CXCL12
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12 -
Overview
SDF-1 (Stromal cell-derived factor-1), also known as PBSF (pre-B-cell growth-stimulating factor), is a recently discovered protein belonging to the alpha chemokine (CXC) family of cytokines. SDF-1α and SDF-1β are the first cytokines initially identified using the signal sequence trap cloning trategy from a human bone-marrow stromal cell line. SDF-1 has chemotactic activity on resting T lymphocytes and monocytes. -
Synonyms
CXCL12;chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12;SDF1, SDF1A, SDF1B, stromal cell derived factor 1;stromal cell-derived factor 1;PBSF;SCYB12;SDF 1a;SDF 1b;TLSF a;TLSF b;TPAR1;intercrine reduced in hepatomas;pre-B cell growth-stimulating factor;IRH;SDF1;TLSF;SDF1A;SDF1B
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rabbit
- Rhesus macaque
- Human/Feline
- Feline
- Rat
- Canine
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus
- Hamster
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Yeast
- HEK293
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
Background
What is CXCL12 protein?
CXCL12 gene (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q11. CXCL12, also known as SDF-1, is a small protein that belongs to the CXC chemokine family. It plays a role in a variety of physiological processes, including cell chemotaxis, migration, and activation, especially in embryonic development, immune surveillance, inflammatory response, tissue homeostasis, and tumor growth and metastasis. CXCL12 functions by binding to its receptors, CXCR4, its main classical G-protein-coupled receptor, and CXCR7, which acts primarily as a scavenger of CXCL12 and also transmits signals through the β-arrestin pathway. The CXCL12 protein is consisted of 93 amino acids and CXCL12 molecular weight is approximately 10.7 kDa.
What is the function of CXCL12 protein?
CXCL12 is a potent chemoattractant for various cell types, including lymphocytes, monocytes, and stem cells, guiding their migration to specific tissues. CXCL12 is critical for the localization and development of hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow. It helps in the trafficking and positioning of immune cells, contributing to the immune response. CXCL12 is involved in the recruitment of immune cells to sites of inflammation. It aids in the recruitment of stem and progenitor cells to damaged tissues, promoting healing and regeneration. It plays a role in the maintenance of bone homeostasis by regulating the function of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, satellite cells, and myoblasts.
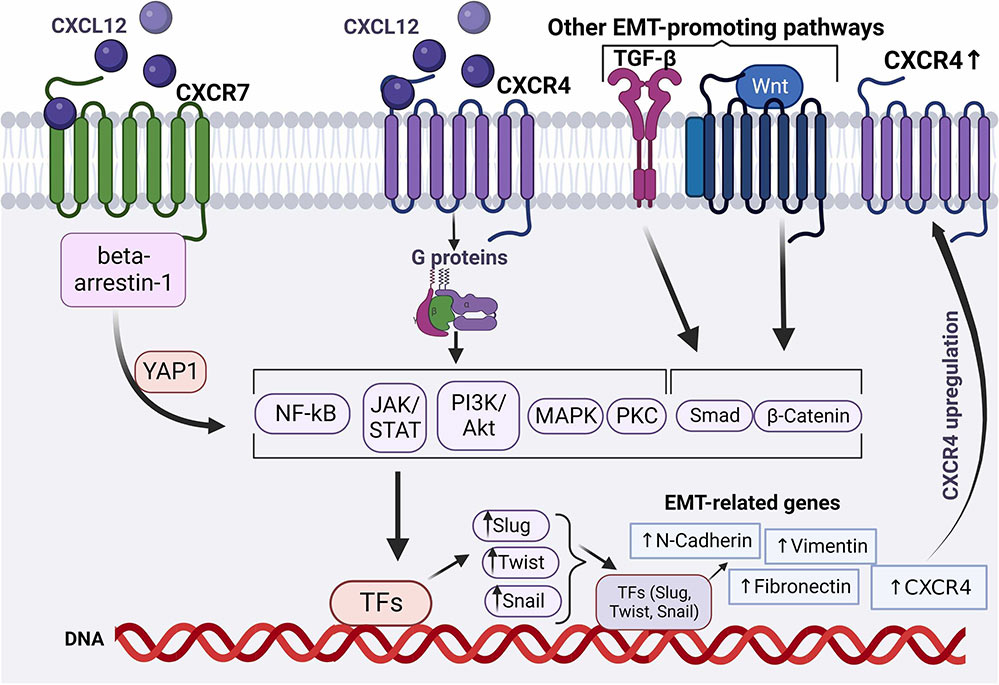
Fig1. Emerging Roles of the CXCL12 Axis in the Regulation of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT). (Dimitra P Anastasiadou, 2024)
CXCL12 related signaling pathway
CXCL12 activates a variety of signaling pathways by binding to CXCR4, such as the PI3K-AKT-NF-κB axis and signaling through MEK1/2 and Erk 1/2, promoting gene expression and cell cycle progression. Activation of these signaling pathways can lead to cell migration and survival, and even proliferation. The roles of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in the tumor microenvironment include promoting tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis, and maintaining tumor cell survival in some hematological malignancies. In addition, the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway is involved in hematopoietic stem cell migration and localization, as well as cell recruitment during tissue injury and repair.
