TDGF1
-
Official Full Name
teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes an epidermal growth factor-related protein that contains a cripto, FRL-1, and cryptic domain. The encoded protein is an extracellular, membrane-bound signaling protein that plays an essential role in embryonic development and tumor growth. Mutations in this gene are associated with forebrain defects. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 2, 3, 6, 8, 19 and X. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2010] -
Synonyms
TDGF1;teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1;CR;CRGF;CRIPTO;cripto-1 growth factor;epidermal growth factor-like cripto protein CR1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Sf21 Cells
- Human
- Human Cells
- Modified human 293 cells
- Mammalian Cells
- GST
- His
- Fc
- Non
- T7
- MBP
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDGF1-3170H | Recombinant Human TDGF1, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-188aa | |
| TDGF1-3350H | Active Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Met1-Thr172 | |
| TDGF1-496H |
Active Recombinant Human TDGF1, Fc Chimera
|
HEK293 | Human | Fc |
|
|
| TDGF1-526H |
Active Recombinant Human TDGF1
|
Sf21 Cells | Human | Non | Leu31-Thr172 & Ser63-Thr172 |
|
| TDGF1-592H |
Active Recombinant Human TDGF1 Protein, Tag Free
|
Human | Human | Non | 31-169 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-78H |
Active Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, T7/His-tagged
|
E.coli | Human | His&T7 | 31-150 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-1048H |
Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein(Met1-Thr172), hFc-tagged
|
HEK293 | Human | Fc | Met1-Thr172 |
|
| TDGF1-1082R | Recombinant Rat TDGF1 Protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Fc | 1-143 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-166R | Recombinant Rat Tdgf1, His tagged | Human Cells | Rat | Non | 1-143 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-27821TH | Active Recombinant Human TDGF1, Fc-tagged | Modified human 293 cells | Human | Fc | 31-169 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-27822TH | Recombinant Human TDGF1, MBP-tagged | E.coli | Human | MBP | Full L. |
|
| TDGF1-2904H | Recombinant Human TDGF1, MBP | E.coli | Human | MBP | 1-188 a.a. |
|
| TDGF1-495H | Recombinant Human Teratocarcinoma-Derived Growth Factor 1 | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| TDGF1-497H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | Leu31-Thr172 |
|
| TDGF1-8718Z | Recombinant Zebrafish TDGF1 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| TDGF1-2432HCL | Recombinant Human TDGF1 cell lysate | Human Cells | Human | Non |
|
|
| TDGF1-832RCL | Recombinant Rat TDGF1 cell lysate | Human Cells | Rat | Non |
|
|
| TDGF1-001H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 Protein, MBP-tagged | E.coli | Human | MBP | 1-188 |
|
| TDGF1-1254R | Recombinant Rat TDGF1 protein(Met1-Cys143), His-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His | Met1-Cys143 |
|
| TDGF1-295H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 Protein, His-tagged(C-ter) | HEK293 | Human | His | Leu31-Thr172 |
|
| TDGF1-3555H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 32-150aa |
|
| TDGF1-3556H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 32-150aa |
|
| TDGF1-562H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 Protein, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | 188 |
|
| TDGF1-572H | Active Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | Met1-Asp150 |
|
| TDGF1-573H | Active Recombinant Human TDGF1 protein, hFc-tagged | HEK293 | Human | Fc | Met1-Asp150 |
|
| TDGF1-6407H | Recombinant Human TDGF1 Protein (Leu31-Ser169), C-Fc tagged | Mammalian Cells | Human | Fc | Leu31-Ser169 |
|
Background
What is TDGF1 Protein?
TDGF1, or Teratocarcinoma-Derived Growth Factor 1, is a protein found in humans, coded by the TDGF1 gene, and is sometimes called CRIPTO. It's a signaling protein located on the cell membrane and is crucial in early development and growth of tumors. If this gene mutates, it can lead to defects in the forebrain. The TDGF1 gene also has pseudogenes on several chromosomes, and due to alternative splicing, it can generate multiple transcript variants. It's involved in many biological processes, such as cell differentiation and development pathways, making it important for both normal cell functions and pathological states.
What is the Function of TDGF1 Protein?
TDGF1, also known as Teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1 or CRIPTO, is a protein in humans that's vital for early embryo development and also linked to tumor growth. This protein is membrane-bound and plays a big role in signaling, affecting how cells talk to each other during development. It's involved in key processes like keeping embryonic stem cells going, defining how cells differentiate and migrate, and it influences heart development. Plus, it has ties to certain forebrain defects when mutations occur. Overall, TDGF1 is a crucial player in both development and disease.
TDGF1 Related Signaling Pathway
TDGF1, or teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1, is a pretty important protein involved in various signaling pathways that affect how cells grow, survive, and change. It's deeply involved in the Nodal signaling path, linked to the TGF-β family, crucial for developing embryos and even how tumors grow. It also triggers other paths, like PI3K/Akt and MAPK, crucial for cell growth and survival. TDGF1 even affects how cells move and change form, steps that are key in cancer progression. Essentially, TDGF1 acts like a switch flipping on signals that dictate cell behavior, growth, and transformation, which is particularly significant in cancer. Grasping its role in these processes might open up new treatments for such diseases.
