IL10,HLA-DQA1,IL13,HLA-DQB1,HLA-DRA,H2-AB1,HLA-DMB,IL3 |
Protein Function
CD40LG has several biochemical functions, for example, CD40 receptor binding,cytokine activity,tumor necrosis factor receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD40LG itself. We selected most functions CD40LG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD40LG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cytokine activity | CCL4,WNT5A,CSF2,FASLG,SLURP1,IFNG1-1,GDF3,IL33,INHBA,OSTN |
| CD40 receptor binding | TRAF2 |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF10L3,TRAF4,CASP8,TNFB,TNFSF13,LTA,ERAP1,TRAF1,TNFSF4,LTB |
Interacting Protein
CD40LG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD40LG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD40LG.
CD40LG Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Britze, A; Palmfeldt, J; et al. 44-plex cytokine profile of cholesteatoma. ACTA OTO-LARYNGOLOGICA 134:41-50(2014).
- Strickland, FM; Hewagama, A; et al. Diet Influences Expression of Autoimmune-Associated Genes and Disease Severity by Epigenetic Mechanisms in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Lupus. ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATISM 65:1872-1881(2013).


.jpg)
.jpg)


