PDGFB
-
Official Full Name
platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (PDGF-AB), where the dimers are connected by disulfide bonds. Mutations in this gene are associated with meningioma. Reciprocal translocations between chromosomes 22 and 17, at sites where this gene and that for collagen type 1, alpha 1 are located, are associated with a particular type of skin tumor called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans resulting from unregulated expression of growth factor. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2013] -
Synonyms
PDGFB;platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide;SIS;SSV;IBGC5;PDGF2;c-sis;PDGF-2;platelet-derived growth factor subunit B;becaplermin;PDGF, B chain;PDGF subunit B;proto-oncogene c-Sis;platelet-derived growth factor 2;platelet-derived growth factor B chain;platelet-derived growth factor, beta polypeptide (oncogene SIS);platelet-derived growth factor beta polypeptide (simian sarcoma viral (v-sis) oncogene homolog)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Bovine
- Canine
- Feline
- Chicken
- Equine
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Pig
- Rhesus macaque
- Rabbit
- E.coli
- Yeast
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- P.pastoris
- CHO
- S.Cerevisiae
- Human
- Non
- His
- mFc
- S
- GST
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PDGFB protein?
PDGFB (platelet derived growth factor subunit B) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer with the platelet-derived growth factor alpha polypeptide (PDGF-AB), where the dimers are connected by disulfide bonds. The PDGFB protein is consisted of 241 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 27.3 kDa.
What is the function of PDGFB protein?
PDGFs are mitogenic during early developmental stages, driving the proliferation of undifferentiated mesenchyme and some progenitor populations. During later maturation stages, PDGF signalling has been implicated in tissue remodelling and cellular differentiation, and in inductive events involved in patterning and morphogenesis. In addition to driving mesenchymal proliferation, PDGFs have been shown to direct the migration, differentiation and function of a variety of specialised mesenchymal and migratory cell types, both during development and in the adult animal. PDGF plays a role in embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell migration, and angiogenesis. PDGF is a required element in cellular division for fibroblast, a type of connective tissue cell. PDGF is also known to maintain proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells.
PDGFB Related Signaling Pathway
By binding to its receptor PDGFR, PDGFB activates downstream signaling pathways, including PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK and other pathways, thereby promoting biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. At the same time, PDGFB can activate NF-κB signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway and inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, so as to regulate the biological behavior of cells.
PDGFB Related Diseases
Mutations in this gene are associated with meningioma, gastrointestinal stromal tumors(GISTs), osteosarcoma and other tumors. Reciprocal translocations between chromosomes 22 and 17, at sites where this gene and that for collagen type 1, alpha 1 are located, are associated with a particular type of skin tumor called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans resulting from unregulated expression of growth factor. PDGFB is involved in nervous system development and repair, and is associated with neurological diseases such as white matter disease and multiple sclerosis.
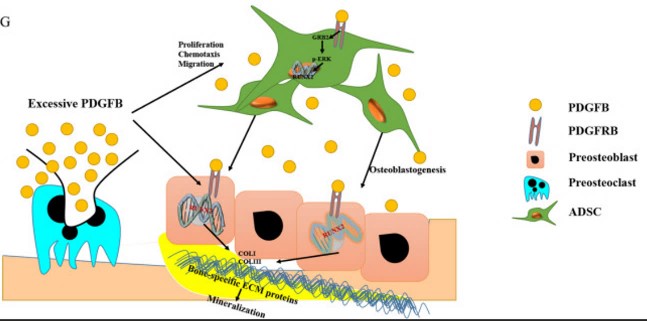
Fig1. Possible mechanism of PDGFB pathogenesis in Ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Bioapplications of PDGFB
As a therapeutic target, PDGFB can assist in the development of inhibitor drugs for related diseases. Several applications of PDGFB have been studied or are undergoing clinical trials.
