Native Human Liver Alkaline Phosphatase
| Cat.No. : | ALPL-8004H |
| Product Overview : | Human Liver Alkaline Phosphatase was purified from Human Liver. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human Liver |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Human Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups in the 5- and 3- positions from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. In human(s), alkaline phosphatase is present in all tissues throughout the entire body, but is particularly concentrated in liver, bile duct, kidney, bone, and the placenta. The optimal pH for the enzyme activity is pH=10 in standard conditions. |
| Form : | Ammonium Sulfate Suspension |
| Stability : | 1 year |
| Storage : | 2-8 °C |
| Concentration : | Typically >5 mg Protein/mL |
| Gene Name | ALPL alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ALPL |
| Synonyms | ALPL; alkaline phosphatase, liver/bone/kidney; HOPS; alkaline phosphatase, tissue-nonspecific isozyme; TNSALP; glycerophosphatase; tissue-nonspecific ALP; alkaline phosphomonoesterase; liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase; alkaline phosphatase live |
| Gene ID | 249 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000478 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000469 |
| MIM | 171760 |
| UniProt ID | P05186 |
| Chromosome Location | 1p36.12 |
| Pathway | Endochondral Ossification, organism-specific biosystem; Folate biosynthesis, organism-specific biosystem; Folate biosynthesis, conserved biosystem; Metabolic pathways, organism-specific biosystem; TNF-alpha/NF-kB Signaling Pathway, organism-specific biosystem; |
| Function | alkaline phosphatase activity; hydrolase activity; metal ion binding; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ALPL-123C | Recombinant Cattle ALPL Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-6912C | Recombinant Chicken ALPL | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-138R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque ALPL Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-641R | Recombinant Rat ALPL Protein | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-327H | Active Recombinant Human ALPL Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| ALPL-66C | Active Native Calf Alkaline Phosphatase | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-5324H | Active Native Human Alkaline Phosphatase | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-25H | Active Native Human ALPL Protein | +Inquiry |
| ALPL-8004H | Native Human Liver Alkaline Phosphatase | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ALPL-3092HCL | Recombinant Human ALPL cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Engelmann C, et al. Sci Rep. 2020
The study explored if recombinant alkaline phosphatase (recAP) could prevent acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) by targeting the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) pathway, which is crucial in liver failure. Rats were subjected to various treatments to mimic liver failure, and recAP was administered before LPS injection. recAP mitigated liver dysfunction and brain edema in the ACLF model by reducing cytokines, chemokines, liver cell death, and brain water, and it decreased LPS activity. However, it was ineffective in acute liver failure. recAP reduced hepatic TLR4 expression in ACLF, suggesting its potential as a novel treatment for preventing ACLF but not acute liver failure.
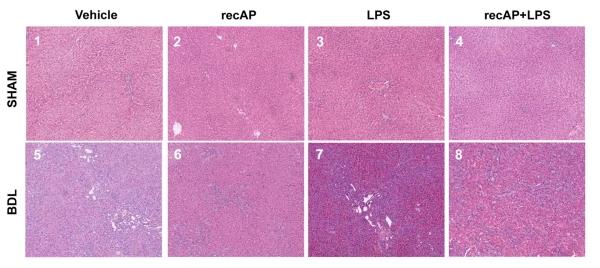
Fig1. Liver tissue from all groups of the ACLF model was stained with H&E.
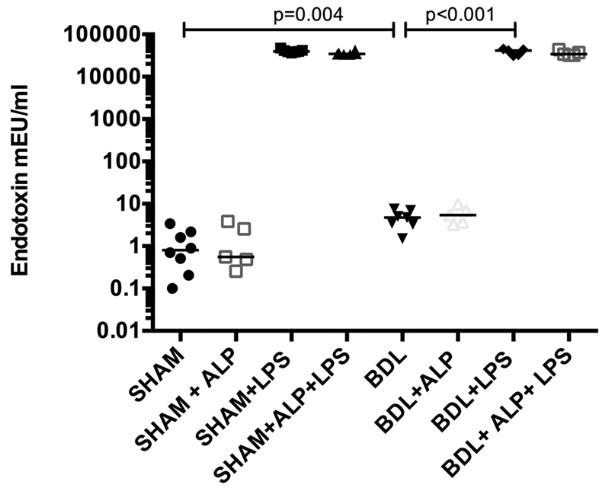
Fig2. Plasma endotoxin quantification by LAL assay.
