MYC
-
Official Full Name
v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a multifunctional, nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. It functions as a transcription factor that regulates transcription of specific target genes. Mutations, overexpression, rearrangement and translocation of this gene have been associated with a variety of hematopoietic tumors, leukemias and lymphomas, including Burkitt lymphoma. There is evidence to show that alternative translation initiations from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site result in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. The synthesis of non-AUG initiated protein is suppressed in Burkitts lymphomas, suggesting its importance in the normal function of this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MYC;v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog;MRTL;MYCC;c-Myc;bHLHe39;myc proto-oncogene protein;proto-oncogene c-Myc;transcription factor p64;class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 39;avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog;v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog;myc-related translation/localization regulatory factor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Cat
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Baculovirus
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- 11R
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- MBP
Background
What is MYC Protein?
MYC gene (MYC proto-oncogene, bHLH transcription factor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q24. This gene is a proto-oncogene and encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein (also called c-Myc) that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with the related transcription factor MAX. This complex binds to the E box DNA consensus sequence and regulates the transcription of specific target genes. Amplification of this gene is frequently observed in numerous human cancers. Translocations involving this gene are associated with Burkitt lymphoma and multiple myeloma in human patients. There is evidence to show that translation initiates both from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site, resulting in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. The MYC protein is consisted of 454 amino acids and MYC molecular weight is approximately 50.6 kDa.
What is the Function of MYC Protein?
MYC protein is a pluripotent transcription factor that plays a wide range of roles in cell proliferation, metabolism, angiogenesis, apoptosis, adhesion and differentiation. It plays a wide range of transcriptional regulatory roles by forming a heterodimer with MAX protein and directly binding to the E-box sequence on DNA (5'-CACGTG-3'). Under normal physiological conditions, the expression of c-Myc is strictly regulated, but when chromosomal translocation or signaling pathway gene mutation occurs, c-Myc will undergo expansion independent of growth factor stimulation, resulting in uncontrolled cell proliferation and tumor generation. Abnormal expression of c-Myc is present in approximately 70% of human tumors. In addition, MYC is involved in the regulation of metabolic diseases, including diabetes and fatty liver, and intestinal MYC has been identified as a new drug target for the treatment of metabolic diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
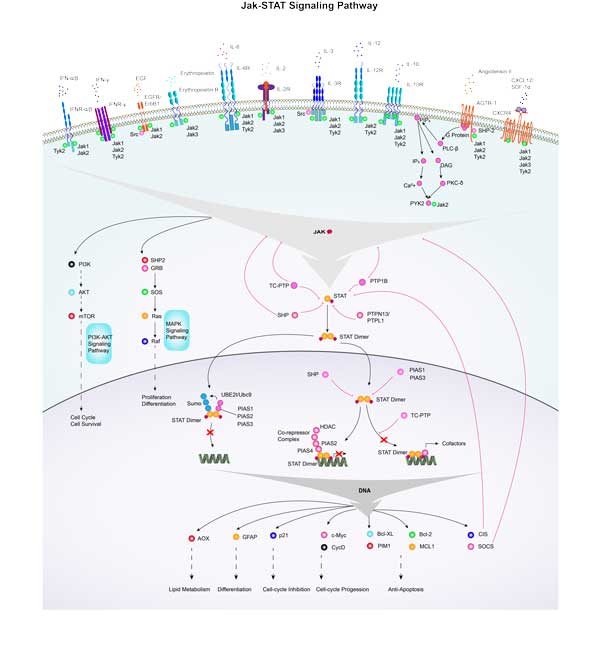
MYC Related Signaling Pathway
c-Myc typically acts as a downstream target of the Ras-ERK signaling pathway, which plays a role in cell growth, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. Similar to the Ras-ERK signaling pathway, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway also plays a key role in cell survival and proliferation, and c-Myc is an important effector. Wnt signaling negatively regulates β-catenin with APC, and the nuclear translocation of β-catenin can participate in trans activation of MYC, so APC deletion leads to constitutive carcinogenic MYC expression. c-Myc affects cell cycle progression and cell survival by regulating the expression of cell cycle related genes and inhibiting apoptosis proteins.
MYC Related Diseases
Abnormal expression and dysregulation of MYC protein play a key role in the development, progression, and treatment resistance of a variety of tumors, including but not limited to Burkitt lymphoma, multiple myeloma, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, and neuroblastoma. In these tumors, MYC gene amplification, overexpression or chromosomal translocation leads to the transcriptional regulation imbalance of its downstream genes, which promotes tumor cell proliferation, metabolic reprogramming, apoptosis inhibition and immune escape, making MYC a widely studied target in cancer therapy.

Fig1. c-MYC is responsible for the crosstalk between breast cancer cells and tumor microenvironment. (Fang-Yan Gao, 2023)
Bioapplications of MYC
MYC protein is a key transcription factor in the development of various tumors, and its central role in cell proliferation, metabolism and apoptosis makes it an important target for cancer therapy. Relevant applications include the development of small molecule inhibitors, peptides or protein drugs targeting MYC, and the use of MYC as a biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of tumors. And to explore the role of MYC in the tumor microenvironment, to provide a new therapeutic idea for the personalized treatment of cancer and the combination of drug strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhaozhong Li, 2012
c-Myc is a transcriptional factor that functions as a central regulator of cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis. Overexpression of c-Myc also enhances DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), genetic instability, and tumorigenesis. However, the mechanism(s) involved remains elusive. Here, researchers discovered that γ-ray ionizing radiation-induced DSBs promote c-Myc to form foci and to co-localize with γ-H2AX. Conditional expression of c-Myc in HO15.19 c-Myc null cells using the Tet-Off/Tet-On inducible system results in down-regulation of Ku DNA binding and suppressed activities of DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) and DNA end-joining, leading to inhibition of DSB repair and enhanced chromosomal and chromatid breaks. Expression of c-Myc reduces both signal and coding joins with decreased fidelity during V(D)J recombination. Mechanistically, c-Myc directly interacts with Ku70 protein through its Myc box II (MBII) domain. Removal of the MBII domain from c-Myc abrogates its inhibitory effects on Ku DNA binding, DNA-PKcs, and DNA end-joining activities, which results in loss of c-Myc's ability to block DSB repair and V(D)J recombination. Interestingly, c-Myc directly disrupts the Ku/DNA-PKcs complex in vitro and in vivo.

