Recombinant Human Collagen, Type I, Alpha 1
| Cat.No. : | COL1A1-1206H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant HumanCOL1A1 was expressed in Pichia pastoris. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | P.pastoris |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Collagen, type I,alpha 1, also known as COL1A1, is a human gene that encodes the majorcomponent of type I collagen, the fibrillar collagen found in most connectivetissues, including cartilage. Collagen is a protein that strengthens andsupports many tissues in the body, including cartilage, bone, tendon, skin and thewhite part of the eye (sclera). The COL1A1 gene produces a component of typeI collagen, called the pro-alpha1(I) chain. This chain combines with anotherpro-alpha1(I) chain and also with a pro-alpha2(I) chain (produced by theCOL1A2 gene) to make a molecule of type I procollagen. These triple-stranded,rope-like procollagen molecules must be processed by enzymes outside thecell. Once these molecules are processed, they arrange themselves into long,thin fibrils that cross-link to one another in the spaces around cells. Thecross-links result in the formation of very strong mature type I collagenfibers. |
| Form : | Liquid, sterilefiltered in 0.01 M HCl. |
| Concentration : | 2.7 mg/ml |
| Purity : | > 99.0% asdetermined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Store at 2-4°C. |
| OfficialSymbol : | COL1A1 |
| Gene Name | COL1A1 collagen, type I, alpha 1 [ Homosapiens ] |
| Synonyms | COL1A1; collagen,type I, alpha 1; OI4; collagen alpha-1 (I) chain; Alpha-1 type I collagen;pro-alpha-1 collagen type 1; collagen alpha 1(I) chain type I; collagen ofskin, tendon and bone, alpha-1 chain |
| Gene ID | 1277 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000088 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000079 |
| MIM | 120150 |
| UniProt ID | P02452 |
| Chromosome Location | 17q21.33 |
| Pathway | Amoebiasis; Cellsurface interactions at the vascular wall; Collagen adhesion via Gp IV;ECM-receptor interaction; Focal adhesion; Inflammatory Response Pathway;Platelet Activation; vWF interaction with collagen; Hemostasis; IL4-mediatedsignaling events; Inflammatory Response Pathway; Integrin cell surfaceinteractions; NCAM signaling for neurite out-growth; Osteoblast Signaling;Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen |
| Function | extracellular matrixstructural constituent; identical protein binding; platelet-derived growthfactor binding; protein binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Col1a1-816M | Recombinant Mouse Col1a1 Protein, His&GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| COL1A1-1206H | Recombinant Human Collagen, Type I, Alpha 1 | +Inquiry |
| COL1A1-113H | Recombinant Human COL1A1, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| COL1A1-66H | Recombinant Human COL1A1 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Col1a1-5382R | Recombinant Rat Col1a1 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| Col1a1-7174M | Native Mouse Col1a1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| COL1A1-26195TH | Native Human COL1A1 | +Inquiry |
| COL1A1-23M | Native Mouse Collagen I Protein | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Xiang G, et al. Genes (Basel). 2022
COL1A1 encodes the type I collagen α1 chain, which shows the highest abundance among members of the collagen family and is widely expressed in different mammalian cells and tissues. However, its molecular characteristics are not completely elucidated. In this study, the molecular profiles of COL1A1 and characteristics of the COL1A1 protein were investigated using a promoter activity assay and multiple bioinformatics tools. The results showed that the 5' flanking region of porcine COL1A1 contained two CpG islands, five core promoter sequences, and twenty-six transcription factor-binding sites. In the luciferase assay, the upstream 294 bp region of the initiation codon of COL1A1 showed the highest activity, confirming that this section is the core region of the porcine COL1A1 promoter. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that COL1A1 is a negatively charged, hydrophilic secreted protein. It does not contain a transmembrane domain and is highly conserved in humans, mice, sheep, and pigs. Protein interaction analysis demonstrated that the interaction coefficient of COL1A1 with COL1A2, COL3A1, ITGB1, and ITGA2 was greater than 0.9, suggesting that this protein plays a crucial role in collagen structure formation and cell adhesion.

