TGFA
-
Official Full Name
transforming growth factor, alpha -
Overview
Transforming growth factors (TGFs) are potent mitogeni c polypeptides. Two classes of TGFs have been identified: TGFα and TGFβ . TGF α is synthesized as a 160 amino acid, trans membrane precursor. The precursor undergoes sequential external proteolytic cleavage, releasing TGFα species ranging in molecular weight from 6-25 kDa. Mature TGFα is an acid- and heat-stable 50 amino acid polypeptide of 5.5 kDa. It is secreted by a variety of transformed cells and tumors, and by a number of embryoni c cells as well as some normal adult tissues including the brain and skin keratinocytes. Mature TGF α is approximately 30% homologous, at the amino acid level, to epidermal growth factor (EGF). TGF α binds to the EGF receptor, mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptor, and promotes anchorage-independent growth of normal rat fibroblasts in soft agar in the presence of transforming growth factor-beta. Transformation of cells, in vitro, by certain viruses including SV40 and polyoma virus, as well as transformation by the activated ras oncogene can lead to increased secretion of TGF α. TGF α may play a role in tumor formation by an autocrine/paracrine mechanism whereby TGFα promotes and sustains the transformed character of the cells from which it is secreted as well as that of neighboring cells. The biological relevance of TGF α in tumor development is supported by reports that multiple molecular weight forms of TGF α may be found in the urine of cancer patients in amounts which differ from those found in normal urine samples. TGF α may also play a role in normal development including wound healing. The major difficulty impeding the investigation of the normal and pathological roles of TGFα in vivo has been the use of activity-based biological assays that do not distinguish between TGFα and other related molecules (e.g., EGF). The TGF α ELISA is highly specific and can detect less than 10 pg/ml of human TGF α in a variety of biological fluids and tissue culture media. -
Synonyms
TFGA;TGF-alpha;protransforming growth factor alpha
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Macaca mulatta
- Sheep
- Rabbit
- E.coli
- Hi-5 Insect Cells
- yeast
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- CHO
- GST
- His
- Non
- Fc
- T7
- Avi
- KSI
Background
What is TGFA Protein?
TGFA, or Transforming Growth Factor-alpha, is a protein that’s a bit like a cellular messenger. It plays a part in telling cells to grow and divide. This protein is especially important in development and healing, but sometimes it joins the wrong team, like in cancer, encouraging tumor cells to multiply and spread. TGFA binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), activating pathways that drive cell growth. It’s a key player not just in normal body functions but also in certain diseases where cell regulation goes haywire. Researchers are interested in it for both its natural roles and its potential as a target in therapy, especially in cancers where it might push things in the wrong direction.What is the Function of TGFA Protein?
TGFA, or Transforming Growth Factor-alpha, acts like a growth promoter in our bodies. It signals cells to multiply, which is vital when you're growing or healing. TGFA connects with cell receptors called EGFR to trigger this growth. But sometimes, it can be overactive, particularly in cancers, where it aids in tumor growth and spread. Because it plays both a helpful and harmful role, TGFA is a significant focus in medical research, especially in understanding and treating cancer.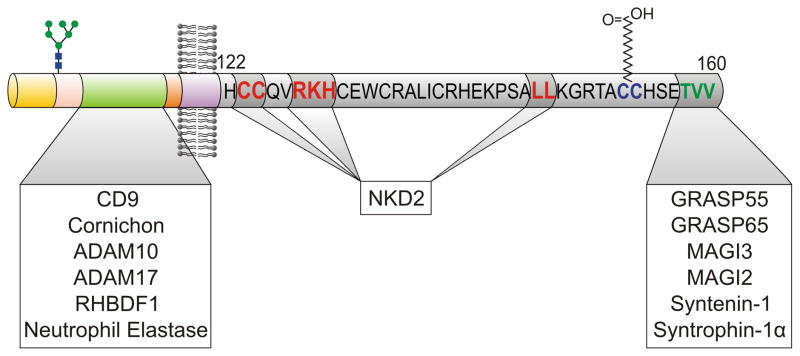
Fig1. TGFA protein characteristics and interacting proteins. (Bhuminder Singh, 2014)
TGFA Related Signaling Pathway
