F2
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor II (thrombin) -
Overview
Thrombin (activated Factor II [IIa]) is a coagulation protein that has many effects in the coagulation cascade. Thrombin is a serine protease (EC 3.4.21.5) that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions. Thrombin is in the form of alpha-thrombin tat is the immediate end product of prothrombin activation, two further thrombin products can be identified, beta- and gamma-thrombin. These are degraded form that may arise from autodigestion of a thrombin preparation. -
Synonyms
F2;coagulation factor II (thrombin);prothrombin;serine protease;prothrombin B-chain;PT;THPH1
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Bovine
- Pig
- Cattle
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Porcine
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Plasma
- Mammalian Cells
- Bovine Plasma
- Pig Blood
- Cattle Blood
- Wheat Germ
- Porcine Blood
- Human Cells
- Human Plasma
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Rat plasma
- Mouse Plasma
- Yeast
- Porcine
- Procine Blood
- rat plasma
- Bovine Blood
- His
- Non
- GST
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- Flag
Background
What is F2 protein?
F2 gene (coagulation factor II, thrombin) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11p11. This gene encodes the prothrombin protein (also known as coagulation factor II). This protein is proteolytically cleaved in multiple steps to form the activated serine protease thrombin. The activated thrombin enzyme plays an important role in thrombosis and hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin during blood clot formation, by stimulating platelet aggregation, and by activating additional coagulation factors. Thrombin also plays a role in cell proliferation, tissue repair, and angiogenesis as well as maintaining vascular integrity during development and postnatal life. Peptides derived from the C-terminus of this protein have antimicrobial activity against E. coli and P. aeruginosa. The F2 protein is consisted of 622 amino acids and F2 molecular weight is approximately 70.0 kDa.
What is the function of F2 protein?
The F2 protein is converted into an activated serine protease, thrombin, during blood coagulation. Thrombin promotes blood clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin, and stimulates platelet aggregation while activating other clotting factors such as factors V, VII, VIII, and XIII. Thrombin not only plays a role in blood clotting, but is also involved in cell proliferation, tissue repair and angiogenesis, maintaining the integrity of blood vessels in development and adulthood. F2 proteins are also involved in the regulation of a variety of biological processes, including protein phosphorylation, proteolysis, acute phase response, and cell surface receptor signaling. The C-terminal derived peptide of F2 protein has antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
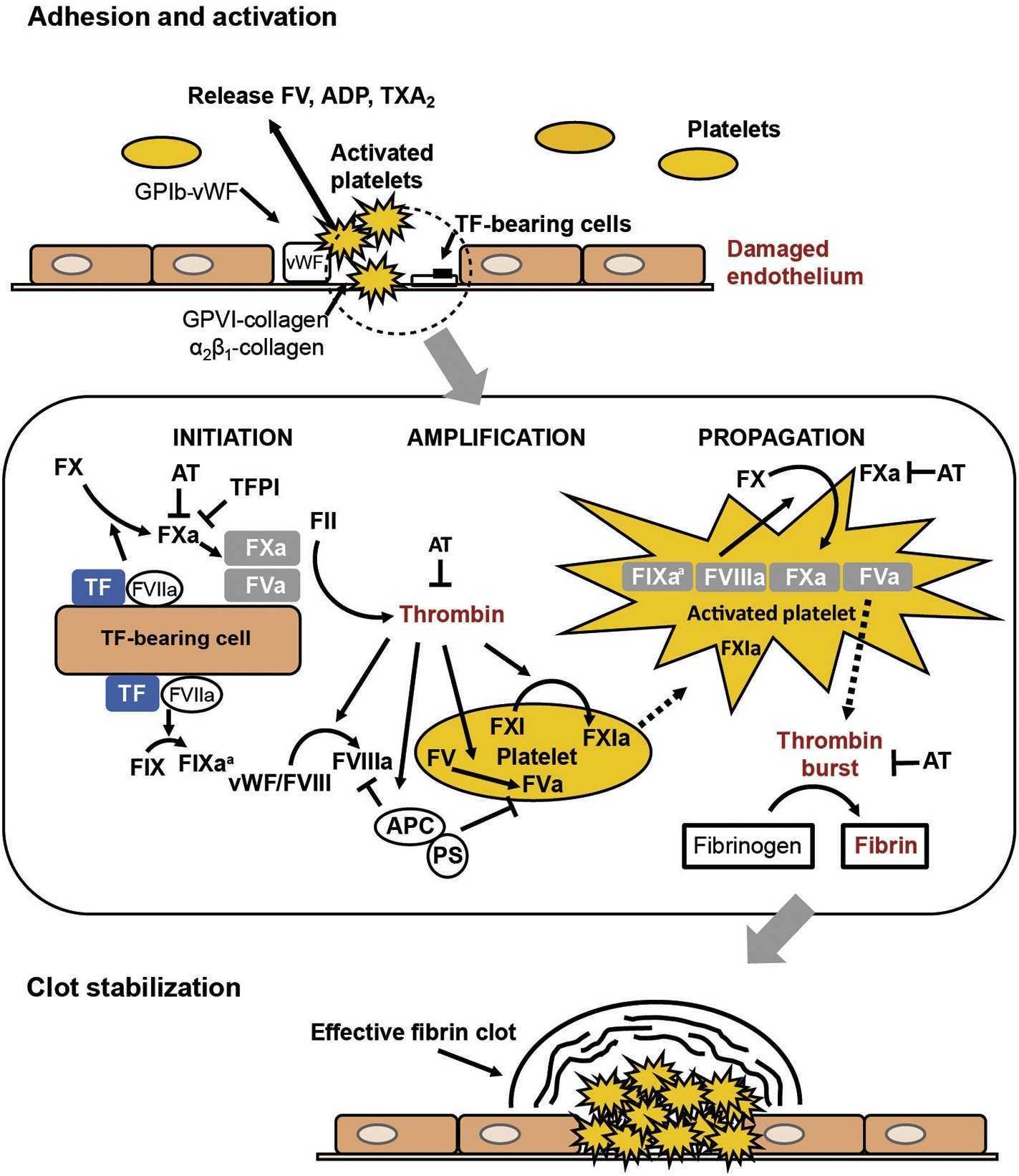
Fig1. The role of thrombin in hemostasis. (Claude Negrier, 2019)
F2 Related Signaling Pathway