Fig1. CpG islands prediction in 5′ flanking region of porcine COL1A1.

Fig2. Hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity prediction of porcine COL1A1.
Case 2: Zhang Z, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2018
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer‑associated mortality, and is a major health problem. Collagen type I α 1 (COL1A1) is a major component of collagen type I. Recently, it was reported to be overexpressed in a variety of tumor tissues and cells. However, the function of COL1A1 in CRC remains unclear. Herein, the present study demonstrated that COL1A1 was upregulated in CRC tissues and the paired lymph node tissues. Transwell assays showed that COL1A1 promoted CRC cell migration in vitro. Moreover, it was revealed that COL1A1 levels were correlated with those of WNT/planar cell polarity (PCP) signaling pathway genes; inhibition of COL1A1 decreased the expression levels of Ras‑related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1‑GTP, phosphorylated‑c‑Jun N‑terminal kinase, and RhoA‑GTP. These results may indicate the mechanisms underlying the oncogenic role of COL1A1 in CRC.

Fig1. Western blot analyses were used to assess COL1A1 protein levels following transfection of the siCOL1A1 plasmid.
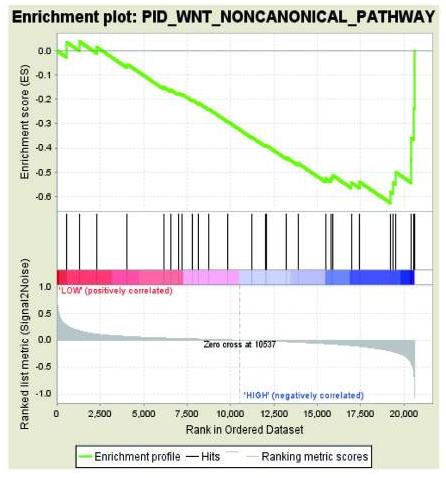
Fig2. GSEA results showing 'WNT non-canonical pathway' signatures enriched in COL1A1 high expression tissue samples.
The recombinant COL1A1 protein, the recombinant type I collagen α1 chain, has shown a wide range of potential applications in several fields due to its good biological properties and importance in the extracellular matrix:
1. Medical materials. COL1A1 plays an important role in tissue repair and regeneration and is widely used to develop biomaterials that promote wound healing and tissue repair, including skin scaffolds and bone repair materials. In addition, it can also be used as biomedical materials for wound healing, skin repair, oral mucositis treatment and other medical devices.
2. Cosmetics and Medical beauty. In the cosmetics industry, recombinant COL1A1 protein is used as a skin care ingredient due to its moisturizing, antioxidant and UV protection properties. In medical cosmetology, it is used to inject fillers and efficacy dressings to improve skin quality.
3. Drug carrier. Due to its good biocompatibility and degradability, COL1A1 is used as a drug delivery system, especially in the sustained release of protein and peptide drugs.
4. Development of biological materials. COL1A1 protein is used to develop novel materials with improved mechanical properties and biocompatibility, such as binding to natural polymers such as chitosan and fibroin protein.
5. 3D printing. In the field of 3D bioprinting, the recombinant COL1A1 protein is used as a printing ink for the creation of biomimetic tissue structures due to its plasticity.
6. Cancer treatment. COL1A1 is highly expressed in some cancers and is associated with cancer progression and prognosis, so it is considered a potential target for cancer treatment. Studies have shown that COL1A1 homologous trimers produced by cancer cells have carcinogenic properties, and its deletion can inhibit tumor progression and enhance the effect of immunotherapy.