CXCL12 related diseases
It plays a key role in tumor growth, angiogenesis, cell adhesion, and metastasis by binding to the CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors. CXCL12 is particularly important in the tumor microenvironment, and its increased expression level is closely related to tumor aggressiveness and prognosis. For example, in tumors, the high expression of CXCL12 can promote the proliferation of tumor cells, enhance the adhesion ability of tumor cells, and participate in the process of tumor metastasis. In addition, the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling pathway is involved in the angiogenesis process after ischemic stroke by promoting the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells. In central nervous system diseases, CXCL12 also plays a role and is strongly associated with diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis may also be involved in inflammatory responses and the mobilization of neural progenitor cells, potentially affecting the repair process after stroke.
Bioapplications of CXCL12
Studies have shown that the use of CXCR4 antagonists can block the interaction between CXCL12 and CXCR4, thereby inhibiting the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells, and may reduce the angiogenesis and metastasis ability of tumors. In addition, blocking the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis may also enhance the immune response in the tumor microenvironment, providing a new strategy for tumor immunotherapy. In addition to tumor therapy, CXCL12 also shows potential in the treatment of other diseases, such as stroke and cardiovascular disease. In addition, CXCL12 also shows great application potential in tissue repair and regenerative medicine. For example, CXCL12 promotes the homing and differentiation of stem cells and helps repair damaged tissues. In terms of drug delivery systems, nanodrug delivery systems based on the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis are being developed to improve drug targeting and therapeutic efficacy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jong Min Hong 2023
In the present study, researchers investigated in detail the formation of the CXCR4-LPA1 heteromer and characterized the unique molecular features and function of this heteromer. The researchers used techniques such as bimolecular fluorescence complementation, bioluminescence resonance energy transfer, and proximity link assays to demonstrate heterodimer formation between CXCR4 and LPA1. In order to clarify the unique molecular properties and functional significance of CXCR4-LPA1 heterodimer, a series of experiments were carried out, including cAMP assay, BRET analysis of G protein activation, β-blockers recruitment, ligand binding, and transpore migration experiments. Results showed that coexpression of LPA1 with CXCR4 reduced CXCL12-mediated cAMP inhibition, ERK activation, Gαi/o activation, and β-arrestin recruitment, while CXCL12 binding to CXCR4 remained unaffected. Ultimately, complete inhibition of cell migration toward CXCL12 and alkyl-OMPT was only achieved in the presence of both CXCR4 and LPA1 antagonists.
