Recombinant Pan paniscus (Pygmy chimpanzee) (Bonobo) SNCA, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | SNCA-3394P |
| Product Overview : | Alpha-synuclein (SNCA) |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Pan paniscus |
| Source : | E.Coli/Yeast |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 140 |
| Form : | This item requires custom production and lead time is between 5-9 weeks. We can custom produce according to your specifications. |
| Purity : | >90% |
| Notes : | Small volumes of SNCA recombinant protein may occasionally become entrapped in the seal of the product vial during shipment and storage. If necessary, briefly centrifuge the vial on a tabletop centrifuge to dislodge any liquid in the container`s cap. Certain products may require to ship with dry ice. |
| Storage : | Store at -20 degree C. For extended storage, store at -20 or -80 degree C. |
| Storage Buffer : | PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol |
| Warning : | This product is for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Gene Name | SNCA synuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor) [ Pan paniscus ] |
| Official Symbol | SNCA |
| Synonyms | synuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid precursor); alpha-synuclein |
| Gene ID | 100984304 |
| mRNA Refseq | XM_003829890 |
| Protein Refseq | XP_003829938 |
| UniProt ID | P61144 |
| Chromosome Location | chromosome: Un |
| Pathway | Alzheimer"s disease, organism-specific biosystem; Alzheimer"s disease, conserved biosystem |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| SNCA-02H | Recombinant Human SNCA Protein | +Inquiry |
| SNCA-7034H | Recombinant Human SNCA, None tagged | +Inquiry |
| Snca-5996M | Recombinant Mouse Snca Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Snca-387R | Recombinant Rat Snca Protein | +Inquiry |
| SNCA-27348TH | Recombinant Human SNCA | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| SNCA-27339TH | Native Human SNCA | +Inquiry |
| SNCA-27345TH | Native Human SNCA | +Inquiry |
| SNCA-27341TH | Native Human SNCA | +Inquiry |
| SNCA-27342TH | Native Human SNCA | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| SNCA-1634HCL | Recombinant Human SNCA 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Balsamo JM, et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024
Aggregated deposits of the protein α-synuclein and depleting levels of dopamine in the brain correlate with Parkinson's disease development. Aggregates of α-synuclein appear to accumulate in the gut years prior to the onset of any motor symptoms. These cells also express the dopamine metabolic pathway and form synapses with vagal neurons, which innervate the gut and brain. Through this connection, Parkinson's disease pathology may originate in the gut and spread to the brain over time. Effective therapeutics to prevent this disease progression are lacking due to a limited understanding of the mechanisms by which α-synuclein aggregation occurs in the gut. Here, researchers develop a new tool, a laser-induced graphene-based electrochemical sensor chip, to track α-synuclein aggregation and dopamine level over time. Using these sensor chips, they evaluated diet-derived catechols dihydrocaffeic acid and caffeic acid as potential inhibitors of α-synuclein aggregation. Also these dietary catechols inhibit α-synuclein aggregation in STC-1 enteroendocrine cells.
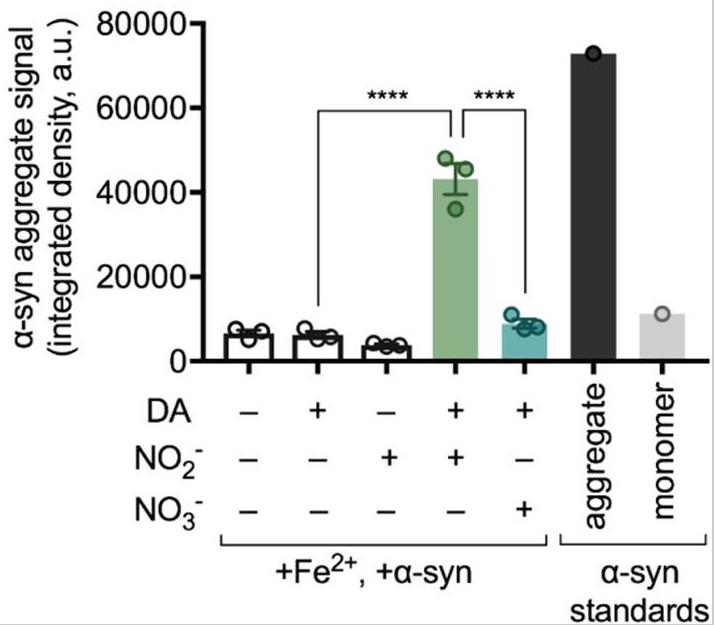
Fig1. Dot blot quantification of α-syn aggregation.
