Tek
-
Official Full Name
TEK tyrosine kinase, endothelial -
Overview
This protein is a protein tyrosine-kinase transmembrane receptor for angiopoietin 1. It may constitute the earliest mammalian endothelial cell lineage marker. Probably regulates endothelial cell proliferation, differentiation and guides the proper patterning of endothelial cells during blood vessel formation. -
Synonyms
TEK;TEK tyrosine kinase, endothelial;TIE2;VMCM;TIE-2;VMCM1;CD202B;venous malformations, multiple cutaneous and mucosal;Angiopoietin-1 receptor;EC=2.7.10.1;Tunica interna endothelial cell kinase;Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TEK;Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2;hTIE2;p140 TEK;OTTHUMP00000021167;OTTHUMP00000227067;OTTHUMP00000227068;OTTHUMP00000227069;soluble TIE2 variant 1;soluble TIE2 variant 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- CHO
- Insect cells
- Fc
- His
- GST
- Non
- T7
- Flag
- Avi
Background
What is TEK Protein?
TEK protein, also known as Tie2 protein kinase, is a type of receptor that sits on cell membranes and is part of the Tie2 kinase family. It's involved in a bunch of key biological activities like forming new blood vessels, helping endothelial cells survive, and keeping things like cell movement and structure in check. TEK keeps blood vessels stable by interacting with certain proteins like ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4. It also helps reduce inflammation by stopping certain blood components and white blood cells from leaking out of vessels. Plus, TEK plays a part in managing blood vessel growth after we're born, making sure they stay stable when they're not growing. The TEK protein is consisted of 1124 amino acids and TEK molecular weight is approximately 125.8 kDa.
What is the Function of TEK Protein?
TEK protein, also known as Tie2 protein kinase, is a kind of receptor found on cell surfaces. It mainly helps with blood vessel-related functions. TEK is crucial in forming new blood vessels, keeping endothelial cells alive, and helping them grow, move, stick together, and change shape. It achieves these by interacting with certain partners like ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4. Besides its role in vessel maintenance, TEK also helps reduce inflammation by preventing unwanted leakage of plasma and white blood cells from vessels. Additionally, it's involved in controlling new vessel growth after birth, keeping blood vessels stable and preventing unnecessary growth in areas where blood flow is steady.
TEK Related Signaling Pathway
TEK protein, aka Tie2 kinase, is pretty interesting as it plays big roles in how our blood vessels work. It's part of a bunch of processes like how new blood vessels form, how these cells move around, stick together, and even change shape. TEK keeps blood vessels in check by hanging out with special partners like ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4. Plus, it helps prevent inflammation by stopping stuff like plasma proteins and white blood cells from leaking out of vessels. After we're born, TEK is key in deciding when new blood vessels should stop growing and instead work on staying stable.
TEK Related Diseases
The TEK protein, also known as Tie2, is like a busy manager in your body, handling a bunch of important tasks. It's part of the receptor tyrosine kinase family, which operates as cell surface receptors. TEK plays a big role in forming new blood vessels, keeping endothelial cells healthy, and helping them move and stick together. It also helps keep blood vessels steady by working with partners like ANGPT1, ANGPT2, and ANGPT4. Plus, it keeps inflammation in check by stopping unwanted leakage of proteins and white blood cells from your blood vessels. TEK doesn't just influence blood vessel growth after birth but also works to stabilize them when they're not growing.