Case 2: Zhu S, et al. Anal Chim Acta. 2024
Elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels are associated with conditions like breast and prostate cancer, bone damage, gingivitis, and liver dysfunction. Accurate ALP monitoring is vital for diagnosing and treating these diseases. While traditional colorimetric detection methods are portable, they lack sensitivity. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) offers high sensitivity but requires bulky equipment. To bridge this gap, we've developed IHP-GT, a novel, one-pot, high-efficiency ALP assay that combines isothermal amplification with a single probe (IGHP) for rapid, sensitive detection. The assay involves a cascade amplification process triggered by ALP, leading to the formation of a G-quadruplex structure that emits a fluorescent signal upon binding with ThT. IHP-GT enables sensitive ALP detection within 90 minutes and has been validated in human serum samples. It also serves as a platform for screening ALP inhibitors. For ease of use, we've formulated the IHP-GT components into a lyophilized powder for point-of-care testing.
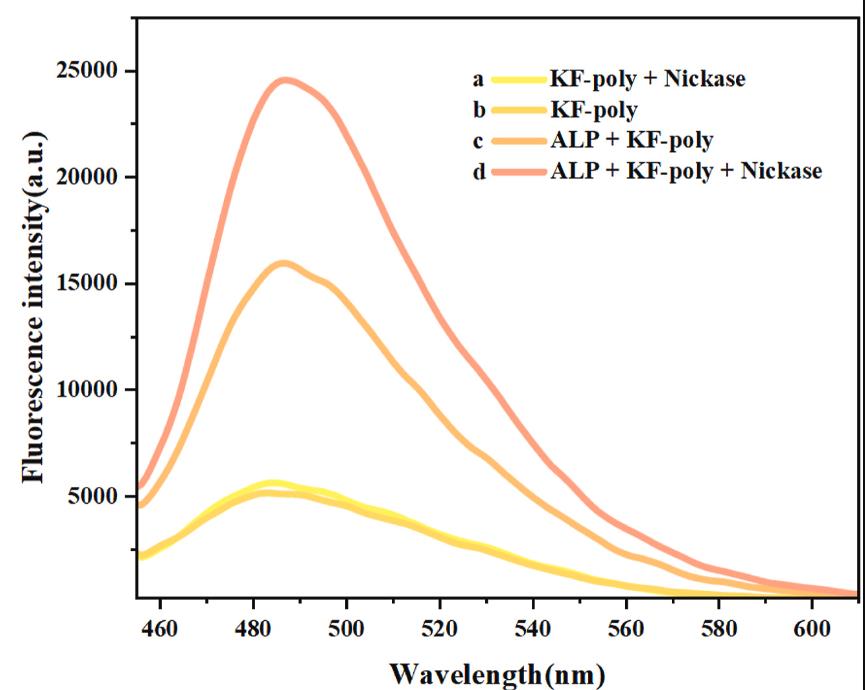
Fig1. Fluorescence spectra induced by different samples.
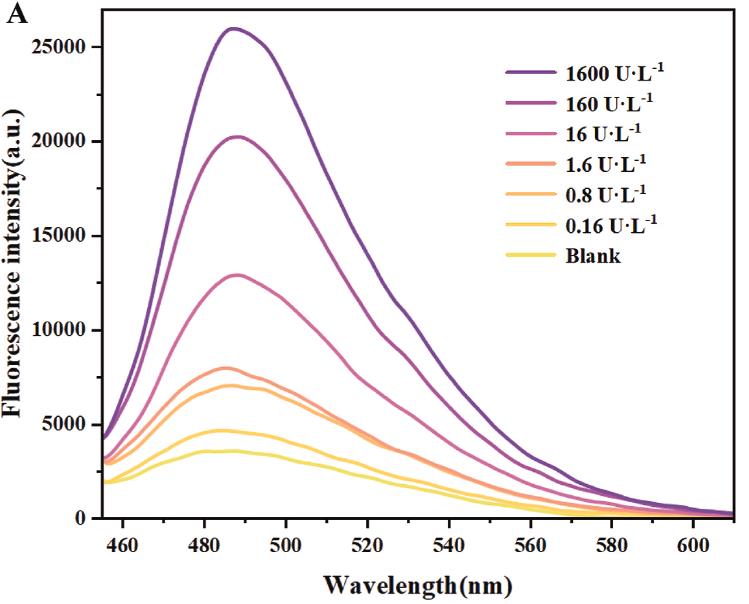
Fig2. Fluorescence spectra of IHP-GT assay induced by different activities of ALP.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is an enzyme distributed in many organs of the human body, especially in the liver, bones, kidneys and placenta. Native Human Liver ALP is an isozyme in the liver that is essential for many biochemical processes and is mainly responsible for catalyzing dephosphorylation reactions. ALP is a dimeric protein with zinc and magnesium ions in its active center. It is most active under alkaline conditions, and its expression level is affected by age, gender, race and health status. It participates in lipid metabolism, bile production, helps the liver excrete bilirubin, and maintains bone health.