Case Study
Case study 1: Weixin Meng, 2018
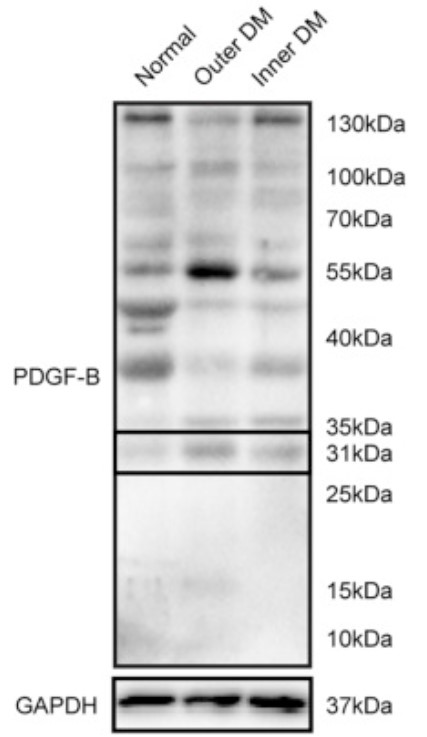
Thoracic aortic dissection (TAD) is a serious condition requiring urgent treatment to avoid catastrophic consequences. The inflammatory response is involved in the occurrence and development of TAD. This study aimed to determine whether expression of PDGF-B (a subunit of PDGF-BB) was increased in TAD patients. Full-thickness ascending aorta wall specimens from TAD patients (n = 15) and control patients (n = 10) were examined for expression of PDGF-B and its receptor (PDGFRB) and in terms of morphology, inflammation, and fibrosis. An increase in elastic fragments in the aorta wall might be responsible for inducing the activation and migration of macrophages to injured sites, leading to elevated expression of PDGF-B.
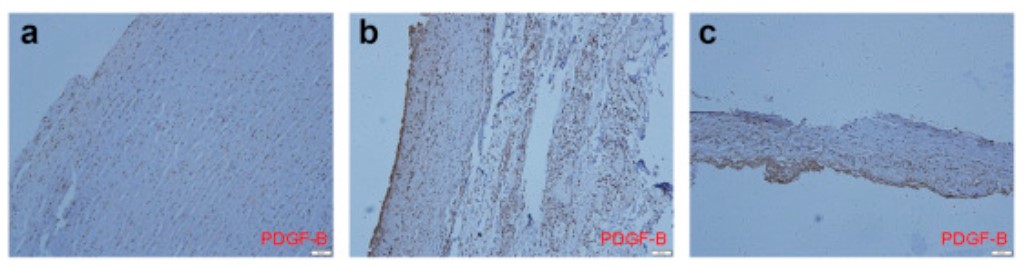
Fig1. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor B (PDGF-B) in ascending aorta wall.
Case study 2: Zhicheng Zhang, 2024
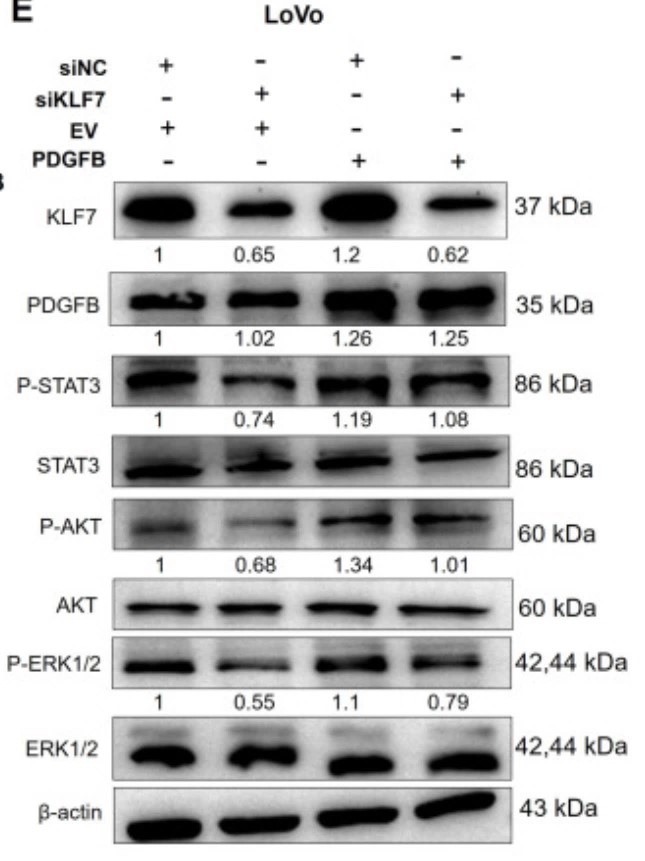
Colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) is the most common malignancy of the digestive tract, which is characterized by a dismal prognosis. No effective treatment has been established presently, thus there is an urgent need to understand the mechanisms driving COAD progression. By constructing stable cell lines (KLF7 overexpression and knockdown) and using a series of cellular and molecular experiments, this study found that KLF7 is overexpressed in COAD tissues. Mechanistically, these findings reveal that KLF7 can specifically bind to the promoter region of PDGFB (TGGGTGGAG), thus promoting the transcription of PDGFB and increasing its secretion. And secreted PDGFB facilitates the progression of COAD by activating MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways through PDGFRβ.
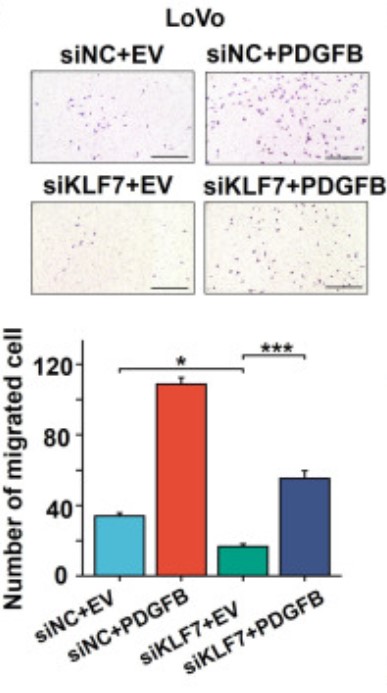
