CTNNB1
-
Official Full Name
catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009] -
Synonyms
CTNNB1;catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa;CTNNB;MRD19;armadillo;catenin beta-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Dog
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- GST
- His&GST
- Flag
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is CTNNB1 protein?
CTNNB1 gene (catenin beta 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p22. The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. The CTNNB1 protein is consisted of 781 amino acids and CTNNB1 molecular weight is approximately 85.5 kDa.
What is the function of CTNNB1 protein?
CTNNB1, encoding β-catenin, is crucial for cell-cell adhesion and acts as a key effector in the Wnt signaling pathway, influencing cell proliferation, differentiation, and embryonic development. Mutations or activation of this pathway can lead to the nuclear translocation of β-catenin, resulting in the activation of Wnt target genes. This protein's dysregulation is implicated in many cancers, including endometrial, colorectal, and hepatocellular carcinomas.

Fig1. Intracellular functions of β-catenin. (Živa Ledinek, 2022)
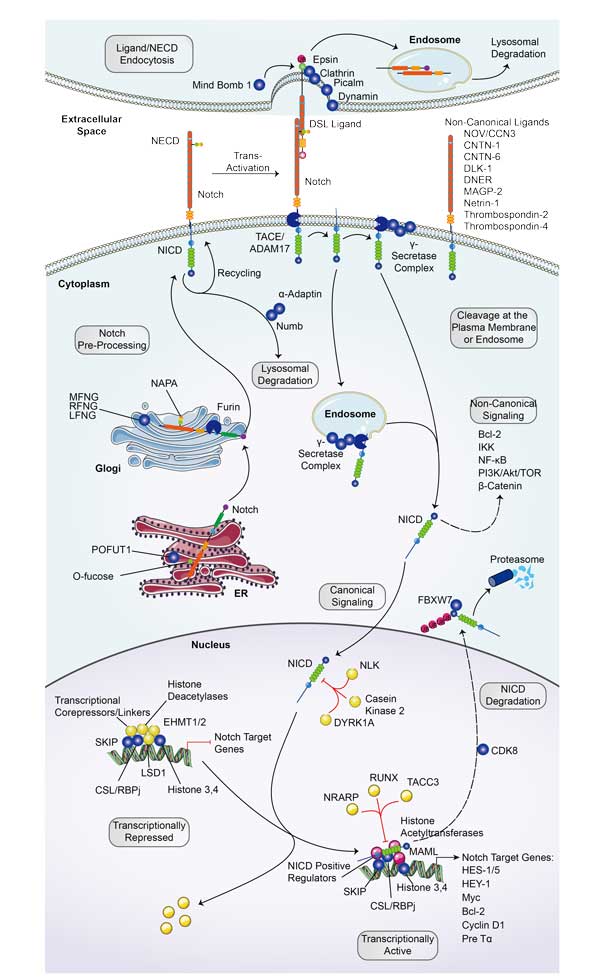
CTNNB1 related signaling pathway
CTNNB1, which encodes β-catenin, is a multifaceted protein involved in cell adhesion and transcriptional regulation. It plays a central role in the Wnt signaling pathway, affecting cell fate, proliferation, and tissue homeostasis. Mutations in CTNNB1 are prevalent in various cancers, including endometrial, liver, and colorectal, where they contribute to tumorigenesis by constitutively activating Wnt signaling.
CTNNB1 related diseases
CTNNB1, also known as β-catenin, is a protein that plays a critical role in cell-cell adhesion, gene expression, and cell signaling. Mutations or dysregulation of CTNNB1 are associated with several diseases, most notably colorectal cancer, where it is frequently implicated in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation. Additionally, aberrations in CTNNB1 have been linked to other malignancies such as hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and ovarian cancer. Moreover, mutations in CTNNB1 can cause developmental disorders like familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and conditions affecting bone formation. Thus, CTNNB1 serves as a key factor in both oncogenesis and developmental biology, making it an important target for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
Bioapplications of CTNNB1
CTNNB1 has significant bioapplications in cancer research and developmental biology. It is a crucial component of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation or mutations in CTNNB1 are implicated in various cancers, including colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and melanoma, making it a potential therapeutic target. Additionally, CTNNB1 plays a pivotal role in cell adhesion through its interaction with cadherins, affecting tissue formation and maintenance. Its involvement in bone development and diseases like familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) further highlights the importance of CTNNB1 in both pathological and physiological contexts.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Gina Chun Kost, 2015
RX-5902 potently inhibits growth in several human cancer cell lines. This research identifies p68 RNA helicase as a target of RX-5902 using the DARTS method and shows that RX-5902 binds to Y593 phospho-p68, inhibiting its β-catenin-dependent ATPase activity. Treatment with RX-5902 downregulates β-catenin pathway genes like c-Myc, cyclin D1, and p-c-Jun. Thus, RX-5902's anti-cancer effect may come from disrupting the Y593 phospho-p68 helicase - β-catenin interaction.

Fig1. ATPase activity was measured in the presence of 1 μg β-catenin.