Fig1. Percentage of abnormal metaphases in the c-Myc-Off or c-Myc-On cells was quantified by T-FISH analysis.

Fig2. WT or each of the c-Myc deletion mutants was transfected into HO15.19 cells. Expression levels of c-Myc were analyzed by Western Blot.
Case Study 2: Ya-Chu Tang, 2021
NRF2, a redox sensitive transcription factor, is up-regulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), however, the associated impact and regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. The regulatory effect of c-MYC on NRF2 was validated by ChIP-qPCR, RT-qPCR and western blot. The impacts of NRF2 on malignant progression of HNSCC were determined through genetic manipulation and pharmacological inhibition in vitro and in vivo. The results showed that NRF2 expression is positively correlated with malignant features of HNSCC. In addition, carcinogens, such as nicotine and arecoline, trigger c-MYC-directed NRF2 activation in HNSCC cells.

Fig3. RT-qPCR analysis of NRF2 mRNA levels in MYC-knockdown OEC-M1 cells.

Fig4. ChIP-qPCR analysis of c-MYC binding at NRF2 promoter in MYC-knockdown OEC-M1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MYC-574H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MYC-5787H)
Involved Pathway
MYC involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MYC participated on our site, such as Acute myeloid leukemia,Apoptosis,Binding of TCF/LEF:CTNNB1 to target gene promoters, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MYC were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| C-MYC pathway | HBP1,KAT5,RUVBL2,ACTL6A |
| CD40/CD40L signaling | TDP2,JAK3 |
| Apoptosis | HIST1H1C,IRAK1,IRF2,CTNNB1,TNFRSFA,BIRC5A,Casp3,CFLAR,SATB1,PPP3CB |
| Cell cycle | CDH1-A,CCNE2,BABAM1,HTATIP,HDAC5,CDC25C,SYCE1,ANAPC5,CEP72,WEE1 |
| Bladder cancer | CXCL8,MAP2K1,EGF,E2F3,MMP2,CCND1,RPS6KA5,TYMP,ARAF,MMP1 |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | NFKB1,RPS6KB1,CEBPA,STAT5B,PIM2,KRAS,MTOR,JUP,CHUK,RAF1 |
| C-MYB transcription factor network | YEATS4,CSF1R,LECT2,PIAS3,ADA,CREBBP,SKI,ADORA2B,COL1A2,MYOD1 |
Protein Function
MYC has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,E-box binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MYC itself. We selected most functions MYC had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MYC. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transcription factor binding | NKX3-1,EPAS1,IRF4,DACT2,HOXA7,NKX3,NR0B2,PITX2,NKX2-1,SP1 |
| protein binding | HNRNPUL1,NOA1,ATL1,SMURF2,DKK1,NAA35,RABGGTB,TUBA3D,CCDC130,CSE1L |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | FOS,NFIB,NR4A1,IRF4,FOXI1,ZFP639,SP1,ARNT2,SOX12,NR4A3 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | IRF4,HLTF,HINFP,CC2D1B,HSF1,EBF2,NKX6,ESRRA,ZBTB7A,CRX |
| E-box binding | TWIST1,PER1,TCF4,NEUROD2,ASCL2,TAL1,ATOH8,GATA3,ZEB1,LMO2 |
| protein dimerization activity | ASCL1B,BHLHE41,PTF1A,MEF2B,BTRC,MNTB,AHR,NEUROD6A,TWIST2,MTOR |
| repressing transcription factor binding | EIF4E,KAT5,GMNN,CTNNB1,HDAC5,HHEX,HMGB1,NOC2L,TLE4,HDAC7 |
| DNA binding | UBN1,PAX3A,ATF4B1,MYCN,HOXD4A,HIF1AL,RPS3,HER8A,GON4L,PRRX1B |
| protein complex binding | NSF,LRP1,CASP8,AP2A1,SH2B3,LZTFL1,NCK2,CDK5RAP1,RIPK3,ABI1 |
Interacting Protein
MYC has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MYC here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MYC.
MAX
MYC Related Signal Pathway
Resources
-
Understanding MYC: From Cell Growth to Cancer in 60 Seconds
-
MYC Protein 101: Function, Cancer Role and Research Tools
Research Area
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Apoptosis Transcription Factors and Regulators
- Inflammatory Mediators
- Transcription Factors in the Akt Pathway
- DNA Damage and Repair
- Cancer Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Epithelial Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transcription Factors and Regulators
- Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Markers
- Pluripotent Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells
- Prostate Cancer Stem Cell Markers
- Glioma/Medulloblastoma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
- Melanoma Biomarkers
- Oncoprotein-Transcription Factors
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Raha, Paromita; Thomas, Scott; et al. Combined histone deacetylase inhibition and tamoxifen induces apoptosis in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer models, by reversing Bcl-2 overexpression.. Breast cancer research : BCR 17:533-533(2015).
- Li, Dan; Mei, Hong; et al. Intelectin 1 suppresses the growth, invasion and metastasis of neuroblastoma cells through up-regulation of N-myc downstream regulated gene 2.. Molecular cancer 14:320-320(2015).