Phosphatidylinositol Accumulation Assay
Background
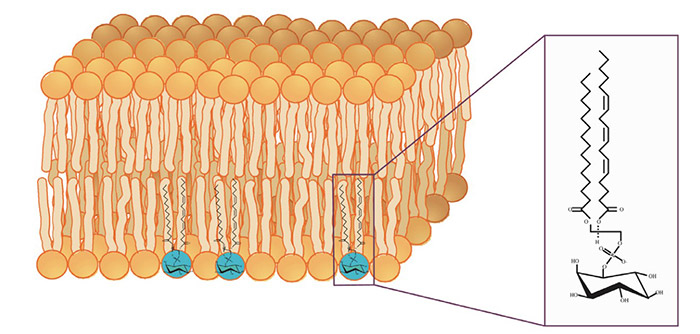
Figure 1. Phosphatidylinositol in its membrane lipid environment. (Wen et al., 2012)
Phosphatidylinositols (PIs) and their phosphorylated derivatives play a pivotal role in cell signaling, cytoskeletal dynamics, membrane trafficking, and more. Their accumulation or dysregulation has been linked to a broad spectrum of diseases, including cancer, neurodegeneration, metabolic disorders, and immune dysfunction.
Quantifying phosphatidylinositol accumulation is a critical tool in understanding PI3K/AKT pathway signaling, GPCR-linked PLC activation, and other lipid signaling cascades. However, due to their low abundance and rapid turnover, accurate and sensitive assays are essential.
At Creative BioMart, we offer specialized Phosphatidylinositol Accumulation Assay Services using state-of-the-art detection methods to quantify PIs and provide insights into their dynamics in response to physiological or pharmacological stimuli.
What We Offer?
Our assay service provides precise quantification of phosphatidylinositol accumulation in cultured cells, tissues, or model organisms. Using radiolabeled, fluorescence-based, or mass spectrometry-based detection platforms, we help you monitor:
- Basal and stimulated PI accumulation
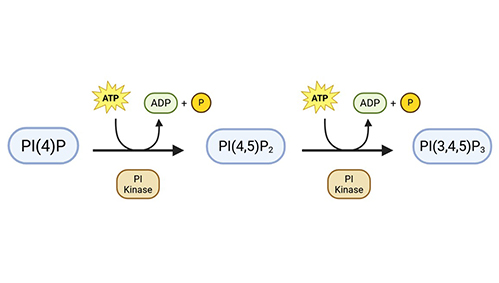
- Enzyme activity of PI kinases and phosphatases
- Impact of drug candidates on inositol turnover
- GPCR and RTK pathway activation dynamics
Our platform is ideal for academic research, pharmaceutical development, and pathway-targeted drug screening.
Service Details
|
Type |
 In-Cell Accumulation Assay |
 In Vitro |
 Mass Spectrometry-Based Quantification |
|
Purpose |
Measures total and specific PI accumulation in living cells. |
Quantifies PI phosphorylation in isolated enzyme or membrane systems. |
Provides absolute PI concentration and phosphorylation status. |
|
Method |
Uses radiolabeled inositol (e.g., [3H]-myo-inositol) or fluorescent PI analogs. |
Fluorescent or MS-based PI product quantification. |
Highly specific, multiplexed analysis of PI species. |
|
Application |
Signal transduction studies, kinase activity assays, drug candidate screening. |
Evaluate activity of PI3K, PI4K, and related enzymes. |
Systems biology, disease profiling, targeted lipidomics. |
Available Assay Formats
-
PI(3)P Mass ELISA
A sensitive competitive ELISA to quantify PI(3)P extracted from cells, enabling assessment of PI3K activity. The assay uses colorimetric detection and is sensitive to as low as 1.5 pmol.
-
PI(3,4)P2 Mass ELISA
A competitive ELISA designed to measure cellular PI(3,4)P2 levels in a 96-well format, supporting studies of PI3K pathway activity and lipid signaling.
-
PI(4,5)P2 Mass ELISA
Quantifies PI(4,5)P2, a key lipid involved in signaling pathways such as PKB/Akt. The assay reveals dynamics of PI3K and PTEN-related processes.
-
PIP3 Mass ELISA
Measures PIP3 levels from cellular extracts using a non-radioactive ELISA platform, offering a safer and faster alternative to traditional 32P-labeled kinase assays.
-
PI(4)P Mass Strip
A straightforward lipid-protein overlay assay that quantifies PI(4)P from cell extracts using pre-spotted nitrocellulose strips. Ideal for high-throughput sample comparison with built-in standards.
