Recombinant Rhesus monkey DEDD Protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | DEDD-1225R |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Rhesus monkey DEDD full length or partial length protein was expressed. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Rhesus macaque |
| Source : | Mammalian Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | >80% |
| Notes : | This item requires custom production and lead time is between 5-9 weeks. We can custom produce according to your specifications. |
| Storage : | Store it at +4 ºC for short term. For long term storage, store it at -20 ºC~-80 ºC. |
| Storage Buffer : | PBS buffer |
| Gene Name | DEDD death effector domain containing [ Macaca mulatta (Rhesus monkey) ] |
| Official Symbol | DEDD |
| Synonyms | DEDD; death effector domain-containing protein; |
| Gene ID | 719875 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001257441 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001244370 |
| MIM | |
| UniProt ID | F6UTR2 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| DEDD-7245H | Recombinant Human DEDD, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| DEDD-2513H | Recombinant Human DEDD Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| DEDD-2810H | Recombinant Human DEDD protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| DEDD-1485R | Recombinant Rat DEDD Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| DEDD-539H | Recombinant Human DEDD Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| DEDD-6995HCL | Recombinant Human DEDD 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| DEDD-6996HCL | Recombinant Human DEDD 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Mori M, et al. J Clin Invest. 2011
The uterine decidua plays essential roles in supporting embryonic growth before establishment of the placenta. Here researchers show that female mice lacking death effector domain-containing protein (DEDD) are infertile owing to unsuccessful decidualization. In uteri of Dedd-/- mice, development of the decidual zone and the surrounding edema after embryonic implantation was defective. This was subsequently accompanied by disintegration of implantation site structure, leading to embryonic death before placentation. Polyploidization, a hallmark of mature decidual cells, was attenuated in DEDD-deficient cells during decidualization. Such inefficient decidualization appeared to be caused by decreased Akt levels, since polyploidization was restored in DEDD-deficient decidual cells by overexpression of Akt.
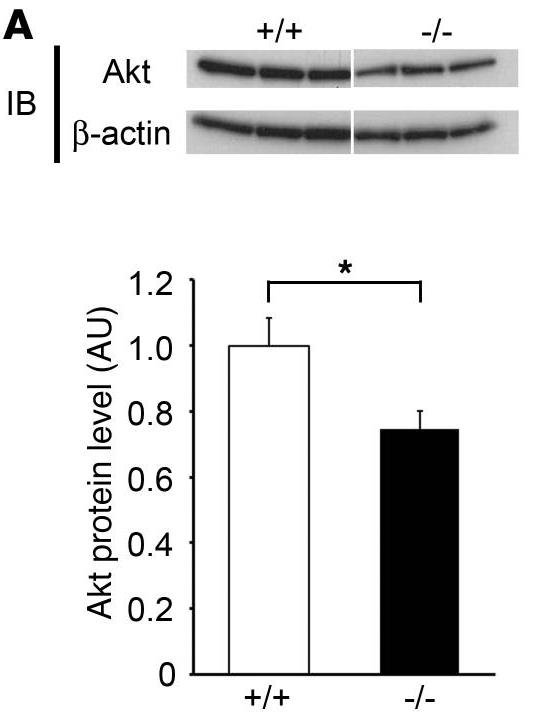
Fig1. Immunoblotting of Dedd+/+ and Dedd–/– uteri at 5.5 dpc for total Akt.
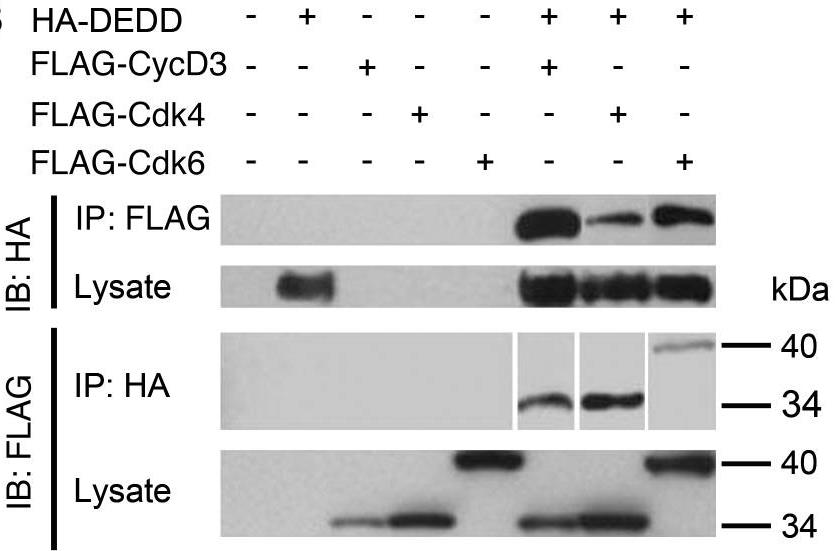
Fig2. Binding study.
Case 2: Arai S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007
Accumulating evidence has shown that many molecules, including some cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and cyclins, as well as the death-effector domain (DED)-containing FADD, function for both apoptosis and cell cycle. Here researchers identified that DEDD, which also possesses the DED domain, acts as a novel inhibitor of the mitotic Cdk1/cyclin B1 complex. DEDD associates with mitotic Cdk1/cyclin B1 complexes via direct binding to cyclin B1 and reduces their function. In agreement, kinase activity of nuclear Cdk1/cyclin B1 in DEDD-null (DEDD-/-) embryonic fibroblasts is increased compared with that in DEDD+/+ cells, which results in accelerated mitotic progression, thus exhibiting a shortened G2/M stage. Interestingly, DEDD-/- cells also demonstrated decreased G1 duration, which perhaps enhanced the overall reduction in rRNA amounts and cell volume, primarily caused by the rapid termination of rRNA synthesis before cell division.