Fig2. Effect of RX-5902 on expression of downstream proteins of p68–β-catenin.
Case Study 2: Ying Bai, 2024
This study investigated the role of β-catenin in atrial fibrosis in human atrial fibrillation (AF) using right atrial appendage (hRAA) tissues. It found that in AF patients, the space between cardiomyocyte gap junctions was wider, and there was a decrease in gap junction proteins Connexin40 and Connexin43, alongside an increase in β-catenin and E-cadherin expression. β-catenin and E-cadherin were found to dissociate and accumulate intracellularly in AF, and the degradation of β-catenin by GSK-3β and APC was reduced. Inhibiting β-catenin in an AF mouse model prevented atrial fibrosis, suggesting β-catenin's potential as a therapeutic target for AF.

Fig3. Western blot analysis of protein expression level of β-catenin and phosphor-β-catenin in human RAA tissues from SR and AF patients.

Fig4. Immunofluorescence analysis of localization of E-cadherin (green) and β-catenin (red).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTNNB1-36H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CTNNB1-5747H)
Involved Pathway
CTNNB1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CTNNB1 participated on our site, such as Adherens junction,Adherens junctions interactions,Adipogenesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CTNNB1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Adipogenesis | KLF6,AGPAT2,GATA2,FRZB,NCOA2,MEF2B,E2F1,DLK1,RETN,NR2F1A |
| Apoptosis | FAS,BIRC2,DNM1L,IL1R1,NMT1,AIFM1,CFLAR,IRAK4,MYC,IL1A |
| Apoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins | CLSPN,STK24,LMNB1,CTNNB2,DBNL,OCLN,PTBP3,PLECA,BMX,SATB1 |
| Adherens junction | CTNNA3,PVRL1B,MLLT4,EGFR,ACP1,VCLA,ACTN3,RHOAB,CTNNA1,MAPK1 |
| Apoptotic cleavage of cell adhesion proteins | DSG3,PKP1,PTBP3,DSP,DSG2,DSG1,OCLN,CTNNB2 |
| Adherens junctions interactions | CDH9,CDH12A,CTNND1,JUP,CDH12,CDH7,CDH6,PVRL2L,CTNNA1,CDH2 |
| Apoptotic execution phase | HIST1H1E,CASP6L2,PLEC,VIML,GAS2,HIST1H1D,HIST1H1A,STK24B,CASP6L1,PLECA |
| Androgen receptor signaling pathway | STUB1,ETV5A,KAT5,RAD9A,KAT7,RNF6,RNF14,CCDC102A,RUNX2A,NCOA2 |
Protein Function
CTNNB1 has several biochemical functions, for example, I-SMAD binding,R-SMAD binding,RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CTNNB1 itself. We selected most functions CTNNB1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CTNNB1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| nuclear hormone receptor binding | SNW1,NCOR1,NRIP1,MED1,NCOA3,ACTN4,BUD31,EP300,TCF7L2,CRY1 |
| transcription regulatory region DNA binding | GFI1,MESP1,BCOR,HHEX,TFE3,ZFP639,ZNF821,HIVEP2A,AHR,CARM1 |
| SMAD binding | FKBP1A,FLNA,HMGA2,STUB1,EID2,TOB1,CREBBP,YY1,SKIL,SKOR1B |
| I-SMAD binding | TGFB1I1,AXIN2,AXIN1,SMAD4,SMAD6,SMAD2,SMURF1,SMAD1,TGFBR1,SMAD7 |
| estrogen receptor binding | MED1,NSD1,MMS19,FUS,FOXL2,PPARG,PPID,DYX1C1,DDX54,TMEM38A |
| enzyme binding | MARCH6,TBP,SNRPD3,CYP2C19,NFKBIA,N4BP2L2,AXIN2,ANK1,PRMT1,IQCB1 |
| transcription factor binding | CHCHD2,ENPP2,MAPK1,APBB2,HEY1,TMEM173,E2F4,TP53,HMGB2,FIGLA |
| RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding | NEUROD1,CREBBP,PITX2,LMO2,IFI27,TBX20,T,BHLHE40,EGR2,EP300 |
| transcription coactivator activity | HCFC1,JMY,MAX,NPM1,CEBPA,ABRA,UBE2L3,LPIN3,SUPT7L,WWTR1 |
Interacting Protein
CTNNB1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CTNNB1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CTNNB1.
TCF7L2
CTNNB1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Early Endodermal Lineage MarkersCancer Stem Cell Transcription Factors
Adherens Junction Proteins in Endothelial Cells
Adherens Junction Proteins in VSMC
Wnt Intracellular Signaling
Mesenchymal Cells and EMT
Neural Stem Cell Markers
Endodermal Lineage Markers
Tumor Antigens
Oncoprotein-Signal Transducers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chen, TC; Lin, KT; et al. Using an in Situ Proximity Ligation Assay to Systematically Profile Endogenous Protein-Protein Interactions in a Pathway Network. JOURNAL OF PROTEOME RESEARCH 13:5339-5346(2014).
- Liszka, L; et al. DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PANCREAS USUALLY RETAINED SMAD4 AND p53 PROTEIN STATUS AS WELL AS EXPRESSION OF EPITHELIAL-TO-MESENCHYMAL TRANSITION MARKERS AND CELL CYCLE REGULATORS AT THE STAGE OF LIVER METASTASIS. POLISH JOURNAL OF PATHOLOGY 65:100-112(2014).