Hmox1
-
Official Full Name
heme oxygenase (decycling) 1 -
Overview
Heme oxygenase, an essential enzyme in heme catabolism, cleaves heme to form biliverdin, which is subsequently converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase, and carbon monoxide, a putative neurotransmitter. Heme oxygenase activity is induced by its substrate heme and by various nonheme substances. Heme oxygenase occurs as 2 isozymes, an inducible heme oxygenase-1 and a constitutive heme oxygenase-2. HMOX1 and HMOX2 belong to the heme oxygenase family. -
Synonyms
32 kD;bK286B10;D8Wsu38e;heat shock protein 32 kD;heat shock protein 32kD;Heat shock protein;Heme oxygenase (decycling) 1;Heme oxygenase 1;Hemox;HMOX 1;Hmox;HMOX1;HMOX1_HUMAN;HO 1;HO;HO-1;HO1;Hsp32
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Human
- Cattle
- Mouse
- Pig
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Human
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- E. coli
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- His&T7
- His&S
- His&GST
- Non
- His&MBP
- N-His
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- Flag
- His&B2M
Background

Fig1. Subcellular localization of HMOX1. (Louise L Dunn, 2014)
What is HMOX1 Protein?
HMOX1, short for heme oxygenase-1, acts like a specialized tool for breaking down heme, a component that originates from hemoglobin. By doing this, it shields cells from the potential harm and stress that heme can create. Beyond just its housekeeping role, HMOX1 has been found to be involved in stabilizing certain structures in DNA known as G-quadruplexes, which can affect DNA replication. In essence, HMOX1 helps guard cells against stress during DNA replication. Without enough HMOX1, cells might experience replication stress, meaning the DNA copying process can get disrupted. This has been shown in experiments using specific cell lines where the absence of HMOX1 leads to more DNA replication issues, highlighting its protective role in maintaining DNA integrity.
What is the Function of HMOX1 Protein?
Picture the HMOX1 protein as your body's cleanup crew for old heme, found in blood's hemoglobin. Its job is to break down heme into several byproducts, like biliverdin. Then, biliverdin gets turned into bilirubin by other processes. This function is pretty important because it helps maintain balance in the body and prevent any potential damage from free heme, which can be toxic. Plus, the process releases carbon monoxide and iron, which have their own signaling roles in the body. So, HMOX1 is kind of like a multitasking manager in your body's natural recycling center!
HMOX1 Related Signaling Pathway
HMOX1, or heme oxygenase-1, plays a big role in various signaling pathways that help our body manage stress, fight inflammation, and keep cells going strong. One of the main roles it plays is in the Nrf2/HMOX1 pathway, which kicks into action when there's oxidative stress. Basically, if Nrf2 gets going, it ramps up HMOX1 and other antioxidants. HMOX1 then steps in to break down heme and helps cut down inflammation and oxidative stress. It's also linked to a special type of cell death called ferroptosis, which involves lipid peroxides and iron. In cancer, the way HMOX1 works can affect how tumors grow and spread, making it a target of interest for treatment. It even takes part in immune responses in conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma, where it can influence how cancer progresses via inflammation. So, HMOX1 is really versatile, intricately involved in how our cells respond to stress and illness. Grasping what it does might pave the way for new treatments for a bunch of conditions where oxidative stress and inflammation play big roles.
HMOX1 Related Diseases
HMOX1, or heme oxygenase-1, is linked to a few health conditions, with its deficiency being a notable one. When the body falls short in producing this protein, oxidative stress and inflammation can ramp up, potentially messing with cardiovascular health and causing issues in the kidneys and liver. You also see it involved in some neurological disorders, mainly because it helps keep oxidative stress in check—a big deal in diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, where stress levels are usually off the charts. Moreover, in the landscape of cancer, the overactivity of HMOX1 might aid tumor growth and resistance to treatments, making it a target for potential therapies. So, in essence, this protein has a hand in managing how our bodies deal with stress and inflammation, and when it's not doing its job right, we might see a raft of health challenges.
Bioapplications of HMOX1
The recombinant HMOX1 protein has found a variety of applications in research and industrial fields. Researchers frequently tap into HMOX1 to dive into its part in cell signaling, especially how it handles stress and inflammation. In the lab, they might use recombinant HMOX1 to dig deeper into its links to diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, aiming to see if it could be a key player in future treatments. On the industrial side, companies might leverage this protein for developing drugs aimed at modulating oxidative stress or targeting specific pathways involving heme metabolism. Overall, recombinant HMOX1 serves as a valuable tool both in advancing scientific understanding and in the biotechnological production of novel therapeutics.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mawieh Hamad, 2021
Iron overload can ramp up reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, but pancreatic β-cells fight back with antioxidants. In this study, RNA-sequencing explored how iron affects gene expression in both diabetic and non-diabetic human islets. Techniques like siRNA silencing, qPCR, and western blotting uncovered the genes involved in protecting against iron stress in human islets and INS-1 cells. Key findings showed high expression of FTH1 and FTL genes, while hepcidin (HAMP) was low. Diabetic islets had different expressions of FXN, DMT1, and FTHL1 genes compared to controls. Knockdown of Hamp in INS-1 cells disrupted insulin secretion and altered essential β-cell genes. In iron-overloaded INS-1 cells, Id1 and Id3 were down-regulated, Hmox1 was upregulated, and these findings were confirmed at the protein level. The differentially expressed genes were linked to TGF-β, stem cell regulation, ferroptosis, and HIF-1 pathways. Silencing Hmox1 in FAC-treated cells boosted Id1 and Id3 expression more than in untreated ones.
