TARDBP
-
Official Full Name
TAR DNA binding protein -
Overview
HIV-1, the causative agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), contains an RNA genome that produces a chromosomally integrated DNA during the replicative cycle. Activation of HIV-1 gene expression by the transactivator Tat is dependent on an RNA regulatory element (TAR) located downstream of the transcription initiation site. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional repressor that binds to chromosomally integrated TAR DNA and represses HIV-1 transcription. In addition, this protein regulates alternate splicing of the CFTR gene. A similar pseudogene is present on chromosome 20. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
TARDBP;TAR DNA binding protein;ALS10;TDP-43;TAR DNA-binding protein 43;TAR DNA-binding protein-43
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- T7
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- SUMO
Background
What is TARDBP protein?
TARDBP gene (TAR DNA binding protein) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p36. The TARDBP gene encodes a protein called TAR DNA-binding protein 43 kDa (TDP-43), which is found inside the cell nucleus and plays a role in a variety of tissues, particularly in nervous system and organ development. The TDP-43 protein is involved in many steps of protein synthesis, it is able to bind DNA and regulate the transcription process, which is the first step in the synthesis of proteins from genes. In addition, TDP-43 can also bind RNA, ensure its stability, and participate in the processing of messenger RNA (mRNA), through different cuts and recombination of mRNA molecules, control the production of different versions of certain proteins, a process known as alternative splicing. The TARDBP protein is consisted of 414 amino acids and TARDBP molecular weight is approximately 44.7 kDa.
What is the function of TARDBP protein?
TDP-43 acts as a transcriptional repressor, binding to TAR DNA to regulate the expression of genes, including the HIV-1 genome. It is involved in various steps of RNA biogenesis and processing, including the regulation of splicing of many non-coding and protein-coding RNAs. The protein plays a role in alternative splicing of pre-mRNA, which allows the production of different protein isoforms from the same gene. It can bind to proteins and is involved in the formation of stress granules, which are cellular structures that form under stress conditions and are involved in the storage and protection of mRNA. TDP-43 is involved in maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis by regulating the processing of mitochondrial transcripts. In response to stress, such as oxidative insult, TDP-43 can associate with stalled ribosomes and contribute to cell survival.
TARDBP Related Signaling Pathway
