Active Recombinant Human EGF protein(Asn971-Arg1023), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | EGF-201H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human EGF (NP_001954.2) (Asn 971-Arg 1023) was expressed in HEK293, fused with the Fc region of Human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | Asn971-Arg1023 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Balb/C 3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.3-1.5 ng/mL. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human Fc/EGF chimera is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 290 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 33 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhFc/EGF monomer is approximately 37 kDa due to the glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | EGF epidermal growth factor [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | EGF |
| Synonyms | EGF; epidermal growth factor; epidermal growth factor (beta urogastrone); pro-epidermal growth factor; beta-urogastrone; URG; HOMG4; |
| Gene ID | 1950 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001178130 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001171601 |
| MIM | 131530 |
| UniProt ID | P01133 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| EGF-6H | Active Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor | +Inquiry |
| EGF-561M | Active Recombinant Mouse Epidermal Growth Factor, MIgG2a Fc-tagged, mutant | +Inquiry |
| EGF-2815P | Recombinant Pig EGF protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| EGF-214H | Recombinant Human EGF, StrepII-tagged | +Inquiry |
| EGF-201H | Active Recombinant Human EGF protein(Asn971-Arg1023), hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| EGF-26462TH | Native Human EGF | +Inquiry |
| Egf-635R | Native Rat Egf | +Inquiry |
| Egf -635R | Native Rat Egf protein | +Inquiry |
| Egf-634M | Active Native Mouse Egf | +Inquiry |
| EGF-23H | Active Native Human EGF protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| EGF-973MCL | Recombinant Mouse EGF cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| EGF-2716HCL | Recombinant Human EGF cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Bavaro T, et al. Sci Rep. 2021
This study engineered hEGF-agarose bioconjugates (CNBr/glyoxyl carriers) for burn wound healing and skin tissue engineering. CNBr-immobilized EGF demonstrated superior fibroblast proliferation (100 ng/mL, 72h) vs. soluble EGF, validated via LC-MS peptide mapping. Findings highlight immobilized EGF’s potential in regenerative therapies, emphasizing carrier-specific bioactivity for optimized skin repair and EGFR-targeted biomaterials.
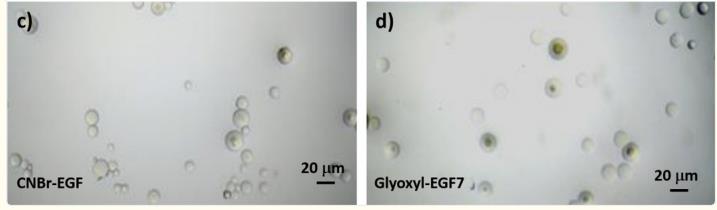
Fig1. Microscopic images of CNBr-activated-agarose and glyoxyl-agarose carriers after EGF immobilization.
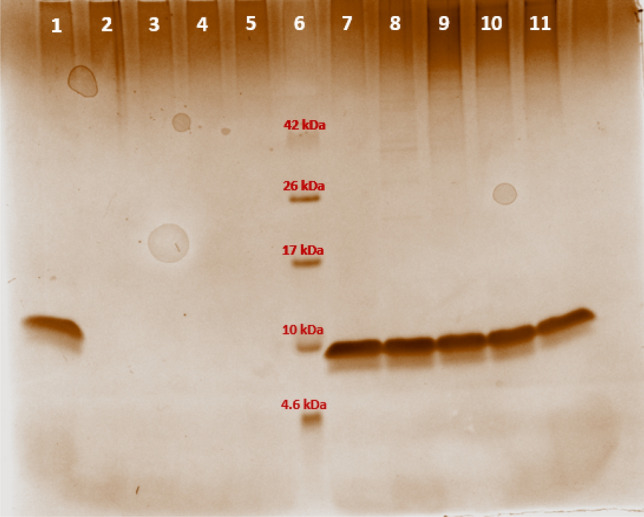
Fig2. Monitoring EGF immobilization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Case 2: Knight C, et al. Cell Signal. 2019
Study reveals EGF activates β-catenin in bone marrow MSCs via time-regulated signaling (early MAPK → delayed β-catenin), driving proliferation by overriding cell cycle suppression. RNA-seq identifies unique EGF/β-catenin gene networks distinct from classical pathways, advancing strategies for bone regeneration and MSC-based therapies.
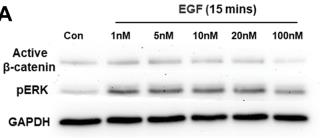
Fig1. Western blot analysis of active β-catenin and pERK expression in primary MSCs in response to treatment with different concentrations of EGF for 15 min and 6 h.