TDGF1 Related Diseases
TDGF1, short for teratocarcinoma-derived growth factor 1, is a protein that's tied to various diseases, especially those relating to development and cancer. It's key in embryogenesis and how cells move. When TDGF1 doesn't work right, it can cause issues like forebrain defects, affecting brain development. It's also linked to congenital heart defects, like ventricular septal defect (VSD), which is pretty common. Studies have found genetic variations in TDGF1 in Chinese patients with VSD, supporting its role in this condition. Moreover, TDGF1's role in cancer is getting clearer; it seems to help tumors grow and aids in the transition of cells from fixed to mobile states (known as EMT), letting them migrate elsewhere in the body. So, TDGF1 is crucial in both developmental disorders and cancer, making it a hot topic for research and possible new treatments.
Bioapplications of TDGF1
TDGF1, often used in research and clinical settings, is a handy tool especially when diving into developmental biology and cancer studies. Researchers love it for how it helps unravel the mysteries of embryonic development—kind of shedding light on how cells decide what they're going to be when they grow up. Its links to cancer progression make it a hot topic for therapeutic development, too. In the lab, you'll often find TDGF1 used to study cell migration and how cells transition during cancer metastasis. It also plays a role in regenerative medicine, where scientists explore its potential in tissue repair and regenerative therapies. In industrial applications, understanding this protein can be critical in designing drugs that could inhibit its role in disease processes, thereby providing therapeutic options for conditions like cancer. So, whether it's sparking up new ideas for treating disease or pushing forward the boundaries of what we know about development and regeneration, TDGF1 is pretty versatile across various research and clinical fronts.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ann N Behrens, 2013
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) is the most common and serious birth defect. Kids with CHD often end up with severe heart issues needing special treatments like transplants. By digging into how genes guide heart cells as they develop, we can better grasp how the heart normally works and what goes wrong in CHD. Plus, this knowledge is paving the way for future treatments. We've zeroed in on certain genes for heart development using transgenic mice. Early research pointed to Tdgf1 being controlled by another gene, Nkx2-5. We've used various lab techniques to confirm that Nkx2-5 does indeed regulate Tdgf1 during early heart formation.
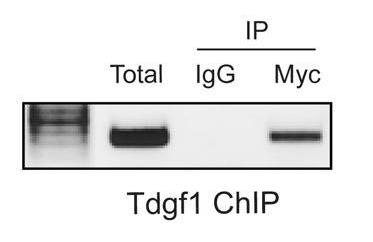
Fig1. ChIP assay for binding of Nkx2-5 to the Tdgf1 promoter.
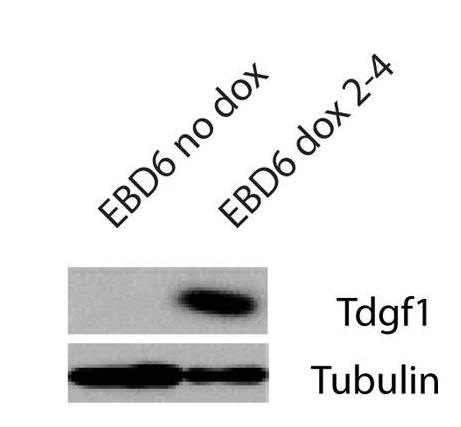
Fig2. Western blot analysis confirms increased expression of Tdgf1 in EBs overexpressing Nkx2-5 following the induction with Dox for 2 days.
Case Study 2: Tracy A. Williams, 2010
Aldosterone-producing adenomas (APA) are a common cause of secondary high blood pressure due to excessive aldosterone release. The exact molecular reasons behind adrenal tumor development and this abnormal hormone secretion aren't fully understood yet. To figure this out, scientists conducted gene expression studies on 8 APAs and 3 normal adrenal glands, followed by additional analysis with more samples. They found that TDGF-1, a growth factor, was significantly higher in APAs. Lab tests showed that TDGF-1 ramps up certain chemical signals within cells, which boosts aldosterone production. This effect can be stopped using specific inhibitors. Additionally, TDGF-1 helps protect cells from dying due to stress by reducing markers of cell death.