The F2 protein is converted into activated thrombin during blood clotting, which is done through a complex series of enzymatic reactions involving multiple clotting factors, ultimately forming a stable clot and preventing excessive bleeding. The F2 protein is associated with the NRF2 (nuclear factor E2 related factor 2) signaling pathway, which plays a central role in the cellular antioxidant response and protects cells from oxidative damage by regulating the expression of multiple antioxidant genes. F2R is a receptor for thrombin and is involved in a variety of biological processes, including cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Studies have shown that the expression level of F2R is related to the prognosis and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer, and its high expression level may be related to the aggressive behavior of the tumor. F2 protein is involved in the process of inflammatory response, regulating the release of inflammatory mediators by activating cell signaling.
F2 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression or dysfunction of the F2 protein, prothrombin, has been linked to a variety of diseases, especially those associated with the process of blood clotting and hemostasis, such as thrombosis and bleeding disorders. In addition, F2 protein's role in inflammation, cell proliferation, tissue repair, and tumor development makes it closely related to the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, and many cancers (such as stomach cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, etc.). The signaling pathway of F2 protein is also involved in the regulation of immune cell function and tumor microenvironment, which may in turn influence response to cancer therapy and prognosis.
Bioapplications of F2
F2 protein (prothrombin) has a wide range of applications in medicine and biology, including as a key enzyme in the blood coagulation cascade for the study and treatment of diseases involving blood coagulation and hemostasis; As a biomarker for predicting disease risk and evaluating treatment effects, particularly in the diagnosis of thrombotic diseases and certain cancers; In drug development, inhibitors of F2 protein or its receptor (F2R) may become potential drugs for the treatment of related diseases; And the ability to use F2 protein to promote cell proliferation and tissue repair in tissue engineering and wound healing research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rebecca A Risman, 2024
Clotting factors, such as thrombin and tissue factor, or blood plasma proteins, such as fibrinogen, play critical roles in fibrin network polymerization. The concentrations and combinations of these proteins affect the structure and stability of clots, which can lead to downstream complications. The present work includes clots made from plasma and purified fibrinogen and shows how varying fibrinogen and activation factor concentrations affect the fibrin properties under both conditions. Researchers used a combination of scanning electron microscopy, confocal microscopy, and turbidimetry to analyze clot/fiber structure and polymerization. They quantified the structural and polymerization features and found similar trends with increasing/decreasing fibrinogen and thrombin concentrations for both purified fibrinogen and plasma clots.
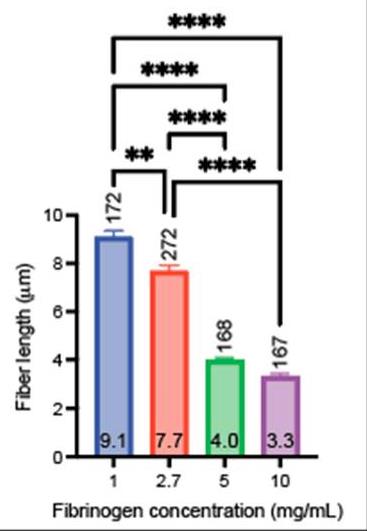
Fig1. Fiber lengths obtained from confocal images.
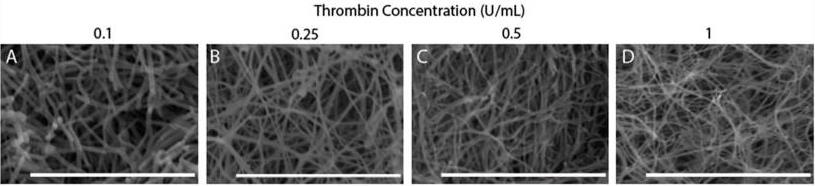
Fig2. SEM images on clots made with varying thrombin concentrations.