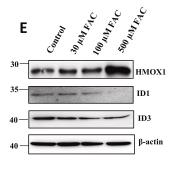
Fig1. Western blot validation of top DEGs (ID1, ID3, and HMOX1) in INS-1 cells treated with different concentrations of FAC.
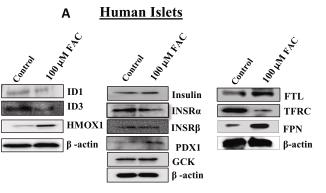
Fig2. Western blot validation of top DEGs (ID1, ID3, and HMOX1) in human pancreatic islets treated with 100 μM of FAC.
Case Study 2: Patryk Chudy, 2024
Heme oxygenase-1, or HO-1, has a key role in breaking down heme to protect cells from oxidative damage. However, heme doesn't just degrade; it stabilizes structures in DNA known as G-quadruplexes, which can mess with DNA duplication. It turns out that HO-1 hangs out with these G-quadruplexes in the cell nucleus and helps get rid of them. In studies with normal and HO-1-lacking HEK293T cells, it was found that without HO-1, more G-quadruplexes piled up, especially when δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) was present, leading to trouble in DNA replication. This stress was seen in more stalled DNA replication sites. Similar results were observed in stem cells from HO-1-deficient mice and human cells from a person lacking HO-1. Interestingly, without HO-1, DNA progressed faster but had issues, suggesting some disruption in typical DNA stress responses, particularly involving p53. It seems that HO-1 affects the movement and build-up of p53 in the nucleus, tied to heme levels. Using ALA was shown to specifically ramp up free heme in cells, unlike hemin, which causes more cell damage due to lipid breakdown.
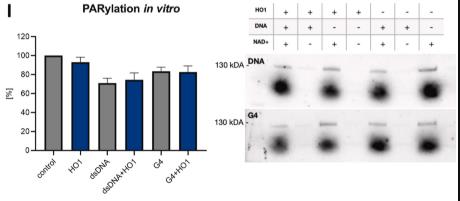
Fig3. Autoparylation in vitro of recombinant PARP1 in the presence of recombinant HMOX1.
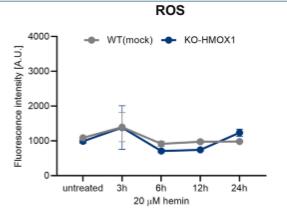
Fig4. Time course of ROS generation after hemin (20 μM) treatment in WT(mock) and KO-HMOX1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HMOX1-2604H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (HMOX1-4884H)
Involved Pathway
Hmox1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Hmox1 participated on our site, such as Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism,HIF- signaling pathway,Mineral absorption, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Hmox1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | UGT1AB,UGT5G1,UGT1A7,UGT1A7C,UGT1A1,COX10,HMBSA,UGT1A2,UGT1A3,UGT1A6B |
| Mineral absorption | MT2,SLC46A1,FTL,ATP7A,TF,ATP1A4,SLC26A3,MT1,ATP1B1,TRPV6 |
| HIF- signaling pathway | PIK3R3,EGLN1,TCEB1,HKDC1,MAP2K1,MAPK1,PIK3CG,ENO3,PFKL,EIF4E1B |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | ABCC1,BMF,KIF23,RAF1,PDGFRB,MAP2K2,MCL1,ABL1,PIM1,PDGFRA |
Protein Function
Hmox1 has several biochemical functions, for example, enzyme binding,heme binding,heme oxygenase (decyclizing) activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Hmox1 itself. We selected most functions Hmox1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Hmox1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| heme binding | CYP2K16,NGB,CYP2AA7,CYP2C38,CYP2B19,EIF2AK1,HBBE2,CYP3C1,CYP2S1,CYP4X1 |
| heme oxygenase (decyclizing) activity | HMOX2,HMOX1A,HMOX2A,HMOX1B |
| phospholipase D activity | PLD1A,PLD2,PLD3,GPLD1,PLD4,PLD1 |
| enzyme binding | PTPLA,APP,VAPB,UGT1A4,UGT1A3,LAMB1,AXIN2,DDC,SIRT3,HIST1H2AD |
| metal ion binding | ECE2,UNC13C,RPE,GNA15,ZNF583,ICN,OVOL2,JMJD1C,ZNF584,LIG4 |
| protein homodimerization activity | FAM109B,PEX11A,GSTZ1,TARS,LILRB1,STOM,MAPK4,ENG,PDCD6IP,PSMD7 |
| protein binding | PRPF8,MUC7,TRIM39,IL33,MYL7,FRMD5,SIX4,MAP2K3,PAX9,SLA |
| signal transducer activity | GPR186,VMN1R41,TAS2R103,RGS11,OPN4.1,DKKL1,TICAM1,PTGER1B,PRLH2R,TAS2R106 |
Interacting Protein
Hmox1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Hmox1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Hmox1.
POT1;CREB3;ASL;TERF1;proS;q7ckk6_yerpe;hemL2;comEA;yvaE;gcvP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Muhsain, SNF; Lang, MA; et al. Mitochondrial targeting of bilirubin regulatory enzymes: An adaptive response to oxidative stress. TOXICOLOGY AND APPLIED PHARMACOLOGY 282:77-89(2015).
- Repesse, Y; Peyron, I; et al. Development of inhibitory antibodies to therapeutic factor VIII in severe hemophilia A is associated with microsatellite polymorphisms in the HMOX1 promoter. HAEMATOLOGICA 98:1650-1655(2013).