The TGFA related signaling pathway is like a complex communication network inside our cells. When TGFA, which is a growth-promoting protein, attaches to the EGFR on the cell surface, it sets off a chain reaction. This is a bit like flipping a switch that sends signals down a pathway called the PI3K/AKT pathway. This pathway tells cells to grow, divide, or even survive under certain conditions. It’s crucial for normal development and healing, but if it goes haywire, it might lead to problems like cancer by making cells grow uncontrollably. Researchers study this pathway not only to understand how cells normally function but also to find potential targets for cancer treatments, trying to block the signals that make tumors grow.TGFA Related Diseases
TGFA, or Transforming Growth Factor-alpha, is a player in several health issues. Normally, it's all about guiding cell growth and repair, but sometimes things go wrong. In cancer, TGFA can boost the growth and spread of tumor cells, making it a bad guy in scenarios like lung, breast, and brain cancers. It's also involved in psoriasis, a skin condition where cell growth regulation is off balance, leading to scaly patches. In the liver, too much TGFA might contribute to chronic liver diseases or even cirrhosis. Because TGFA is linked to these conditions, scientists are keen on finding ways to block its effects, hoping to slow down or stop disease progression, especially in cancer.Bioapplications of TGFA
TGFA, short for Transforming Growth Factor-alpha, is grabbing attention in various bioapplications due to how it promotes cell growth and healing. In regenerative medicine, TGFA could aid in creating treatments for faster wound healing or tissue repair because it naturally gets cells to grow. In the cancer field, figuring out TGFA's role might lead to new drugs that block its action, potentially slowing or halting tumor development. Researchers are also looking into using TGFA for liver repair, as it might help regenerate damaged areas. Its influence on cell behavior makes TGFA a promising focus for new medical therapies.Case Study
Case Study 1: García-Alonso S. et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021
Kidney cancer treatment has gotten better with kinase inhibitors and immunotherapies, but it's still tough to treat advanced cases. Since many kidney cancer drugs target receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), researchers checked out other RTKs not hit by current meds. In 44 kidney cancer samples, they found EGFR activity high in tumors, along with more TGFα. Blocking EGFR or TGFα slowed cancer cell growth in lab tests. Interestingly, tumor TGFα stays on the membrane, unlike the processed form in normal tissue.-
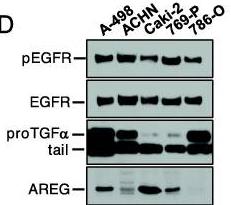 Fig1. Protein levels of phosphorylated and total EGFR, as well as two ligands (TGFα and amphiregullin) in kidney cancer cell lines.
Fig1. Protein levels of phosphorylated and total EGFR, as well as two ligands (TGFα and amphiregullin) in kidney cancer cell lines. -
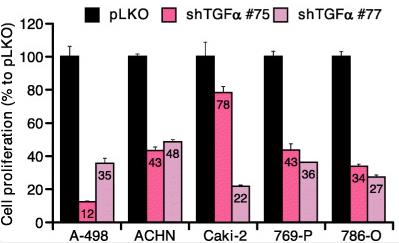 Fig2. TGFα knockdown effect on the proliferation of renal cancer cells.
Fig2. TGFα knockdown effect on the proliferation of renal cancer cells.
Case Study 2: Xia M. et al. J Cancer. 2022
Long noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs) play big roles in cell processes, including in lung cancer. Researchers aimed to find new lncRNAs affecting lung cancer's progression. Data from the Cancer Genome Atlas showed that the lncRNA LASTR was much higher in lung cancer tissues compared to normal ones. Patients with more LASTR had shorter survival. Lab tests showed lung cancer cells had more LASTR, and reducing it slowed their growth and spread. LASTR works via the miR-137/TGFA axis and activates the PI3K/AKT pathway, confirmed by western blotting.-
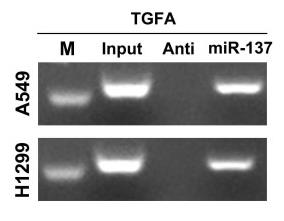 Fig3. NA pulldown assay showed that miR-137 could bind to more TGFA relative to its anti-probe.
Fig3. NA pulldown assay showed that miR-137 could bind to more TGFA relative to its anti-probe. -
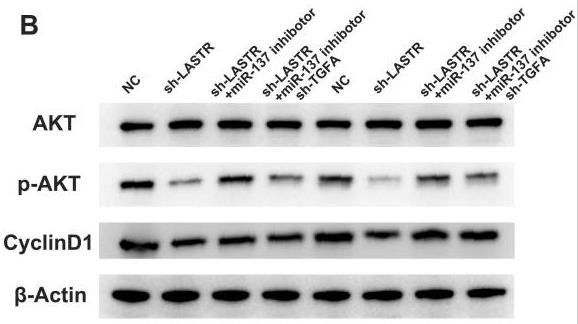 Fig4. The changes of key marker in PI3K/AKT pathway was validated by western blotting assay.
