FGF1
-
Official Full Name
fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic) -
Overview
Fibroblast growth factors, or FGFs, are a family of growth factors involved in angiogenesis, wound healing, and embryonic development. The FGFs are heparin-binding proteins and interactions with cell-surface associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans have been shown to be essential for FGF signal transduction. FGFs are key players in the processes of proliferation and differentiation of wide variety of cells and tissues. -
Synonyms
FGF1;Fibroblast Growth Factor-acidic;FGF-acidic;Basic fibroblast growth factor;BFGF;FGF 2;FGF B;FGF2;FGF2 basic;FGF2_HUMAN;FGFB;Fibroblast growth factor 2 (basic);HBGF 2;HBGF-2;HBGF2;HBGH 2;HBGH2;Heparin binding growth factor 2 precursor;Heparin-binding growth factor 2;Prostatropin
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Bovine
- Canine
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Sheep
- Pig
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Mouse/Rat
- Cattle
- E.coli
- Insect Cell
- yeast
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- Bovine Brain
- Oryza Sativa
- Mammalian Cell
- Human Cell
- Mouse
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- Non
- His
- StrepII
- His&GST
- His&T7
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&SUMO
Background
What is FGF1 protein?
FGF1 gene (fibroblast growth factor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5q31. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein functions as a modifier of endothelial cell migration and proliferation, as well as an angiogenic factor. It acts as a mitogen for a variety of mesoderm- and neuroectoderm-derived cells in vitro, thus is thought to be involved in organogenesis. The FGF1 protein is consisted of 155 amino acids and FGF1 molecular weight is approximately 17.5 kDa.
What is the function of FGF1 protein?
FGF1 protein is a multifunctional cytokine that plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival and angiogenesis. By binding to its receptor family members, FGF1 activates a variety of signaling pathways, including MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and PLCγ, which play a role in tissue repair, wound healing, embryonic development, nervous system formation, and tumorigenesis. In addition, FGF1 plays a key role in bone development and mineral homeostasis, influencing the function of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which in turn regulates bone formation and remodeling. These functions of FGF1 make it a potential target for the treatment of a variety of diseases, including promoting wound healing, treating osteoporosis, and anti-cancer strategies.

Fig1. Mechanistic insights into the metabolic actions of FGF1. (Emanuel Gasser, 2022)
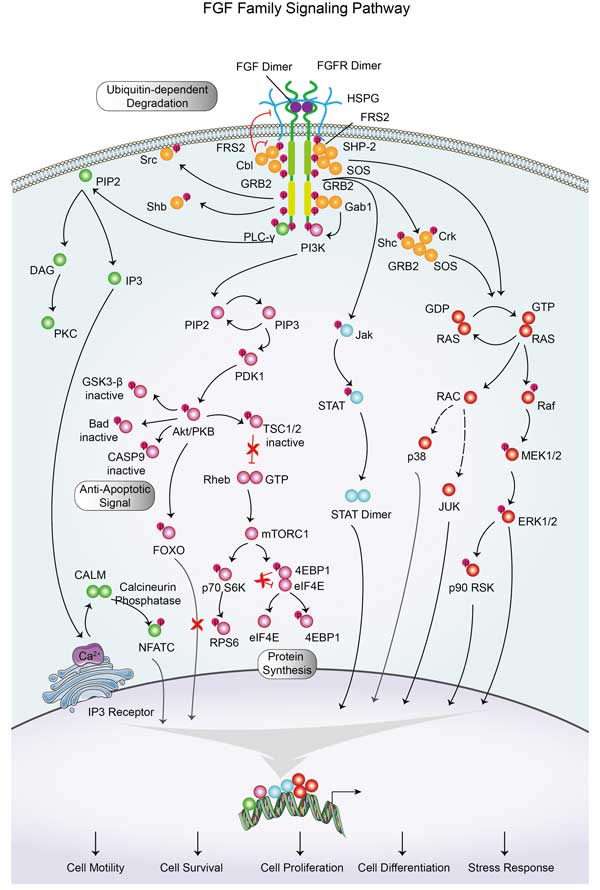
FGF1 related signaling pathway
FGF1 is activated by binding to four different FGF receptors (FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, FGFR4), triggering multiple signaling pathways including but not limited to Ras-MAPK, PI3K-Akt, PLC-γ, and JAK-STAT. These signaling pathways play key roles in a variety of biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, angiogenesis, and wound healing. These functions of FGF1 are particularly important in tissue repair, embryonic development, nervous system formation, and tumor development. Abnormalities in FGF1 signaling have been linked to a variety of diseases, including certain cancers, bone disorders, and metabolic diseases. FGF1 and its receptor system are of great value in biomedical research and therapeutic strategy development.
FGF1 related diseases
FGF1 plays an important role in a variety of diseases, especially in metabolic diseases and cancer. By binding to members of the FGF receptor family, FGF1 activates signaling pathways including MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT and PLCγ to regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and survival. In the treatment of diabetes, FGF1 has shown significant hypoglycemic effects, enhancing insulin sensitivity, inhibiting glucose production in the liver, and possibly lowering blood sugar levels by affecting metabolic processes in adipose tissue. In addition, FGF1 has been implicated in the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, where it may promote the proliferation and survival of tumor cells, and may also inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in some cases.
Bioapplications of FGF1
FGF1 has shown potential in the treatment of a variety of diseases, especially metabolic diseases and cancer. FGF1 regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and survival by activating FGFR receptors and triggering signaling pathways including MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT and PLCγ. In the treatment of diabetes, FGF1 is able to enhance insulin sensitivity, improve insulin resistance, and lower blood sugar levels by affecting metabolic processes in adipose tissue. In addition, FGF1 has shown potential therapeutic effects in the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers. These effects of FGF1 make it a potential target for the treatment of related diseases and are currently undergoing further research and drug development.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Fahad Kidwai, 2020
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) can simulate skeletal organogenesis and disease, providing a platform for research. To reflect the development of the human bone, the hPSC differentiation method should encompass osteogenic progenitor cells (OPs) from three distinct embryonic lineages: paraxonal mesoderm, pleural mesoderm, and neural crest. Although OP differentiation protocols exist, which lineages they originate from, as well as their genetic and molecular differential characteristics, have not been fully reported. Thus, lineage-specific OPs were generated from human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells by differentiating paraxial mesodermal cells, lateral lamella mesodermal cells, and neural cristoid cells into their respective OP subsets in a step-by-step way. Successful differentiation confirmed by gene expression and in vivo experiments enabled the identification of transcriptomic signatures of all three cell populations. High FGF1 levels in neural crista-derived OPs are reported for the first time, a finding that is particularly important given the critical role of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in osteogenesis and mineral homeostasis.