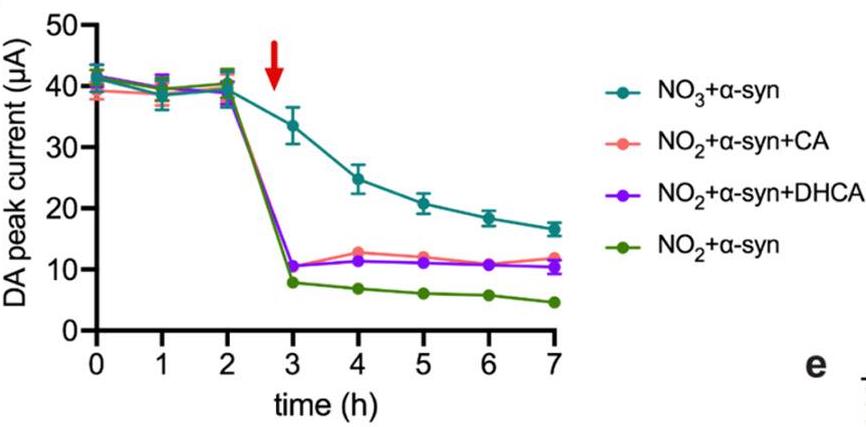
Fig2. DA peak current for NO3 + α-syn, NO2 + α-syn, NO2 + α-syn + DHCA, and NO2 + α-syn + CA.
Case 2: Bernal-Conde LD, et al. Life (Basel). 2024
Parkinson's disease (PD) caused by SNCA gene triplication (3XSNCA) leads to early onset, rapid progression, and often dementia. Understanding the impact of 3XSNCA and its absence is crucial. Three different genotypes were evaluated in this study: patient-derived hiPSCs with 3XSNCA, a gene-edited isogenic line with a frame-shift mutation on all SNCA alleles (SNCA 4KO), and a normal wild-type control. This study confirms successful in vitro differentiation into neuronal lineage in all cell lines. However, the SNCA 4KO line showed unusual LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 alpha (Lmx1a) extranuclear distribution. Crucially, both 3XSNCA and SNCA 4KO lines had reduced Th+ neuron expression, despite initial successful neuronal differentiation after two months post-transplantation. This indicates that while the SNpc environment supports early neuronal survival, SNCA gene alterations-either amplification or knock-out-negatively impact Th+ dopaminergic neuron maturation.
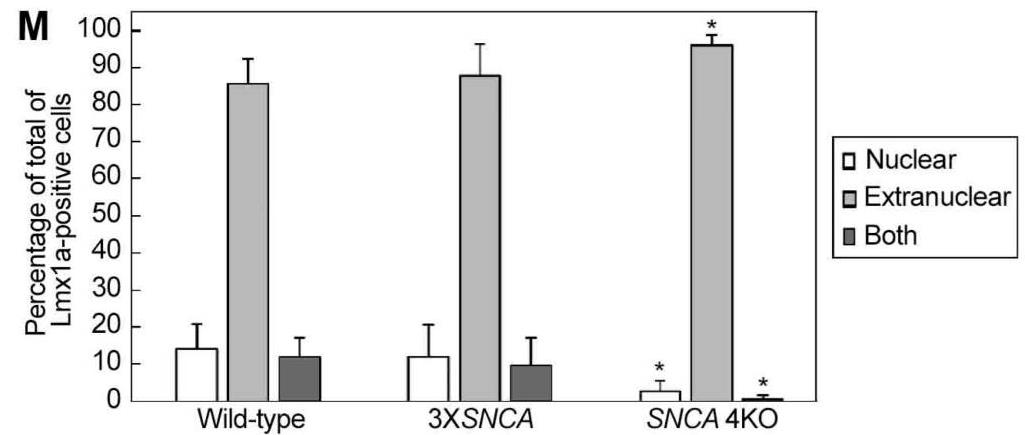
Fig1. Analysis of Lmx1a-positive cells shows a significant reduction in nuclear and extranuclear expression in the SNCA 4KO line compared to wild-type and 3XSNCA lines.
