Recombinant Mouse MAFA Protein
| Cat.No. : | MAFA-9437M |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Mouse MAFA full length or partial length protein was expressed. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Mouse |
| Source : | Mammalian Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Form : | Liquid or lyophilized powder |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | >80% |
| Notes : | This item requires custom production and lead time is between 5-9 weeks. We can custom produce according to your specifications. |
| Storage : | Store it at +4 ºC for short term. For long term storage, store it at -20 ºC~-80 ºC. |
| Storage Buffer : | PBS buffer |
| Gene Name | Mafa v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family, protein A (avian) [ Mus musculus ] |
| Official Symbol | MAFA |
| Gene ID | 378435 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_194350.1 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_919331.1 |
| MIM | |
| UniProt ID | Q8CF90 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| MAFA-9437M | Recombinant Mouse MAFA Protein | +Inquiry |
| MAFA-28859TH | Recombinant Human MAFA | +Inquiry |
| MAFA-5296M | Recombinant Mouse MAFA Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| MAFA-6582C | Recombinant Chicken MAFA | +Inquiry |
| MAFA-5302Z | Recombinant Zebrafish MAFA | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| MAFA-4562HCL | Recombinant Human MAFA 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Matsuoka TA, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015
The mouse Mafa transcription factor plays a crucial role in regulating postnatal β-cell function, influencing insulin production and secretion, and β-cell mass. Its human counterpart, MAFA, is significantly downregulated in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) islet β-cells, including those from the db/db mouse model of T2DM. To investigate Mafa's impact on glycemic control under diabetic conditions, researchers created transgenic mice with conditional Mafa expression in db/db β-cells. This led to reduced blood glucose, increased insulin levels, and a larger β-cell mass, along with upregulation of insulin and genes that alleviate β-cell stress, such as Gsta1 and Gckr. Similarly, human GSTA1 levels were diminished in T2DM islets. These findings underscore the critical role of Mafa in maintaining β-cell function during pathophysiological challenges.
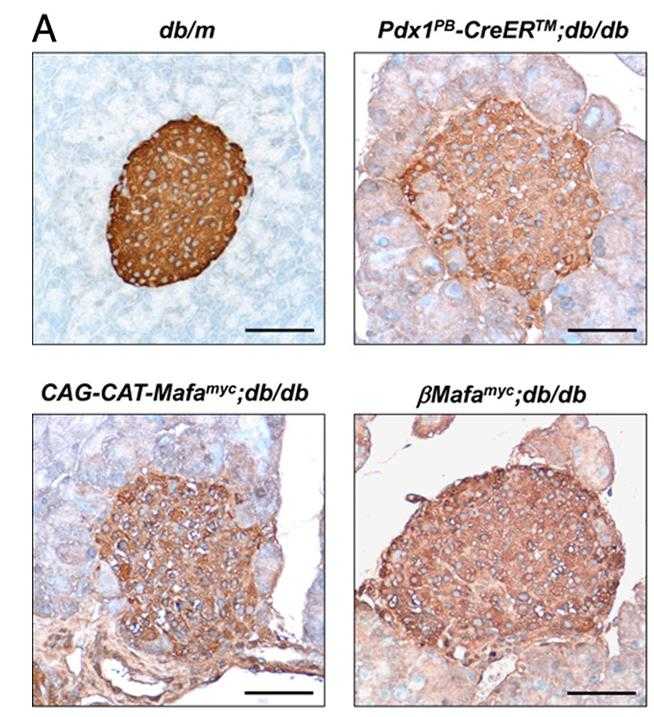
Fig1. Diaminobenzidine peroxidase immunodetection was used to measure the islet insulin+ cell area in the 18-week-old βMafamyc.