In clinical diagnosis, elevated ALP levels are often associated with liver diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, and can also be used to diagnose bone diseases and obstructive jaundice. In the field of scientific research, ALP is used as an enzyme marker due to its stability, especially in ELISA experiments, and is also used to study molecular dephosphorylation processes. In addition, ALP promotes bone tissue formation by regulating activity in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. At the same time, in the food industry and environmental science, the determination of ALP activity helps to detect the effectiveness of heat treatment and evaluate the impact of pollutants on microbial activity.
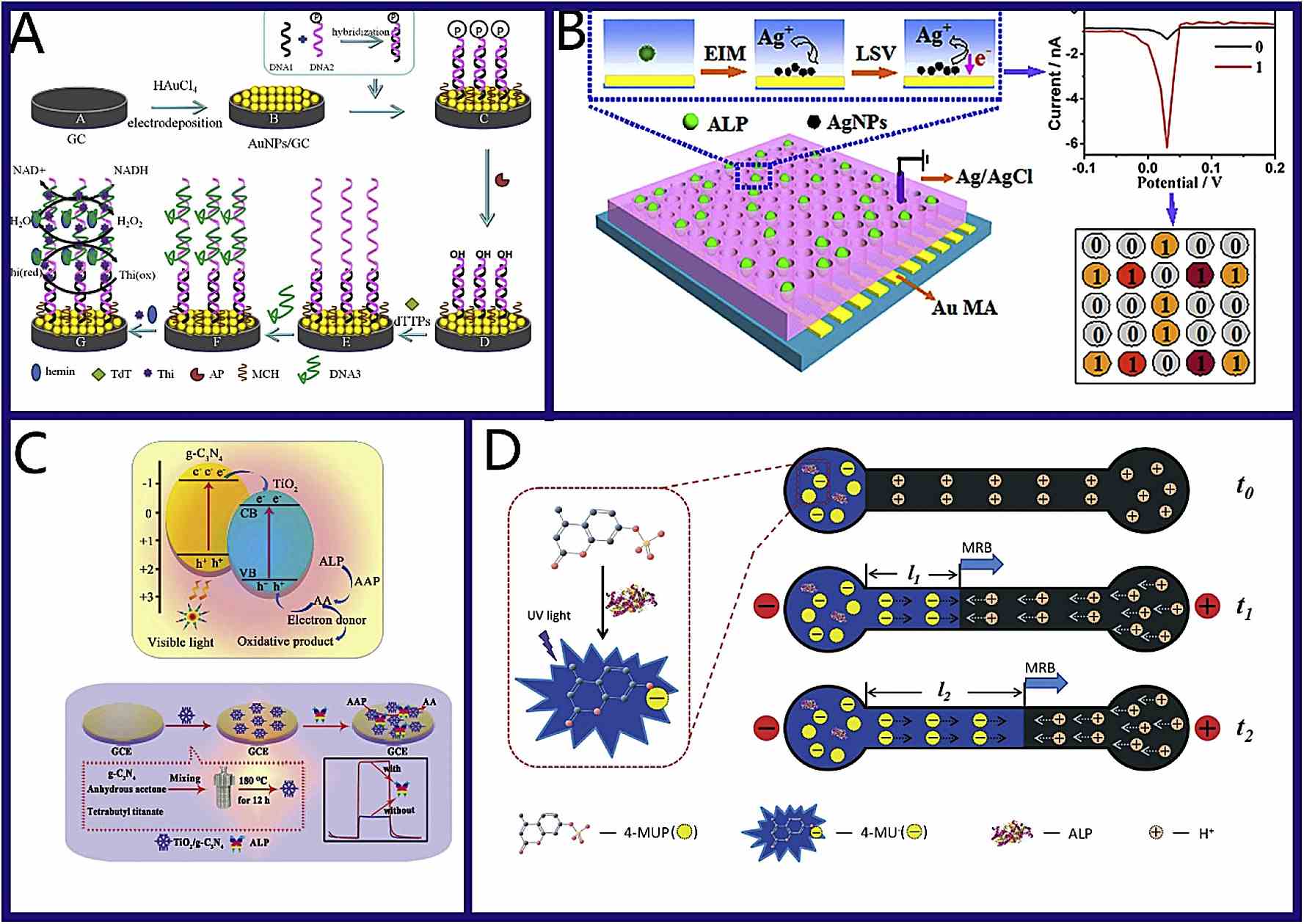
Fig1. Schematic illustration of representative advances for ALP detection based on electrochemical strategies. (Zhenwei Tang, 2019)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ALPL Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ALPL Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