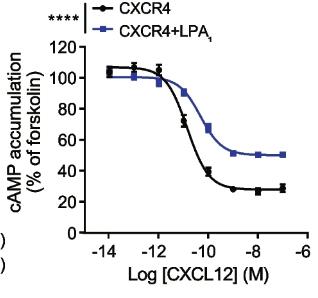
Fig1. CXCL12-induced inhibition of cAMP production was measured.
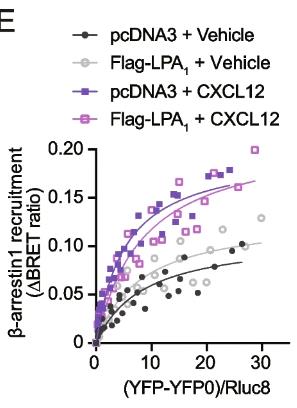
Fig2. Ligand-induced β-arrestin1 BRET assay was performed in HEK293A cells.
Case Study 2: Mei Zheng, 2022
This study investigated the expression of CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 near the hair follicle and its effect on hair growth. CXCL12 was highly expressed in dermal fibroblasts and increased during the degenerative and resting stages of the hair cycle. CXCR4 was expressed in the dermal papilla and outer root sheath. Hair organ culture showed that recombinant CXCL12 therapy induced alopecia, delayed the transition from resting to growth, and shortened hair length. Conversely, inhibiting CXCL12 with neutralizing antibodies and siRNA promoted transition and increased hair length. Neutralization of CXCR7 had little effect on hair growth, while inhibition of CXCR4 significantly promoted hair growth. In addition, conditioned media from CXCL12 SiRNA-treated fibroblasts significantly increased hair length in hair organ culture and induced proliferation of dermal papilla and outer root sheath cells. CXCL12 increased the phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT5 in DP and ORS cells by activating CXCR4, while blocking CXCL12 and CXCR4 decreased their phosphorylation.
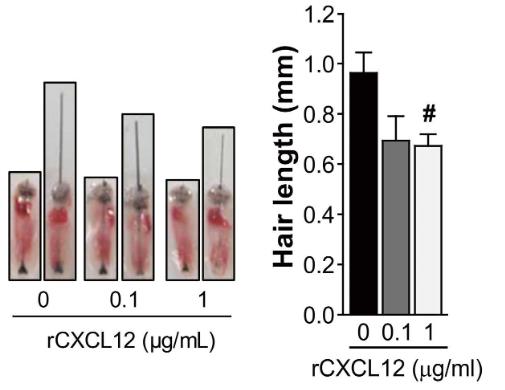
Fig3. rCXCL12 treatment significantly inhibits the length of mouse vibrissa follicle.
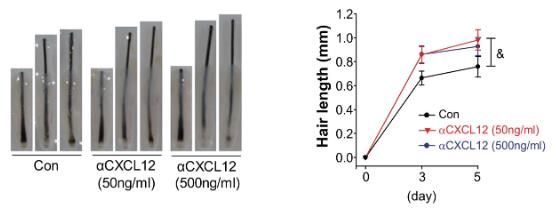
Fig4. αCXCL12 significantly increased the length of human hair follicles.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CXCL12-2160H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CXCL12-519H)
Involved Pathway
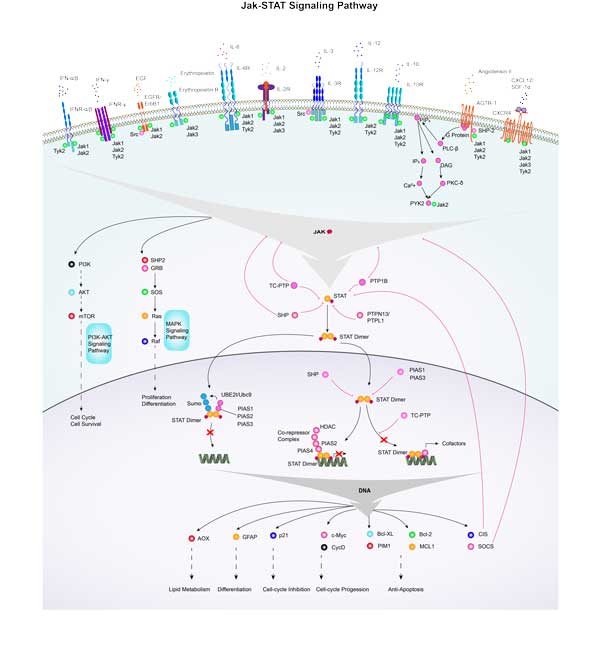
CXCL12 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CXCL12 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway,NF-kappa B signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CXCL12 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | Ccl21a,PIK3R2,STAT2,CCL27,PPBP,CCL21,CDC42,CCL16,Ccl12,SHC3 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | CFLAR,MAP3K14,BCL10,BLNK,RIPK1,BCL2L1,BCL2A1,TRAF3,TRAF2,TNF |