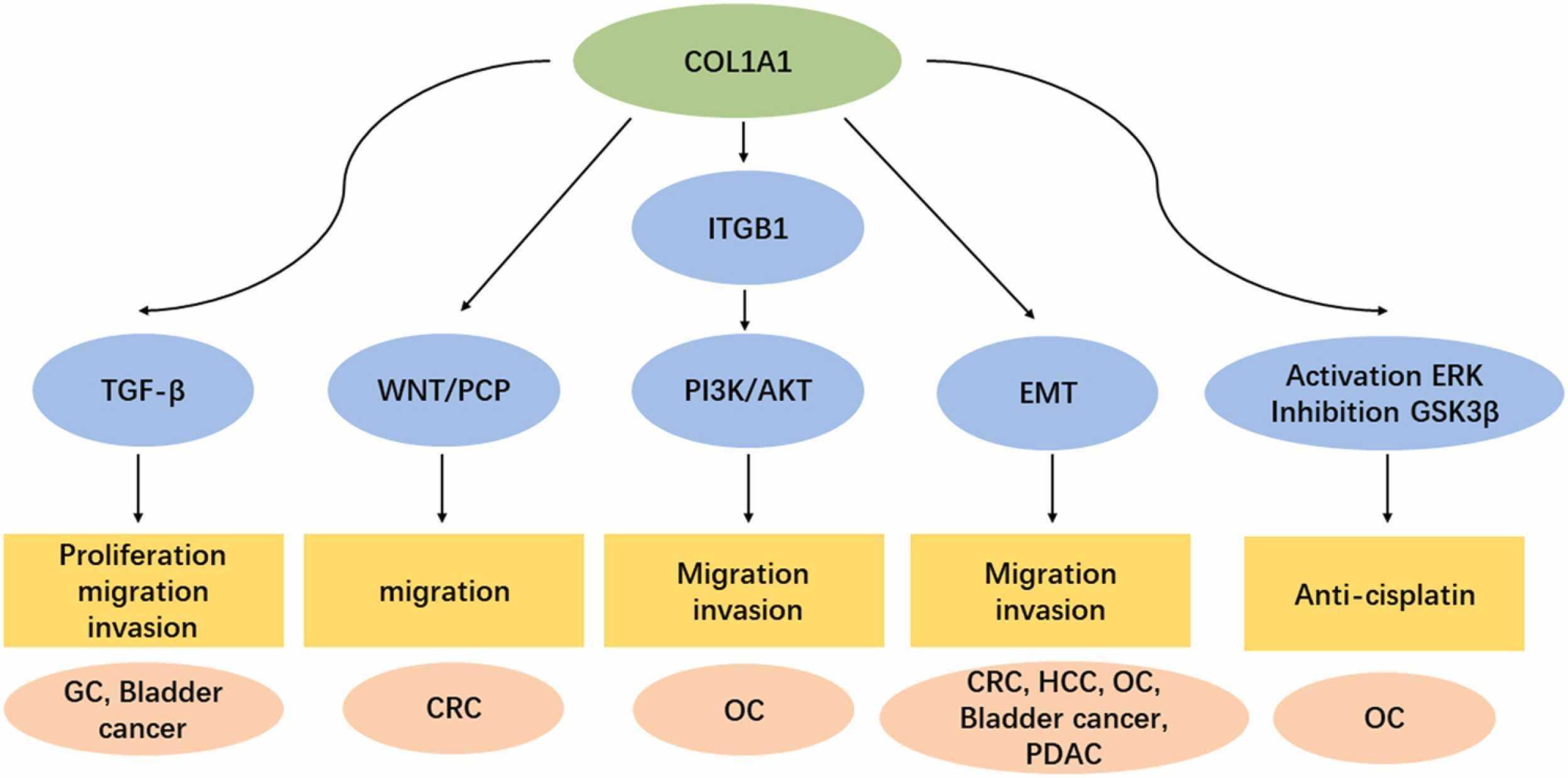
Fig1. Pathways of COL1A1-mediated promotion of different cancers by affecting cell proliferation, migration, invasion and drug resistance. (Xue Li, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All COL1A1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All COL1A1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


