Recombinant Human CAMK2B protein(Met1-Gln503), His&GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CAMK2B-970H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CAMK2B isoform 2 (Q13554-3) (Met 1-Gln 503) was expressed in Insect Cells, fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | GST&His |
| Protein Length : | 1-503 a.a. |
| Form : | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 2mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% gly, pH 8.0 |
| Bio-activity : | The specific activity was determined to be 300 nmol/min/mg using Autocamtide-2 synthetic peptide (KKALRRQETVDAL-amide) as substrate. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CAMK2B/GST chimera consists of 740 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 84.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 85 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 60 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CAMK2B calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II beta [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CAMK2B |
| Synonyms | CAMK2B; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II beta; calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase) II beta , CAMKB; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II subunit beta; calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase type II beta chain; CaM kinase II beta subunit; CaM kinase II beta chain; CAM2; CAMK2; proline rich calmodulin dependent protein kinase; caMK-II subunit beta; CaM-kinase II beta chain; proline rich calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; CAMKB; MGC29528; |
| Gene ID | 816 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001220 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001211 |
| MIM | 607707 |
| UniProt ID | Q13554 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CAMK2B-2286H | Recombinant Human CAMK2B Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK2B-0173H | Recombinant Human CAMK2B Protein (A2-Q666), Tag Free | +Inquiry |
| CAMK2B-0812H | Recombinant Human CAMK2B Protein (Met1-Lys301), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK2B-0328H | Active Recombinant Human CAMK2B Protein, GST-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK2B-10682H | Recombinant Human CAMK2B, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CAMK2B-596HCL | Recombinant Human CAMK2B cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Shugg T, et al. Heart Rhythm. 2018
Sustained stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors (β-AR) in heart failure leads to pathological changes, including inhibition of the IKs current. This study explored how CaMKII affects KCNQ1, the main part of IKs, during β-AR stimulation. Using various techniques, we found that sustained β-AR stimulation increases phosphorylation at KCNQ1 sites T482 and S484, notably S484 by δCaMKII, reducing IKs function. The CaMKII inhibitor CN21 reversed these effects. Overexpressing δCaMKII similarly decreased IKs, except in a dephosphorylated S484 variant, showing CaMKII’s role in modulating IKs during heart failure.
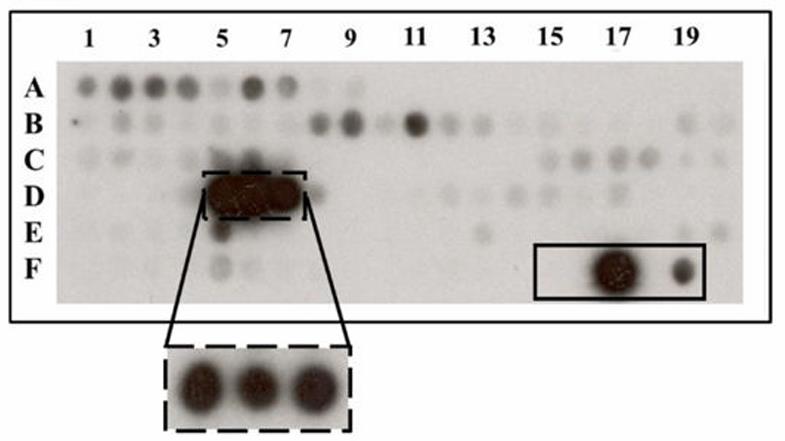
Fig1. Peptide fragments corresponding to the intracellular regions of KCNQ1 were exposed to activated δCaMKII.
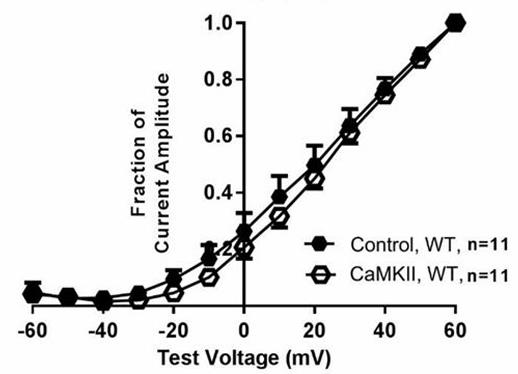
Fig2. Normalized activation curves for WT KCNQ1 when expressed in CaMKII overexpression and control.