TDP-43 plays a key role in multiple stages of RNA metabolism, including transcriptional regulation, pre-mrna splicing, RNA processing, and RNA localization. These functions are particularly important for neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS and FTD. TDP-43 is involved in regulating the splicing of many non-coding and coding Rnas, including protein mrnas associated with nerve survival and mrnas encoding proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. TDP-43 is usually located in the nucleus, but can also shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nucleus to perform a variety of cellular functions. Its location and level are finely regulated by the negative feedback mechanism. TDP-43 is capable of undergoing phase transitions, forming droplets or accumulating into irreversible cytoplasmic aggregates, which play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases.
TARDBP Related Diseases
The TDP-43 protein encoded by the TARDBP gene plays a key role in a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, and its abnormal aggregation is a pathological feature of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal degenerative disease (FTD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), and borderline dominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE). These diseases are often associated with loss of motor neuron function, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes, and the abnormal behavior of TDP-43, including its abnormal accumulation in the cytoplasm and loss of intranuclear function, is thought to be an important cause of nerve cell dysfunction and degenerative changes.
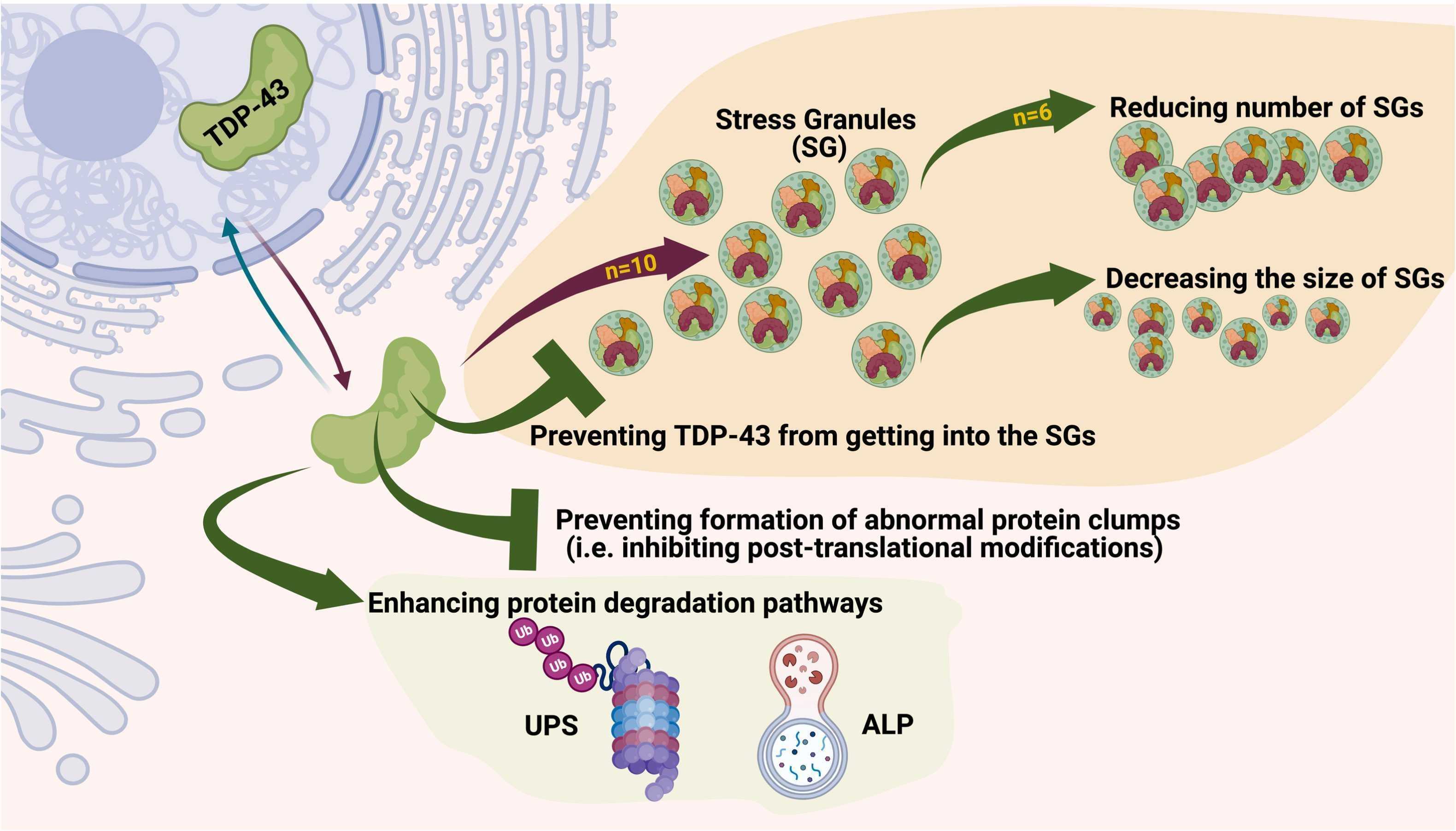
Fig1. Potent small-molecule mechanisms of actions targeting TDP-43 proteinopathies. (Afshin Babazadeh, 2023)
Bioapplications of TARDBP
Abnormal aggregation of TDP-43 is a key biomarker in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS and FTD, which helps to identify and classify these diseases early. Drug development targeting the functional and aggregation properties of TDP-43 may provide new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of related diseases. Regulating the expression of TARDBP gene through gene editing or gene silencing techniques may provide a new way to treat TDP-43-related diseases. The role of TDP-43 in neuroprotection and cellular stress response provides a potential molecular target for developing neuroprotective strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Eliana Lauranzano, 2015
PPIA is also a translational biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and its normal function in the central nervous system is unknown. Here researchers show that PPIA is a functional interacting partner of TARDBP (also known as TDP-43). PPIA regulates expression of known TARDBP RNA targets and is necessary for the assembly of TARDBP in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes. The data suggest that perturbation of PPIA/TARDBP interaction causes 'TDP-43' pathology. Consistent with this model, they show that the PPIA/TARDBP interaction is impaired in several pathological conditions. Moreover, PPIA depletion induces TARDBP aggregation, downregulates HDAC6, ATG7 and VCP, and accelerates disease progression in the SOD1(G93A) mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
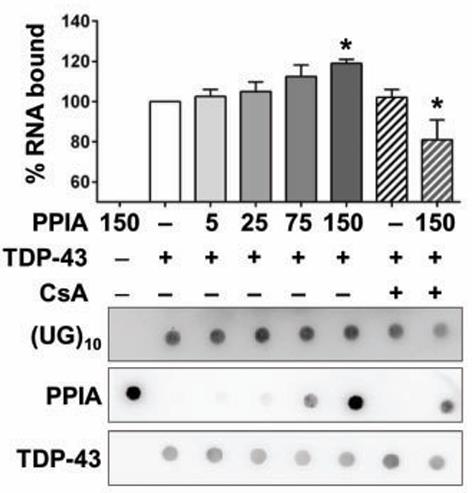
Fig1. The influence of PPIA on interaction of TARDBP with (UG)10 was assessed by a filter binding assay.
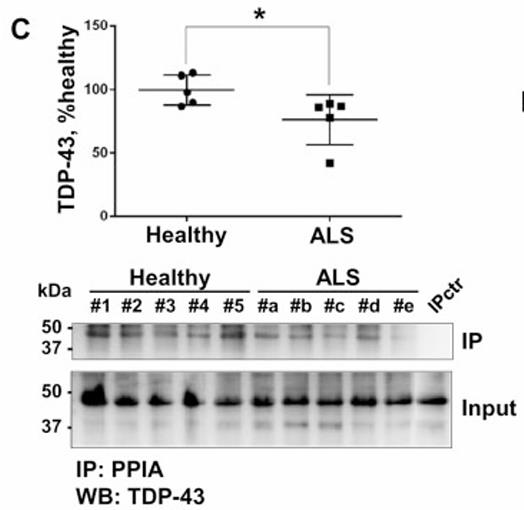
Fig2. TARDBP was co-immunoprecipitated using an anti-PPIA polyclonal antibody from PBMCs of patients with ALS.