Fig3. Effects of PDGFB in KLF7 transient knockdown or control LoVo cells were determined by migration.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
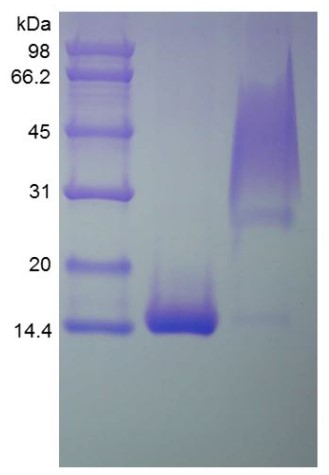
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PDGFB-528H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
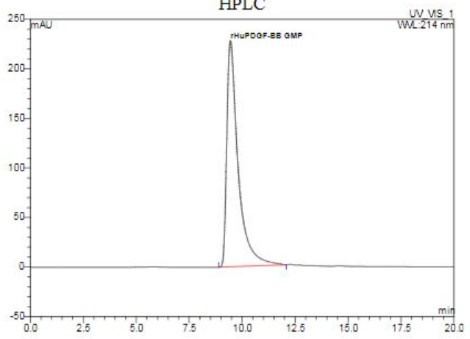
Fig2. Activity Data. (PDGFB-4346HG)
Involved Pathway
PDGFB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDGFB participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDGFB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| HTLV-I infection | FZD2,ITGB2L,RRAS2,SPI1,TBPL1,KAT2A,NRAS,RB1,ATF1,RRAS |
| Phospholipase D signaling pathway | PPAP2A,ARF6,AVPR1B,PIP5K1B,PDGFD,MTOR,AGPAT5,RHEB,PLCG2,PRKCA |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | IL7,LAMB1,IGF1R,IL2RB,TLR4,PPP2R2A,ITGA10,FGFR2,Itga10&Itgb1,COL27A1 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | EGLN2,RAP1A,PIK3R2,PIK3R1,PIK3R3,HGF,VHL,RAP1B,PIK3CD,AKT1 |
| Focal adhesion | COL6A5,RAC1A,RHOB,ITGA3,RHOAC,DOCK1,ACTN4,LAMB1,PTK2AA,RHOAA |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | GDF5,IFNPHI1,CCR6,EPO,TNFRSF18,CXCR3.1,CXCL2,IL9R,IFNA12,CXCL9 |
| Rap signaling pathway | RAPGEF5,PFN1,GNAI1,FGF7,P2RY1,FGF13,FGF11,FGF19,PDGFRB,SIPA1L2 |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | CDC25A,IRS1,STMN1,IRS2,KRAS,FSCN1,DNMT3B,CDC25C,FGFR3,MCL1 |
| Gap junction | DRD2B,PLCB2,ADCY1A,GNA15.1,PDGFAB,PDGFRB,GNAI2B,MAP2K1,TUBA1L,GRB2A |
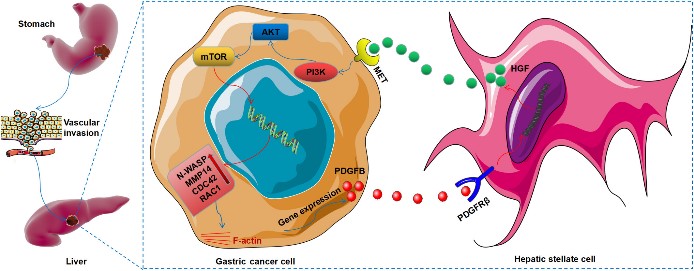
Fig2. Schematic illustration of the potential mechanism of gastric cancer with liver metastasis (GCLM). (Chuanfu Ren, 2023)
Protein Function
PDGFB has several biochemical functions, for example, chemoattractant activity,collagen binding,growth factor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDGFB itself. We selected most functions PDGFB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDGFB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chemoattractant activity | BMP4,CCL3,VEGFA,LGALS3,VEGFB,MIF,CCL5,CCL16,SCG2,CCL15 |