Case 2: Bhattacharyya M, et al. Elife. 2020
Human CaMKII variants differ in linker lengths, affecting how they connect kinase domains to the enzyme’s hub. This influences their autophosphorylation, shifting between activation and inhibition. Using mammalian cells and single-molecule analysis, we found that CaMKII-α, with a short linker, favors activation, while CaMKII-β, with a long linker, leans towards inhibition. This shows how calcium signal responses in CaMKII can be adjusted by changing the proportion of isoforms with different linker lengths.
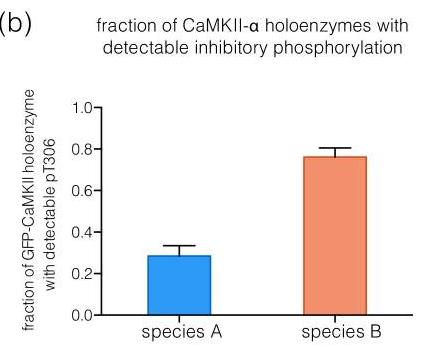
Fig1. Fraction of CaMKII-α holoenzymes with detectable phosphorylation at Thr 305/306 is plotted for each species.
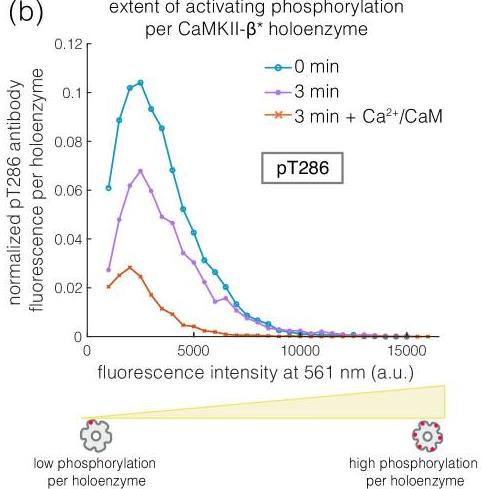
Fig2. Intensity distribution of pThr 286 (561 nm) for CaMKII-β* holoenzymes with detectable phosphorylation.
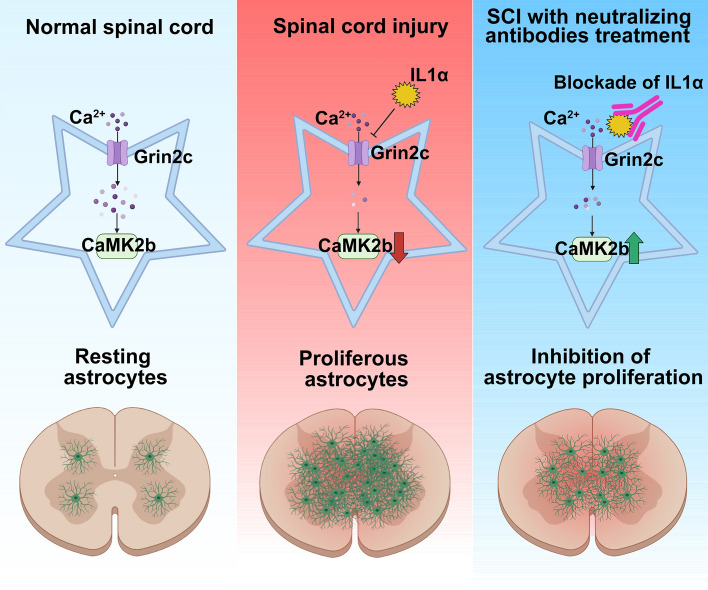
Fig1. Schematic showing that after spinal cord injury, IL1α induces astrocyte proliferation by inhibiting Grin2c, resulting in decreased intracellular Ca2+ concentration and CaMK2b levels. (Yu Xia, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All CAMK2B Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CAMK2B Products
Required fields are marked with *