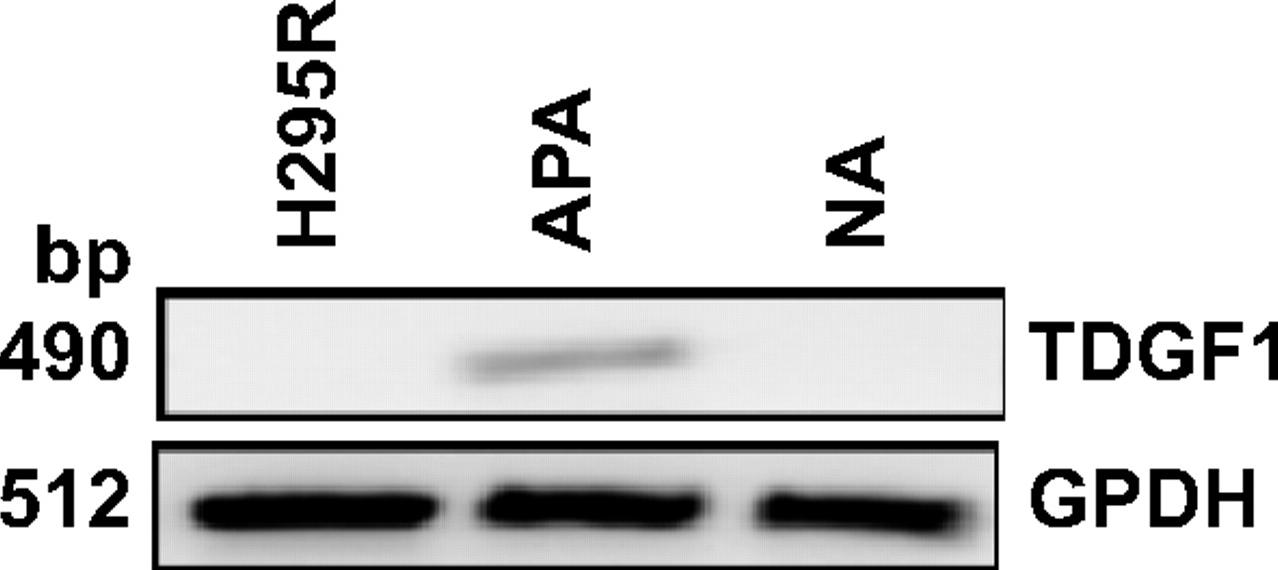
Fig3. Semiquantitative RT-PCR of TDGF-1 in H295R cells and adrenal samples.
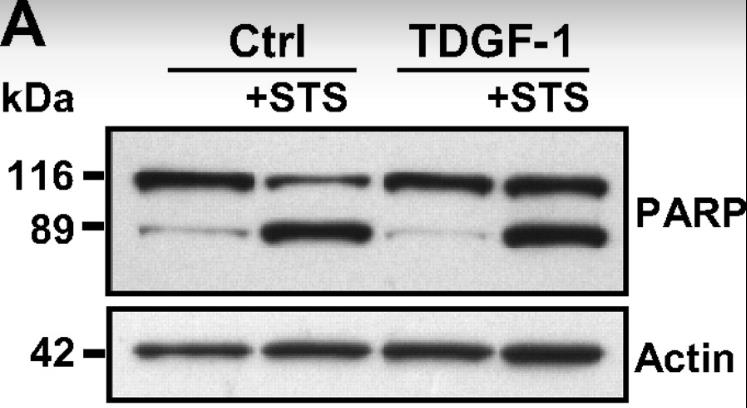
Fig4. The hydrolysis of full-length PARP to the inactive form analyzed by Western blotting of lysates of TDGF-1 or control (Ctrl) plasmid-transfected cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TDGF1-497H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TDGF1-001H)
Involved Pathway
TDGF1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TDGF1 participated on our site, such as Developmental Biology,Glypican 1 network,POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TDGF1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Developmental Biology | CFC1,FOXD3,MED15,PEA15,SCN2A,MED29,KCNQ2,MED9,DPYSL5B,COL9A3 |
| Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells | NR5A1,SALL4,FOXD3,HIF3A,LIN28A,POU5F3,NR6A1,PRDM14 |
| Regulation of signaling by NODAL | CFC1,ACVR1C,LEFTY1 |
| POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation | NR6A1,FOXD3 |
| Signaling by NODAL | LEFTY1,CFC1,FOXH1,PCSK6,GDF1,DRAP1,ACVR1C |
Protein Function
TDGF1 has several biochemical functions, for example, growth factor activity,protein binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TDGF1 itself. We selected most functions TDGF1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TDGF1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor binding | ADAM10,PTK2AA,EDN3,SSFA2,MCHR1,MLYCD,LAMA3,RARA,IDE,MTSS1 |
| growth factor activity | GDF5,FGF2,NUDT6,FGF6,GMFG,VEGFAB,NGF,LFT1,NENF,GDNFA |
| protein binding | CNKSR3,TCEANC2,VARS2,PPP1CB,VTI1B,ISOC2,CEP85,ETS2,HMGN2,SCFD1 |
Interacting Protein
TDGF1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TDGF1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TDGF1.
GPC1;GDF9;ANG;FBLN1;BAG6;AP2S1;RIF1;COPS6;FARSA
Resources
Research Area
Cardiac Stem Cell MarkersEmbryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Markers
TGF-beta Family Receptor
Related Services
Related Products
References