-
Ins(1,4,5)P3 Assay
This assay platform enables identification of InsP3-binding proteins via pull-down and SDS-PAGE, and quantification of Ins(1,4,5)P3 accumulation in lysates or in vitro samples.
-
PI3 Kinase Activity ELISA
Evaluates PI3-K activity by detecting the conversion of PIP2 to PIP3, offering insights into pathways involved in proliferation, survival, and disease progression.
Service Procedure

Why Choose Us?
- Precision and Sensitivity: We use the latest detection technologies to capture even subtle changes in phosphatidylinositol levels.
- Diverse Detection Platforms: Choose from radiometric, fluorescence, or LC-MS/MS methods depending on your needs.
- Expertise in Lipid Signaling: Our team includes lipid biochemists and cell signaling specialists who guide project design and analysis.
- Custom Assay Development: We develop custom protocols and optimize conditions for your specific models and pathways.
- End-to-End Solutions: From sample prep to data interpretation, we deliver complete, ready-to-use insights for your research or drug discovery efforts.
- Validated Across Systems: Proven assay performance in various cellular and tissue models.
Case Study
* NOTE: We prioritize confidentiality to safeguard our clients’ technology and intellectual property. As an alternative, we present selected published research articles as representative case studies. For details on the assay services and products used in these studies, please refer to the relevant sections of the cited literature.
Case 1: Arg1 from Cryptococcus neoformans lacks PI3 kinase activity and conveys virulence roles via its IP3-4 kinase activity
Desmarini et al., 2024. doi:10.1128/mbio.00608-24
This study shows that the catalytic activity of inositol tris/tetrakis phosphate kinases (IP3-4K) is essential for the virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida albicans. A catalytically inactive mutant (dkArg1) lacked IP3-4K activity and displayed major virulence defects, including impaired growth, capsule formation, and avirulence in an insect model. Unlike their human or yeast counterparts, these fungal IP3-4Ks do not act on lipid substrates. The results confirm that fungal virulence depends on IP3-4K enzyme function, not just its structural role, and suggest divergence in the IPK pathway across species.
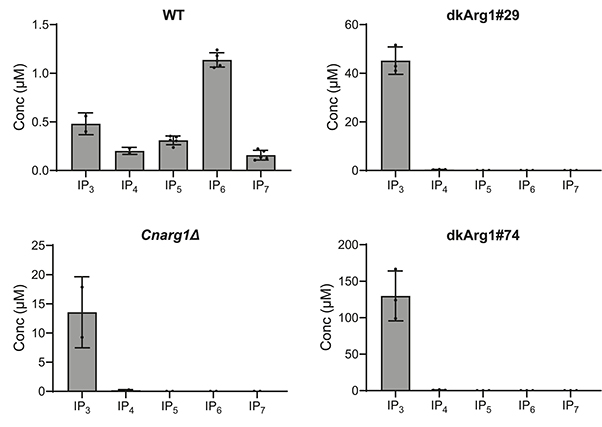
Figure 2. Inositol phosphates (IPs) from WT and dkArg1 were extracted with perchloric acid, enriched with titanium dioxide beads and subjected to CE-ESI-MS. The IP profiles of the dkArg1 strains are like that of CnArg1Δ, with IP3 accumulating, and IP4, IP5, IP6, and IP7 depleted, relative to WT. (Desmarini et al., 2024)
Case 2: Inositol depletion regulates phospholipid metabolism and activates stress signaling in HEK293T cells
Suliman et al., 2022. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159137
This study highlights the essential role of inositol in human cell viability, signaling, and metabolism. By knocking out the ISYNA1 gene in HEK293T cells, researchers created a model deficient in de novo inositol synthesis, which led to an “inositol-less death” phenotype similar to that seen in yeast. Lipidomic and transcriptomic analyses revealed that inositol deprivation globally altered phospholipid metabolism—notably reducing phosphatidylinositol (PI) and increasing cardiolipin-related lipids—and triggered major changes in gene expression, including ERK signaling and protein processing pathways. This study provides the first comprehensive view of how inositol regulates metabolic and signaling networks in human cells.