Fig1. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for FGF1 in culture medium.

Fig2. Western blot analysis of ERK1, ERK2, and β-actin (housekeeping) after NC-OP treatment with Con-siRNA and FGF1-siRNA.
Case Study 2: Yu Gao, 2022
The endocrine system plays a significant role in breast cancer development, and FGF1 is implicated in this process. However, the detailed cellular mechanisms of FGF1 in breast cancer remain unclear. This study used breast cancer cells to explore FGF1's cellular behavior, finding that it internalizes into cells over time. Both clathrin- and caveolin-mediated endocytosis contribute to FGF1/FGFR internalization and nuclear localization, with Rab5 also playing a crucial role. Notably, nuclear FGF1 and FGFR were found to be closely linked to breast cancer cell proliferation.

Fig3. FGF entered into different types of endosomes.

Fig4. Cyclin D1 expression was down-regulated in non-nuclear-localized FGF group.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FGF1-564H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FGF1-09H)
Involved Pathway
FGF1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FGF1 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FGF1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ras signaling pathway | PLA2G4A,PDGFC,FOXO4,MAPK1,PLCG2,GRB2,NRAS,PLA2G4C,GNGT1,RGL2 |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | SSH2,ITGA4,ITGA9,ITGA2B,RRAS2,MAPK6,MYL10,MLCK2,FGF20B,ACTN2 |
| Melanoma | CDH1,FGF14,PIK3R2,PDGFRB,FGF5,RB1,HGF,MITF,FGF13,RAF1 |
| Hippo signaling pathway | BMP6,YWHAH,WNT9B,RASSF1,PPP2R2C,CTGF,PPP1CB,FRMD6,SMAD7,YAP1 |
| Rap signaling pathway | CALM4,LAT,FGF17,PIK3R5,FGF8,SIPA1L1,RAC3,FGF3,CALM2,LPAR4 |
| Pathways in cancer | VEGFB,DAPK1,TGFA,WNT4,RXRG,GNG4,STK4,ARAF,WNT1,GNAQ |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | FGF20,IL6R,TNN,PTEN,ITGA2,YWHAG,IFNA12,PRKCA,COL27A1,RPS6 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | HSPB1,FGFR4,PRKCA,PPP3CCB,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PRKACAB,ARRB1,CACNG2A,NLK1,NR4A1 |
Protein Function
FGF1 has several biochemical functions, for example, S100 protein binding,fibroblast growth factor receptor binding,growth factor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FGF1 itself. We selected most functions FGF1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FGF1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| heparin binding | AAMP,PCOLCE2,ADAMTS1,COMP,LIPG,UBE4A,CRISPLD2,FGFR1,NELL2,PCOLCE |
| growth factor activity | CXCL12,PRL2C2,BMP8B,FGF21,FGF7,CTGF,BMP10,PSPN,DKK1,FGF10 |
| protein binding | APBB2,RCOR2,KDM5A,ZRANB2,NLRX1,TBCA,MAPK8,CBR2,POLDIP2,CGA |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor binding | FGF8A,FGF20A,FGF10A,FGF6B,FGF22,FRS3,FGF8,FGF21,FGF2,FGF18A |
| S100 protein binding | S100A6,S100A11,AGER,ANXA2,S100A1,DDX1,KCNK3,ANXA11,S100B,EZR |
Interacting Protein
FGF1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FGF1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FGF1.
FGFR1;FGFR2;heparin;intg_av_b3_human;FGFR3;copper(2+);SRPK1;FGFR4;HSPG2
FGF1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
FGF FamilyReceptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Negative Regulators of the Jak/STAT Pathway
Receptors in the Jak/STAT Pathway
EMT Induction
Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition
FGF Ligands
Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF)
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Tiede, C; Tang, AAS; et al. Adhiron: a stable and versatile peptide display scaffold for molecular recognition applications. PROTEIN ENGINEERING DESIGN & SELECTION 27:145-155(2014).
- Aizman, I; Tirumalashetty, BJ; et al. Comparison of the neuropoietic activity of gene-modified versus parental mesenchymal stromal cells and the identification of soluble and extracellular matrix-related neuropoietic mediators. STEM CELL RESEARCH & THERAPY 5:-(2014).