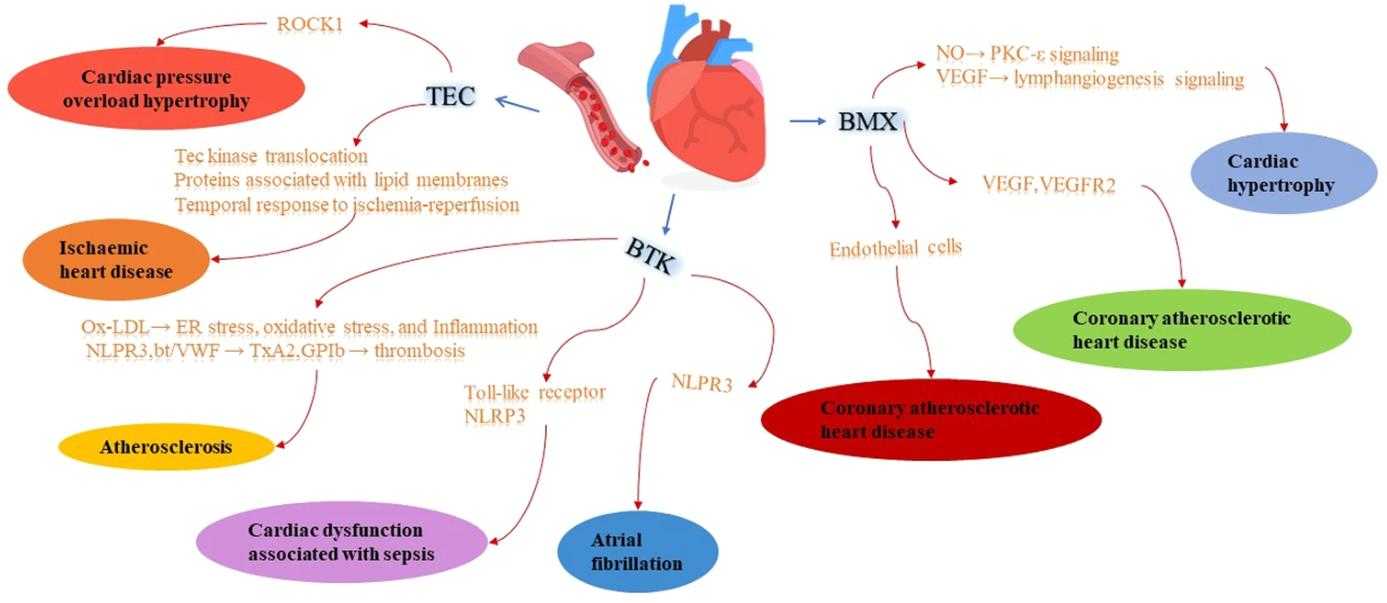
Fig1. The regulation and functions of Tec family kinases in cardiac and vascular disease. (Zeyu Yin, 2022)
Bioapplications of TEK
Recombinant TEK protein is a handy tool in research and industrial settings, especially in studies related to blood vessel formation and health. Scientists use it to get a better understanding of how blood vessels grow and repair themselves, which is crucial for developing treatments for conditions like cancer, where blood vessel growth can feed tumors. It's also used in drug testing to see how new medicines might affect blood vessel behavior. Plus, in industrial production, it's used in assays to test the impact of various compounds on vascular health. This protein's applications extend to helping us figure out ways to create better therapies that target blood vessel diseases and improve drug delivery systems.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mohammad B Hossain, 2016
Certain pathways in DNA repair help cancer cells withstand damage from therapies meant to harm them. Tyrosine kinase receptors (TKRs), like TIE2, play a role here. TIE2, in particular, is found at high levels in aggressive human gliomas. When these cells face ionizing radiation, TIE2 moves into the nucleus, boosting their ability to repair DNA through a process called nonhomologous end-joining, making them more resistant to radiation. Once in the nucleus, TIE2 interacts with DNA repair components and adds a phosphate group to histone H4 at a specific spot, tyrosine 51. This modification is then detected by the proto-oncogene ABL1, suggesting that nuclear TIE2 acts like a sensor for stress that damages DNA by altering histones. This connection between modifying histones and activating the DNA repair process shows how cells respond to and fix DNA damage.
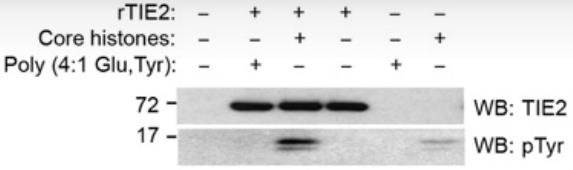
Fig1. rTIE2 potentially phosphorylates core histones at tyrosine residues.
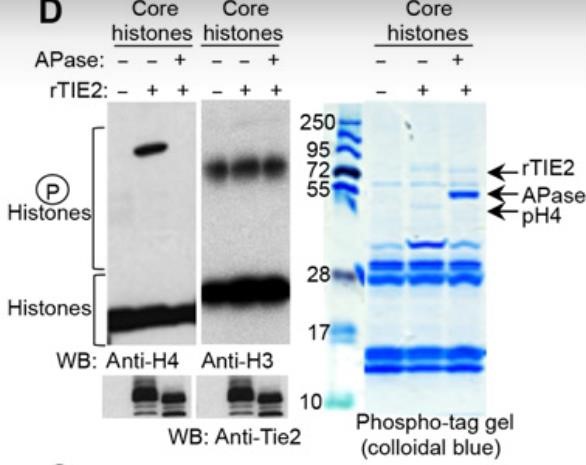
Fig2. rTIE2 phosphorylates H4 as assayed using a phospho-tag gel.
Case Study 2: Shuang-Xi Xiong, 2020
Pollen walls have complex layers that create unique patterns for different species. In Arabidopsis, a transcription factor called ABORTED MICROSPORE (AMS) is in charge of forming the exine layer, while another factor, TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENT SILENCING VIA AT-HOOK (TEK), focuses on the nexine layer. However, the timing of TEK's role in pollen wall development isn't well understood. When TEK-GFP was expressed early in the tapetal cells, it caused male sterility in certain transgenic lines. This early expression led to issues with callose production and abnormal exine patterns. Normally, CALLOSE SYNTHASE5 (CalS5) is needed for callose production, but its expression dropped in these modified plants. We found that TEK regulates CalS5 expression after a certain stage in development. Premature TEK-GFP can directly repress CalS5 through changes in histone modifications. This shows that TEK's timing is key for proper pollen wall patterning, and the coordination of gene regulation helps in stopping callose wall synthesis, aiding in the release of microspores and proper pollen wall development.