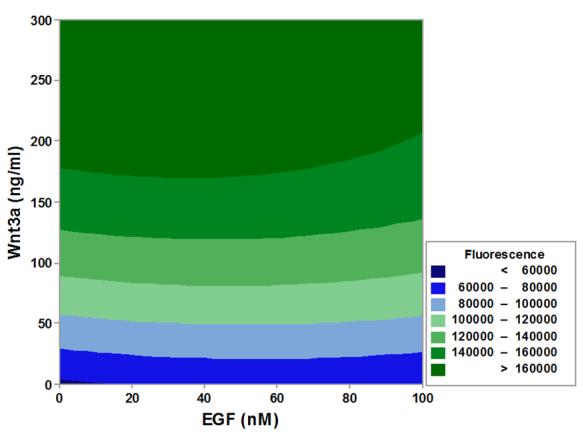
Fig2. Contour plot showing the effects of Wnt3a and EGF on the TCF-EGFP response.
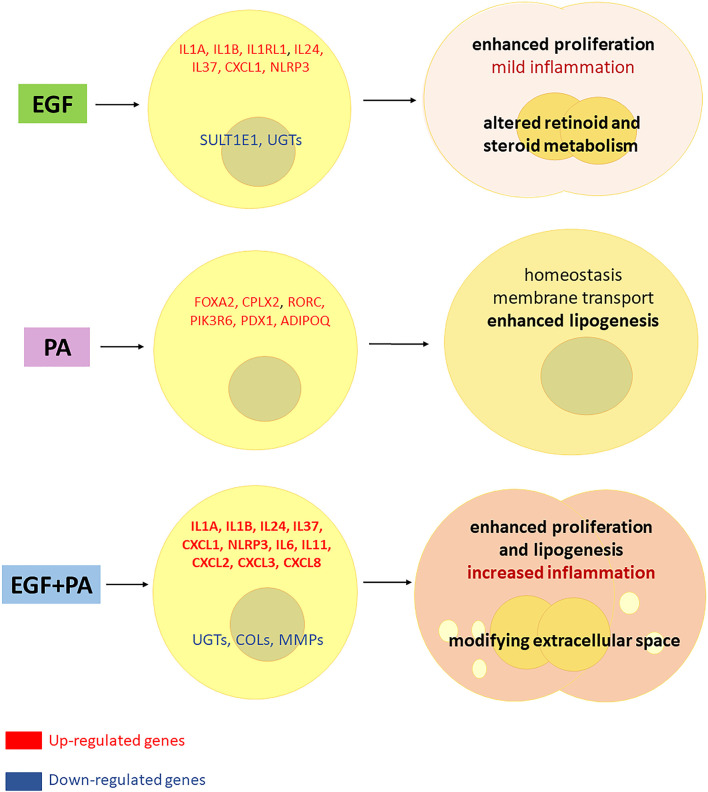
Fig1. Interaction between EGF and PA to modulate cell proliferation, lipogenesis and inflammatory responses in sebocytes. (Dániel Törőcsik, 2021)
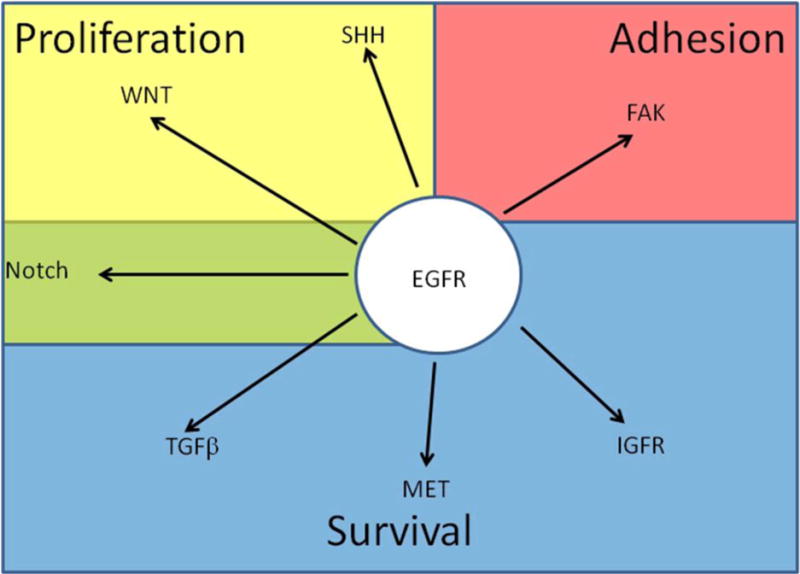
Fig2. Crosstalk between EGFR signaling and other signaling pathways affected in cancer. (Stephan Lindsey, 2015)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All EGF Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All EGF Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