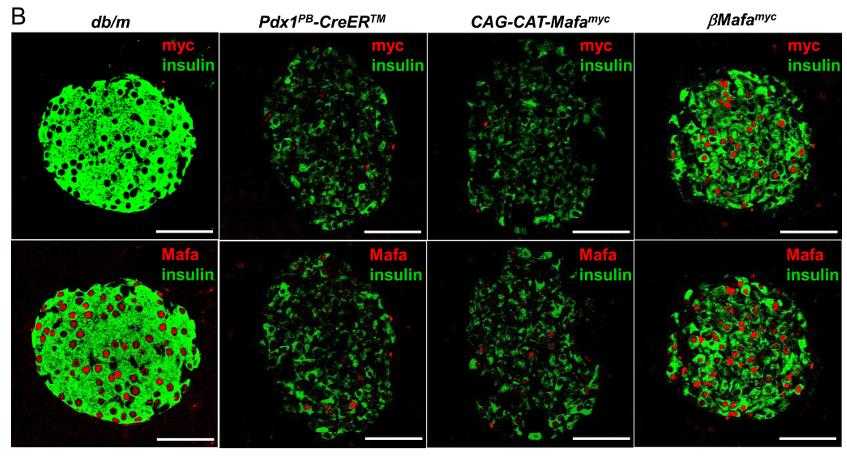
Fig2. Pancreatic db/db islets from 18-week-old βMafamyc, CAG-CAT-Mafamyc, Pdx1PB-CreERTM mice were immunostained.
Case 2: Eto K, et al. PLoS One. 2014
Postnatal growth and maturation of pancreatic β-cells, essential for adult glucose homeostasis and diabetes susceptibility, are marked by elevated MafA levels, a key insulin gene regulator. MafA knockout studies indicate its necessity for β-cell function, influencing genes like Glut2, ZnT8, Granuphilin, Vdr, Pcsk1, Urocortin 3, Prlr, and Ccnd2. MafA's inhibition in mice reduces Prlr and Ccnd2, affecting β-cell proliferation. MafA also transactivates the Prlr promoter, and prolactin's stimulation leads to Stat5B phosphorylation and increased nuclear Ccnd2, suggesting a MafA-Prlr-Ccnd2 axis in β-cell growth. These insights are vital for stem cell differentiation into functional β-cells.
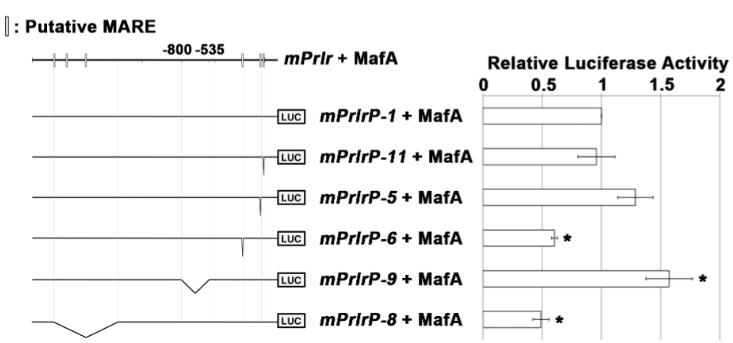
Fig1. Luciferase activities of the mPrlrP-1 construct (−2232 to +127) with MafA compared to the luciferase activities of constructs with deletions.