Fig4. The changes of key marker in PI3K/AKT pathway was validated by western blotting assay.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TGFA-6744H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TGFA-6744H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TGFA-522H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TGFA-522H)
Involved Pathway
TGFA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TGFA participated on our site, such as ErbB signaling pathway,Pathways in cancer,Renal cell carcinoma, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TGFA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ErbB signaling pathway | MAPK10,SRC,AKT3A,NRG2,CAMK2B,SHC3,RPS6KB1B,CDKN1BB,ERBB3B,SOS1 |
| Renal cell carcinoma | HRAS,EPAS1,MET,VHL,PAK6,KRAS,RAC1,EGLN1,NRAS,RAP1A |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | MAPK3,PDPK1,NRAS,STK4,TP53,RASSF1,PIK3R5,ARAF,SOS1,ALK |
| Prostate Cancer | TP53,ATF4,MAP4K1,PDGFRB,NFKBIA,MTOR,AKT1,ARID1A,Ar,EP300 |
| Pancreatic cancer | TGFBR2,PIK3R1,PIK3CG,CDC42,NFKB1,SMAD4,TRP53,BRAF,TGFBR1,VEGFA |
| Glioma | SHC4,TP53,CAMK2G,PLCG1,PIK3CB,PIK3R1,TRP53,IGF1,PDGFRA,PLCG2 |
| Pathways in cancer | HSP90AB1,MMP9,WNT1,LEF1,EP300,FH,GNG5,RET,IGF1,LAMA2 |
-
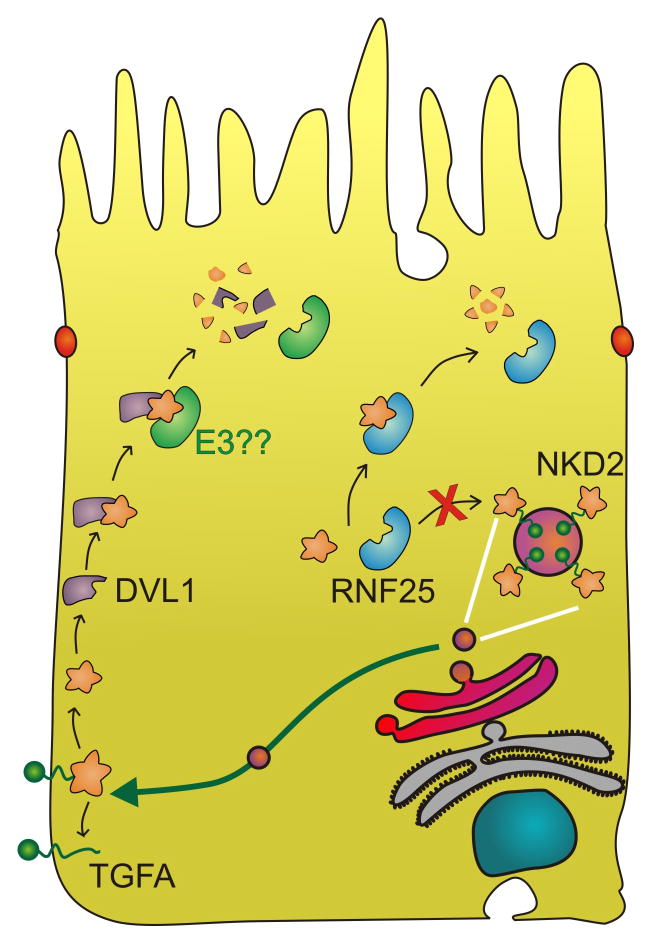 Fig1. Proposed model for sequential action of NKD2 in basolateral targeting of TGFA and dampening of canonical Wnt signaling. (Bhuminder Singh, 2014)
Fig1. Proposed model for sequential action of NKD2 in basolateral targeting of TGFA and dampening of canonical Wnt signaling. (Bhuminder Singh, 2014) -
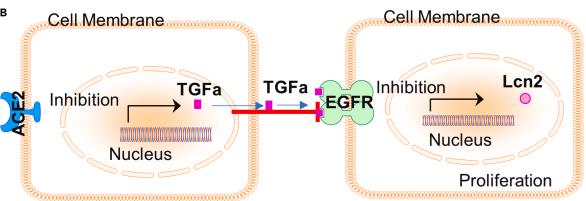 Fig2. A diagram summarizing how ACE2 negatively regulates limbal epithelial proliferation via inhibiting TGFA/EGFR signaling. (Huimin Jiang, 2024)
Fig2. A diagram summarizing how ACE2 negatively regulates limbal epithelial proliferation via inhibiting TGFA/EGFR signaling. (Huimin Jiang, 2024)
Protein Function
TGFA has several biochemical functions, for example, epidermal growth factor receptor binding,growth factor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TGFA itself. We selected most functions TGFA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TGFA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | GLA,TCEA2,DYRK4,PIK3R4,DNAJB5,XRCC1,ANLN,RBM12B,BRPF1,UBE2H |
| epidermal growth factor receptor binding | MS4A1,HBEGFB,FAM83B,BTC,LINGO1B,SNX4,LINGO1,SNX1,EGF,FER |
| growth factor activity | EREG,IGF2,FGF8,PDGFC,PDGFAA,FGF13B,FGF11,KITLG,FGF1,NTF3 |
Interacting Protein
TGFA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TGFA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TGFA.
EGFR;SGTA;Magi3;MAGI3;MAGI2;ERBB2;ADAM17;NKD2;Gorasp2
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References