| identical protein binding | NFKB1,ADIPOR1,VPS4B,DYNLT3,S100A4,PARP1,VAMP2,IRF3,C14orf166,HSP90AA1 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | SNX2,SLC51A,CLCN3,SPTAN1,TGFB2,NPAS4,MEIS1,RAB3GAP2,HMG20A,CHRAC1 |
| collagen binding | ANTXR1,ACHE,PCOLCE2,CTSS,MMP13,ITGA1,ABI3BP,CTSB,NID2,SERPINH1B |
| platelet-derived growth factor binding | PDGFA,COL6A1,COL4A1,COL1A2,COL5A1,COL3A1,COL1A1,COL2A1,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PDGFRA |
| platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding | PDGFAB,PDGFRA,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PTEN,PDGFRB,PDGFD,PDGFC,ITGB3,FIGF,TYMP |
| protein binding | DDB2,FPR1,Abcb1b,ERCC3,FST,CAPN3,ABCG2,LPXN,BUD31,CCND2 |
| growth factor activity | CSF1,NTF4,TDGF1,RABEP1,VEGFC,JAG2,PDGFAB,BMP15,MDKA,NDR1 |
| protein homodimerization activity | QPRT,PRMT2,ALS2,NFKB1,SLC30A8,RAB11FIP4,CADM2,CIB2,HRSP12,ACAT1 |
Interacting Protein
PDGFB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDGFB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDGFB.
PDGFRB;PDGFRA
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Borkham-Kamphorst, E; Alexi, P; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D modulates extracellular matrix homeostasis and remodeling through TIMP-1 induction and attenuation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 gelatinase activities. BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 457:307-313(2015).
- Yoshida, S; Ikenaga, N; et al. Extrahepatic Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-beta, Delivered by Platelets, Promotes Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Biliary Fibrosis in Mice. GASTROENTEROLOGY 147:1378-1392(2014).