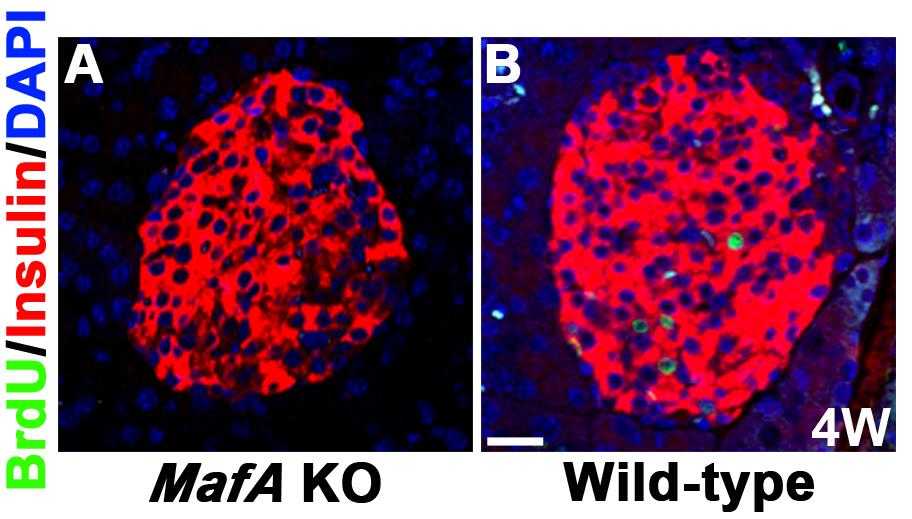
Fig2. Representative islets of MafA KO mice and their wild-type littermates 24 hours after the injection of BrdU.
The Recombinant Mouse MAFA Protein is an important transcription factor that is mainly expressed in mature islet beta cells. The MAFA protein plays a key role in the maturation, functional maintenance, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of islet beta cells. MAFA expression is reduced in type 2 diabetes, which is associated with a decline in beta cell function and disease progression. The molecular biology of MAFA protein is very complex, involving multiple transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory nodes.
In islet beta cells, the MAFA protein activates transcription of the insulin gene by binding to specific elements on the insulin gene promoter. In addition to insulin, MAFA also increased the expression of a range of genes related to beta cell function, including genes involved in glucose sensing, insulin processing, calcium influx, and oxidative phosphorylation. The expression and activity of MAFA are regulated by a variety of transcription factors and post-transcriptional modifications such as phosphorylation, SUMO, and ubiquitination.
In terms of practical applications, the study of MAFA protein contributes to our understanding of the function of islet beta cells and the pathogenesis of diabetes. For example, by studying the regulatory mechanisms of MAFA, scientists can explore new therapeutic targets to improve beta cell function and treat diabetes. In addition, MAFA protein can also be used to develop new diabetes treatment drugs, or as an important biomarker in diabetes treatment.
In experimental studies, the researchers have developed a mouse model that tracks the promoter activity of MAFA by expressing the fluorescent protein Kusabira Orange (KOr) in beta cells, which facilitates the study of beta cell differentiation, maturation, regeneration, and function. With this model, the researchers can more intuitively observe and analyze the role of MAFA in islet beta cells.
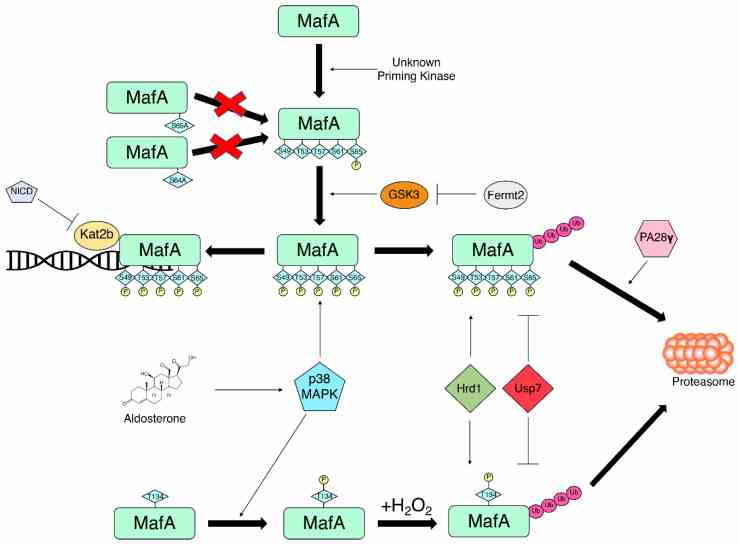
Fig1. Regulators of MafA phosphorylation and ubiquitination fine-tune the balance between MafA transcriptional activity and MafA degradation. (Jiani Liang, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All MAFA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All MAFA Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