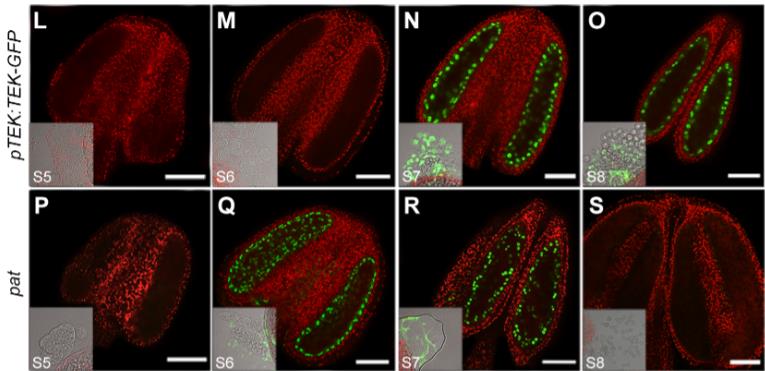
Fig3. Precocious expression of TEK transcripts and TEK-GFP proteins driven by the AMS promoter in pat.
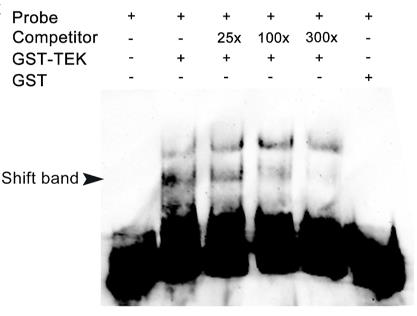
Fig4. EMSA assay was performed with the GST–TEK fusion protein.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TEK-243H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TEK-535H)
Involved Pathway
Tek involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tek participated on our site, such as Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway,HIF- signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tek were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | ATP6AP1,TNFSF13,ATP6V0B,CCL3,TLR4,ATP6V1A,ATP6V1B1,HLA-DRB1,IL17A,ATP6V1E1 |
| Rap signaling pathway | MAP2K1,Kitl,PRKCG,FGFR4,KLK1B4,GNAS,RAP1A,SIPA1L2,ITGB2,INS1 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | ITGA8,CCND2,GNGT1,Il2,IFNA17,LPAR2,YWHAG,IL3,PRKCA,IGF1 |
| Ras signaling pathway | GNGT2,PDGFA,GNB3,PDGFRB,PLA2G2F,FGF2,FGFR4,NFKB1,PIK3CB,PAK3 |
| HIF- signaling pathway | SLC2A1,PIK3R2,EPO,INS,TFRC,ANGPT4,STAT3,EIF4E1B,FLT1,IGF1R |
Protein Function
Tek has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,growth factor binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tek itself. We selected most functions Tek had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tek. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase activity | ROCK2B,EPHA2A,DYRK1B,MAP3K5,PLK5,JAK2,BRAF,RPS6KA3B,CSNK1G2B,CDK7 |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | DYRK1B,MAP2K7,TTN,ERBB3B,EPHB2,FGFR3,TNK2,EPHA2A,EPHA7,MAP3K9 |
| growth factor binding | ACVR1C,RPL37,BMPR2,RHBDF2,GHRHR,FLT1,KDR,NRP1,ACVR2A,HTRA1A |
| protein binding | BAG6,MID1,FOXK1,GNAS,WBP11,TESK1,PCGF6,C4BPA,DSTN,CFI |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | ERBB4,EPHB4,ROS1,EPHA2,CSF1RA,IGF1RB,TYRO3,RYK,NTRK3A,EPHB2B |
| ATP binding | DAK,ALPK1,VRK1,PAPSS2A,NOL9,PL10,ATAD2B,INSR,MCM6L,DDX18 |
| receptor activity | CADM1B,NLGN2B,GABRA5,LILRA2,ADIPOR1B,XPR1,CD5,CD86,GUCY1A3,KLRK1 |
Interacting Protein
Tek has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tek here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tek.
ANGPT2;SHC1;Angpt2;PTPRC;PKM;PTPRB;PTPRG;PTPN12;PTPRJ;PTPRK
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chen, JY; Liu, ZJ; et al. Proangiogenic Compositions of Microvesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Kobayashi, M; Shelley, WC; et al. Functional B-1 progenitor cells are present in the hematopoietic stem cell-deficient embryo and depend on Cbf beta for their development. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 111:12151-12156(2014).