| ne network for IgA production | CD80,CD40,IL4,Icosl,TGFB1A,H2-AA,HLA-DPA1,CXCR4A,MHC2A,CCR10 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | VCAM1,RASSF5,MYL12A,PIK3R1,CLDN18,MSN,VCL,RAP1B,PTK2B,RHOA |
| Axon guidance | EFNB3,LIMK2,PLXNC1,UNC5C,ITGB1,EPHA2,PAK4,PAQR3A,EVL,ANK2B |
| Pathways in cancer | PTCH1,Fasl,FLT3,CKS2,WNT6,WNT7B,MSH6,CBLC,GNB2,RASGRP3 |
| Intestinal i | HLA-DQA1,HLA-DOA,CCR10,CCL25,IL5,ICOSLG,H2-AA,CD40LG,MHC2DCB,BLB2 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | IL-8,MMP3,TNFSF13,HLA-DQA1,IL1A,CCL3L3,IL18,H2-AB1,ATP6V1E1,ITGB2L |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CXCR4A,IL2RB,CCR3,CRFB4,GM10591,CSF1,KDRL,IL12RB1,CCL8,HGF |
Protein Function
CXCL12 has several biochemical functions, for example, CXCR chemokine receptor binding,chemoattractant activity,chemokine activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CXCL12 itself. We selected most functions CXCL12 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CXCL12. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chemokine activity | CCL7,CXCL11.8,CXCL20,CXCL10,CCL25B,XCL1,CCL44,IL-8,CXCL16,CCL3L3 |
| CXCR chemokine receptor binding | CXCL5,CXCL6,ITCH,IL8L2,CXCL1,CXCL12A,CXCL12B,PPBP,AMCF-II,CXCL3 |
| chemoattractant activity | CXCL12B,VHL,VEGFA,VEGFB,SAA2,CCL5,SAA3,HGF,HMGB2,SCG2 |
| growth factor activity | RABEP1,IL9,CDNF,CSF2,IL4,FGF1A,BMP15,NRG2,IGF1,CNTF |
| receptor binding | EHHADH,PTK2AA,SMARCD3,LAMA4,ENSA,DHRS4,CAV1,CX3CL1,CD72,AMH |
| chemokine receptor binding | CCL19,CCL5,CCL25,S100A14,CCRL2,Ccl21a,CCL21,XCL1,Ccl21c,CCL21B |
Interacting Protein
CXCL12 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CXCL12 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CXCL12.
DPP4;DAZAP2
CXCL12 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
NeuroinflammationInflammatory Cytokines & Chemokines
B Cell Chemotaxis, Migration, and Adhesion
Megakaryocytes
Cytokines and Chemokines in B Cell Development
CXC Chemokines
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wirtz, TH; Tillmann, S; et al. Platelet-derived MIF: A novel platelet chemokine with distinct recruitment properties. ATHEROSCLEROSIS 239:1-10(2015).
- Asquith, DL; Bryce, SA; et al. Targeting cell migration in rheumatoid arthritis. CURRENT OPINION IN RHEUMATOLOGY 27:204-211(2015).