Case Study 2: Sang-Hoon Yi, 2014
To understand the mechanisms of pathological TDP-43 processing and identify potential biomarkers, researchers generated novel phosphorylation-independent monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) using bacteria-expressed human full-length recombinant TDP-43. Remarkably, they identified a distinctive MAb, No. 9, targeting an epitope in amino acid (aa) region 311-360 of the C-terminus. This antibody showed preferential reactivity for pathological TDP-43 inclusions, with only mild reactivity for normal nuclear TDP-43. MAb No. 9 revealed more pathology in FTLD-TDP type A and type B brains and in AD brains compared to the commercial p409/410 MAb. Using synthetic phosphorylated peptides, they also obtained MAbs targeting the p409/410 epitope. Interestingly, MAb No. 14 was found to reveal additional pathology in AD compared to the commercial p409/410 MAb, specifically, TDP-43-immunopositive deposits with amyloid plaques in AD brains. These unique immunopositivities observed with MAbs No. 9 and No. 14 are likely attributed to their conformation-dependent binding to TDP-43 inclusions.
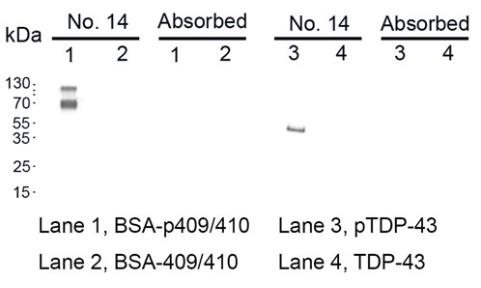
Fig3. The specificity of MAb No. 14 was verified through Western blotting using the TDP-43 protein phosphorylated in vitro.
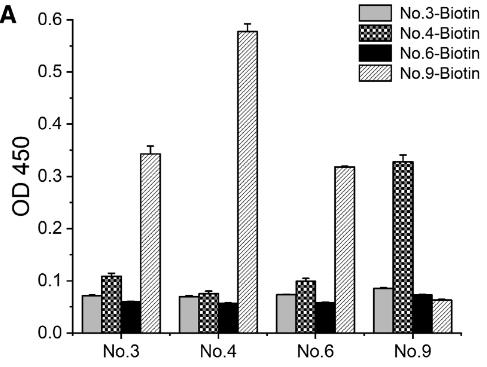
Fig4. To screen the antibody pairs using sandwich ELISA analysis, 20 ng/mL of TDP-43 protein was introduced to the plates.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TARDBP-40H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TARDBP-39H)
Involved Pathway
TARDBP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TARDBP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TARDBP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
TARDBP has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,double-stranded DNA binding,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TARDBP itself. We selected most functions TARDBP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TARDBP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| poly(A) RNA binding | RBMX2,RPL5B,ETF1A,PIN4,FCF1,EPPK1,NCL,HLTF,SAMSN1,DARS |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific binding | SIX6,CDX1,MIXL1,POU4F1,ZEB2,FUBP1,SFPI1,HMGA1,SIX3,CUX1 |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | CREMB,POU5F3,RARAA,NR1H4,RXRA,ZKSCAN14,RCAN1,ZFP879,HIVEP3,TLX2 |
| protein binding | COG5,EPN1,EXOC7,SAMD4A,SH2D3A,BSCL2,PDE4C,KLRK1,BLCAP,UACA |
| nucleotide binding | OXSR1B,NOX4,CAMK2B1,RBM25,NME2B.2,AGAP2,DNM3A,MYEF2,PSMC1A,PTBP2B |
| identical protein binding | FUS,PCBD1,PLK4,PSMA7,GOT2A,BCAT1,SELK,PTS,CDC42BPA,C1S |
| mRNA 3-UTR binding | RBMS3,RNF20,FXR1,TUT1,RBM24A,ELAVL2,CPEB2,ELAVL4,IGF2BP3,CARHSP1 |
| RNA binding | IFIT14,PABPC1L2A,RAVER2,QKI2,UPF3A,RPS5,TEP1,RBM39B,RBM4.1,PRAC |
| double-stranded DNA binding | DDX11,IFI203,NTHL1,MTERF2,LSM14A,XRCC6,ERCC5,HMGB2,PYDC3,MEN1 |
Interacting Protein
TARDBP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TARDBP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TARDBP.
IRAK2;HLA-B
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Droppelmann, CA; Wang, J; et al. Detection of a novel frameshift mutation and regions with homozygosis within ARHGEF28 gene in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND FRONTOTEMPORAL DEGENERATION 14:444-451(2013).
- El-Assaad, I; Di Bari, JA; et al. Differential expression of TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) in the central nervous system of horses afflicted with equine motor neuron disease (EMND): a preliminary study of a potential pathologic marker. VETERINARY RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 36:221-226(2012).