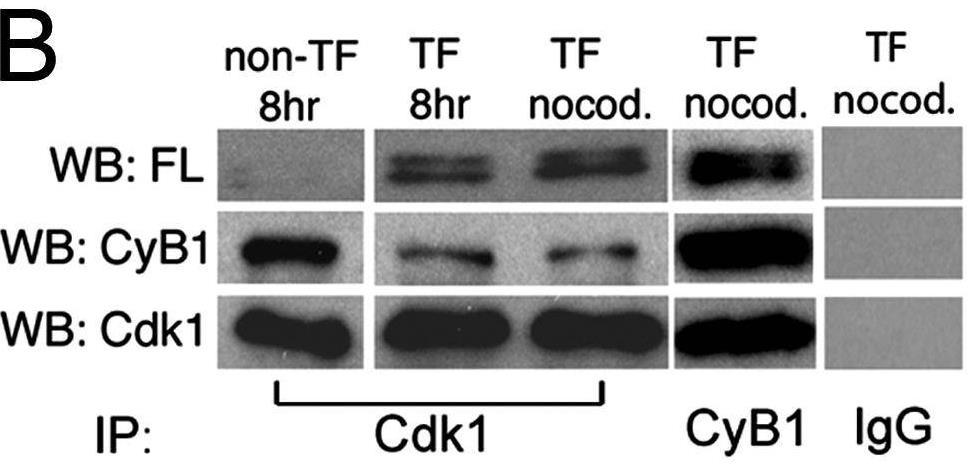
Fig1. In vivo binding assay.
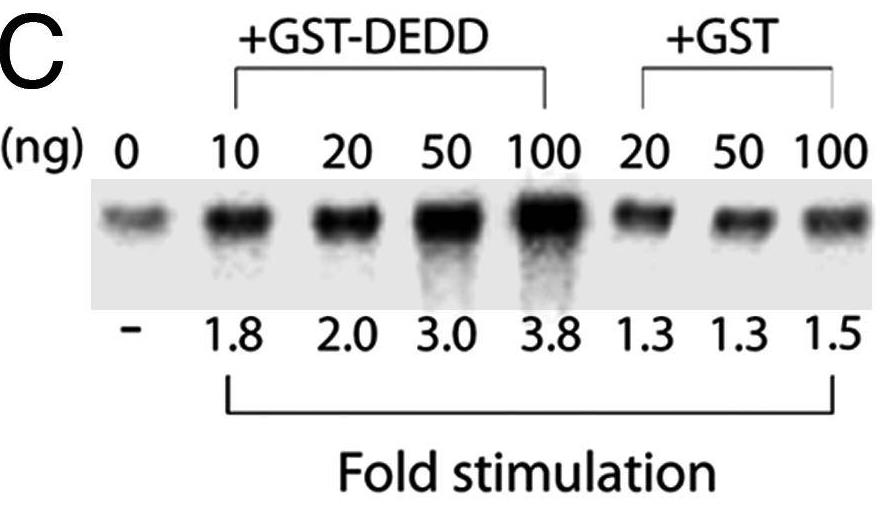
Fig2. Addition of recombinant GST-DEDD stimulates Pol.I transcription in vitro.
The application of DEDD protein (Death Effector Domain-associated protein) mainly focuses on the following aspects:
1. Immunological research: DEDD protein is closely related to apoptosis of immune cells, and the recombinant protein can be used in immunological research to explore how immune cells regulate their apoptosis process.
2. Cell biology research: DEDD protein is involved in the regulation of cell cycle and cell death, and recombinant Rhesus monkey DEDD protein is helpful to study these basic cell biology events.
3, disease model research: Recombinant DEDD protein can be used to establish disease models to study changes in apoptosis in specific diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases.
4, Diagnostic reagent development: Recombinant proteins may be used to develop diagnostic reagents to help detect disease markers associated with DEDD proteins.
5. Protein engineering and structural biology: By studying the structure and function of recombinant DEDD proteins, scientists can design new proteins or peptides for therapeutic use or as research tools.
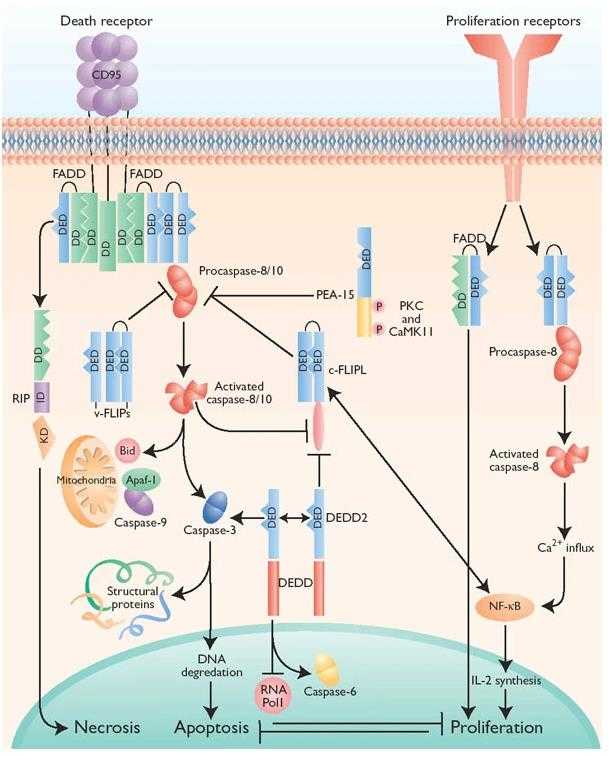
Fig1. The functions and interacting roles of DED-containing proteins. (Michael D Tibbetts, 2003)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All DEDD Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All DEDD Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