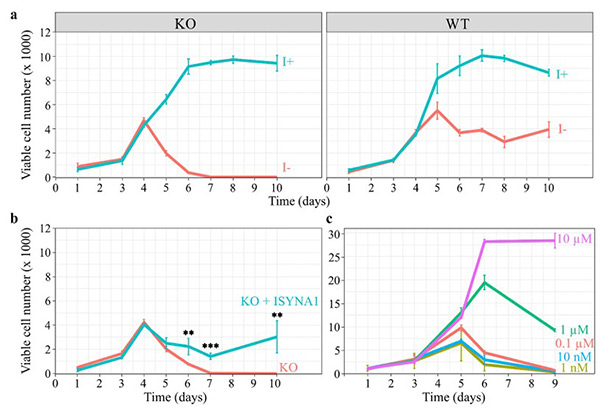
Figure 3. Inositol depletion leads to cell death. HEK293T WT and KO cells were cultured in 96-well plates, and viable cell numbers were estimated by the viability assay described in ‘Materials and methods.’ (a) Inositol (1 mM) promotes the growth of WT and KO cells, while inositol deprivation decreases the viability of KO cells after 4 days, eventually leading to total cell death by day 6. (b) Overexpression of ISYNA1 rescues viability of ISYNA1-KO cells when cultured in inositol-free medium. (c) A range of inositol concentrations was used to determine the minimum concentration requirements to sustain cell viability. (Suliman et al., 2022)
Customer Testimonials
-
“Creative BioMart’s PI(3)P Mass ELISA service gave us quantitative clarity we simply couldn’t get in-house. Their assay turnaround was quick, data reproducibility was solid, and their technical team even helped us troubleshoot pathway artifacts we were seeing in our PI3K inhibitor screen. Excellent collaboration from start to finish.”
— Principal Scientist | Oncology Discovery Unit, Biotech Startup
-
“We used Creative BioMart’s phosphoinositide accumulation assays to evaluate GPCR activation in neuronal cell lines. Their use of [3H]-inositol labeling and LiCl trap method was textbook perfect. The dataset helped us refine our lead compound series.”
— Academic PI | Neuropharmacology Department, Research University
-
“Creative BioMart’s Phosphatidylinositol Accumulation Assay was key to profiling lipid signaling in our metabolic disorder model. The team helped us customize the protocol for mouse hepatocytes and provided crystal-clear LC-MS analysis of PI species. Their attention to technical detail was top-notch.”
— R&D Director | Nutraceuticals & Functional Foods Company
-
“Our team had tight timelines to profile PI(4,5)P2 turnover in engineered HEK293 cells. Creative BioMart stepped up with fast radioisotope-based assays and strong assay validation data. Their team even suggested a follow-up PLCγ1 phosphorylation assay we hadn’t considered—super insightful.”
— Group Leader | Signal Transduction Research, Global Pharma
-
“We collaborated with Creative BioMart to measure phosphoinositide dynamics during viral infection in macrophages. Their expertise in non-radioactive IP1 assays helped us generate reproducible, publication-ready results. Would absolutely work with them again for immunology signaling studies.”
— Senior Postdoc | Infectious Disease Institute, Government Lab
FAQs
-
Q: What sample types can you accept?
A: We work with cultured cells, tissues, recombinant proteins, and lipid extracts. -
Q: How do you ensure specificity for different PI species?
A: We use species-specific standards in MS and apply targeted detection in fluorescent/radiometric assays. -
Q: What is the turnaround time?
A: Standard delivery is 2–3 weeks, depending on assay complexity and sample volume. -
Q: Do you offer inhibitor profiling or drug screening services?
A: Yes, we can integrate PI accumulation assays into high-throughput inhibitor screens or dose-response testing. -
Q: Can you analyze downstream signaling changes?
A: Definitely. We offer complementary services such as phospho-protein analysis, pathway reporter assays, and transcriptomics.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References:
- Desmarini D, Liu G, Jessen H, et al. Arg1 from Cryptococcus neoformans lacks PI3 kinase activity and conveys virulence roles via its IP3-4 kinase activity. Alspaugh JA, ed. mBio. 2024;15(6):e00608-24. doi:10.1128/mbio.00608-24
- Suliman M, Case KC, Schmidtke MW, Lazcano P, Onu CJ, Greenberg ML. Inositol depletion regulates phospholipid metabolism and activates stress signaling in HEK293T cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2022;1867(6):159137. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159137
- Wen PJ, Osborne SL, Meunier FA. Phosphoinositides in neuroexocytosis and neuronal diseases. In: Falasca M, ed. Phosphoinositides and Disease. Vol 362. Springer Netherlands; 2012:87-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5025-8_4
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