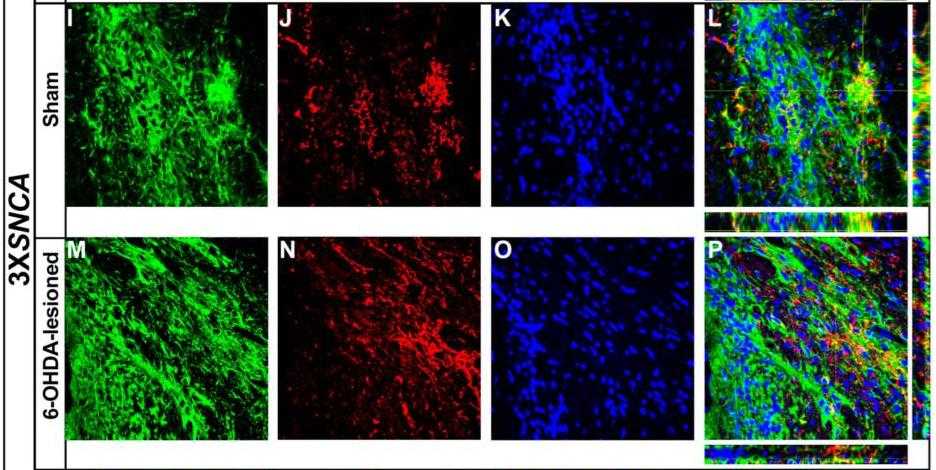
Fig2. Tyrosine hydroxylase expression in transplanted hiPSC-derived floor-plate progenitors at two months post-transplantation.
The SNCA [Pan paniscus (pygmy zee)] protein, also known as Alpha-synuclein, is a protein found in nerve cells. In non-human primates such as bonobos (Pan paniscus), the study of this protein helps us understand its function in humans and related diseases. Specifically, there are the following applications:
1. Neuropathological study. Alpha-synuclein is a major component of Lewy bodies, one of the main pathological features of Parkinson's disease. The study of α-synuclein polymorphisms in different ethnic and genetic contexts is helpful to understand the pathogenesis of PD and search for new therapeutic strategies. Abnormal forms of alpha-synuclein can be neurotoxic, and studying how these forms affect the survival and function of neurons is critical to understanding the pathogenesis of PD.
2. Disease diagnosis and drug development. The aggregation of α-synuclein is considered to be a key event in the course of PD, therefore, the development of drugs that can regulate the level of α-synuclein or prevent its aggregation is an important direction of PD treatment research. Changes in the level and form of alpha-synuclein may serve as biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases such as PD, contributing to early diagnosis and monitoring of the disease.
3. Other basic research. The SNCA gene encodes alpha-synuclein, and mutations in this gene are associated with the development of PD. The study of SNCA gene polymorphisms and mutations contributes to the understanding of genetic risk factors for PD. Targeting SNCA genes through gene-editing techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9 to explore the possibility of reducing α-synuclein expression or altering its function to treat PD.
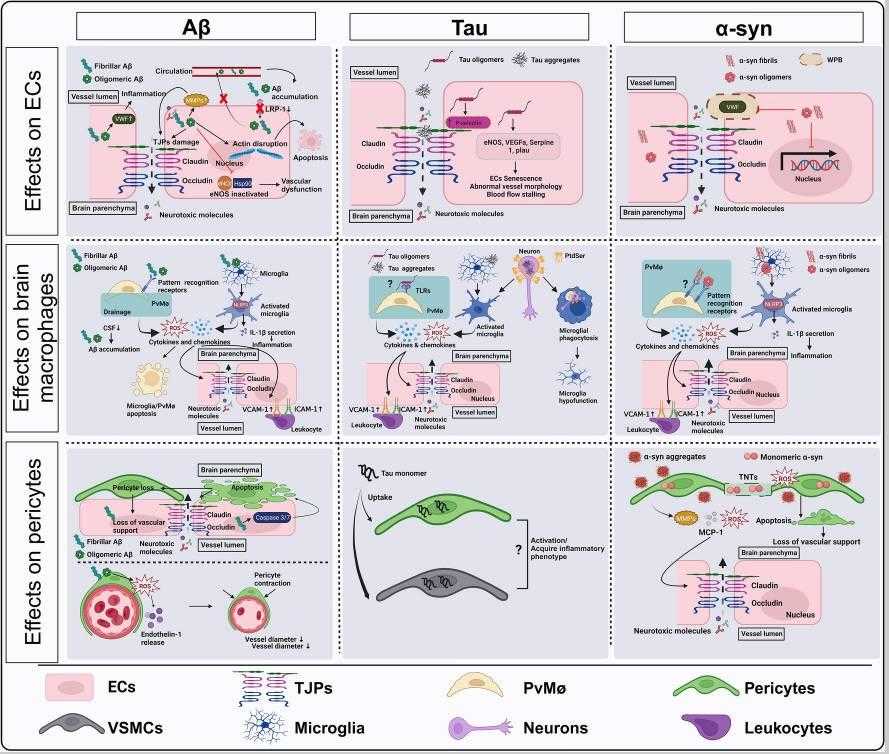
Fig1. Overview of the impact of Aβ, Tau and α-syn on ECs, brain macrophages and pericytes. (Ying-Chieh Wu, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All SNCA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SNCA Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