Case Study 2: Bing Zhao, 2020
Tumor cells transform into endothelial cells by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, which is characterized by vasculogenic mimicry (VM). However, very little is currently known about the molecular determinants that enable VM. Nevertheless, the association between thrombin and VM formation remains largely unknown. Researchers found that VM was associated with the overall survival of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, and that thrombin expression was closely related to VM formation. This research revealed that thrombin induced VM formation via PAR-1-mediated NF-κB signaling cascades. The novel thrombin inhibitors r-hirudin and DTIP inhibited VM formation and spontaneous metastases in subcutaneous tumors. Clinical pathological analysis confirmed that NSCLC patients with thrombin-positive/PAR-1-high expression had the poorest prognosis and were the most likely to form VM.
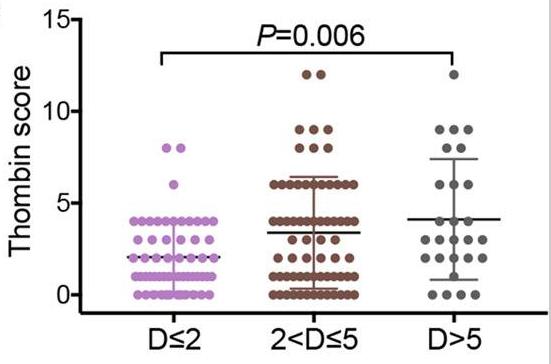
Fig3. The association of thrombin expression with tumor size in NSCLC samples.
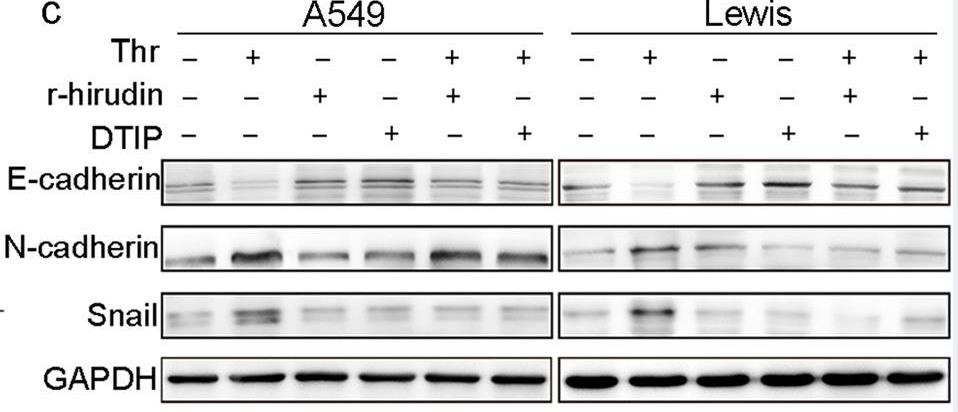
Fig4. The effect of thrombin, r-hirudin and DTIP on the expression of snail and other EMT markers.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F2-698H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F2-3610H)
Involved Pathway
F2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F2 participated on our site, such as Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction,Complement and coagulation cascades,Regulation of actin cytoskeleton, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | ABI2B,GSNB,ITGB1A,FGF5,FGF6,PAK2,PIK3CA,CYFIP2,RAF1B,GNG12A |
| Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | PRLHR2B,GRM2,TAAR64,CNR2,HRH1,GALR3,PRLHR2A,CSH1,NPY4R,TAAR7D |
| Complement and coagulation cascades | CD59A,F3,C3,C1RA,PROS1,C4BPA,CR2,C8G,F5,PROC |
Protein Function
F2 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,growth factor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F2 itself. We selected most functions F2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| growth factor activity | GDF10B,FGF16,DKK1,CLEC11A,INHBE,FGF8B,IL7,RABEP2,INHBA,FGF13 |
| calcium ion binding | PLSCR3,S100A9,ANXA5B,GUCA1A,MASP1,Amy1,EFCAB1,UMODL1,MBL2,CDH12 |
| protein binding | TCP1,UTP11L,SHC1,DNAAF2,BMP7,ADD1,KRTAP8-1,STYX,ADM,PDPK1 |
| thrombospondin receptor activity | CD47,SDC4 |
| receptor binding | EHHADH,CAV1,POU2F1,NPY,LRP6,STRAP,WIPI1,LYN,FGF20B,GFRA1 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | PRSS22,C1S,MCPT8,PRSS27,PCSK7,KLKB1,TPP1,KLK1B24,PLG,KLK13 |
Interacting Protein
F2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F2.
q846v4_staau;anti-thrombin_mus_pe;C1QBP;THBD
Resources
Research Area
Serine Proteases and RegulatorsCoagulation Factors
Acute Phase Proteins
Complement Regulatory Proteins
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhou, FF; Sun, RL; et al. Myostatin Gene Mutated Mice Induced with Tale Nucleases. ANIMAL BIOTECHNOLOGY 26:169-179(2015).
- Roslaniec, L; Jurkov, AS; et al. Design of Single-Switch Inverters for Variable Resistance/Load Modulation Operation. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS 30:3200-3214(2015).



