FXN
-
Official Full Name
frataxin -
Overview
This nuclear gene encodes a mitochondrial protein which belongs to FRATAXIN family. The protein functions in regulating mitochondrial iron transport and respiration. The expansion of intronic trinucleotide repeat GAA results in Friedreich ataxia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2009] -
Synonyms
FXN;frataxin;FA;X25;CyaY;FARR;FRDA;frataxin, mitochondrial;Friedreich ataxia protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Cynomolgus
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
Background
What is FXN?
FXN protein, also known with the scientific name of frataxin, plays a vital role in our bodies, especially in the well-being of our cells. Altered functions and defects in this protein can result in various diseases, reinforcing its importance in human health.
FXN protein was discovered by two independent research groups in 1997 when they were studying Friedreich's ataxia (FA), a debilitating neurodegenerative condition. The disease was observed to result from mutations in the FXN gene, thus leading to the discovery of the FXN protein.
The background of the frataxin gene showcases a long history of biological investigation. The FXN gene, the gene coding for frataxin, lies on the human chromosome 9q21.1. This region comprises exons, which are vital for the construction of functional frataxin proteins in the human body. This gene locus is pivotal because, if altered or interrupted, the frataxin protein's structure and function will be greatly affected, thereby leading to health complications.
What Is The Structure of FXN Protein?
The FXN protein, or frataxin, adopts a unique α/β structure. Characterized by seven-strand β-sheets flanked by α-helices, its formation allows for the formation of a central cleft, which houses an iron ion. Often bound to iron-sulfur clusters, the FXN protein plays a crucial role in iron metabolism in the mitochondria – the powerhouses of our cells.
What Is The Function of FXN Protein?
In terms of its function, frataxin is involved in several essential cellular roles. Mainly, it acts as an iron chaperone, regulating iron levels and contributing to the biosynthesis of iron-sulphur clusters. These structures, in turn, are crucial components of protein machineries involved in processes such as DNA repair and energy metabolism. Moreover, frataxin is also involved in heme synthesis, antioxidant defenses, and iron detoxification.
Frataxin is a key component of the iron-sulfur cluster (ISC) pathway. The protein's involvement in ISC synthesis is currently believed to be a primary role. With reduced levels of frataxin, cells experience defective ISC biosynthesis leading to a buildup of harmful cellular byproducts, like free radicals, which can cause cellular damage and stress.
FXN Protein Related Diseases
Alterations in the FXN protein and its related pathways can result in a variety of diseases. Foremost among these is Friedreich's ataxia (FA), a disease caused primarily by a decrease or a complete absence of frataxin, due to expansions of a GAA triplet repeat in the FXN gene. FA is characterized by neurodegeneration, cardiomyopathy, and increased risk of diabetes. Other conditions that can result from frataxin-related dysfunction include cancer, atherosclerosis, and several neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
Given the extensive influence of the FXN protein on human health, understanding and harnessing this protein holds major therapeutic potential. Current treatment strategies for FA focus on symptomatic management and slowing disease progression. However, research into frataxin biology could lead to more targeted and effective treatments. For instance, gene therapy techniques are being explored to correct the FXN gene defect and enhance frataxin production.
Moreover, understanding the FXN protein's function in iron metabolism could have broader impacts on developing treatments for other diseases involving iron toxicity or deficiency. This includes conditions like anemia, hemochromatosis, and numerous neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants and iron chelators are also being studied for their potential to mitigate frataxin deficiency by reducing iron-mediated oxidative damage.
FXN Protein's Applications
In terms of biotechnological applications, the frataxin protein has been used as a biomarker for rapid, accurate testing of FA. The proactive assessment of FXN levels could enable early diagnosis and timely intervention for FA, contributing to an improved prognosis.
In conclusion, the FXN protein, with its multifaceted roles in iron metabolism, antioxidant defenses, and DNA repair, is a crucial player in human physiology and disease. Ongoing research into this protein carries the keys to unlock novel diagnostic tools and transformative treatments for a range of conditions, underscoring the indispensable value of frataxin in biomedical applications. As we continue to decode the mysteries of this protein, its potential value in the field of medicine, especially therapeutics, seems limitless.
Case Study
Case 1: Du J, et al. Redox Biol. 2020.
Ferroptosis is a newly discovered form of non-apoptotic regulated cell death and is characterized by iron-dependent and lipid peroxidation. In the present study, researchers demonstrate that the protein Frataxin (FXN) is a key regulator of ferroptosis by modulating iron homeostasis and mitochondrial function. This paper suggests that FXN is a novel ferroptosis modulator, as well as a potential provided target to improve the antitumor activity based on ferroptosis.
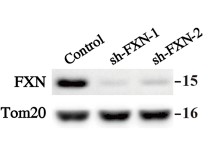
Fig1. Western blot analysis of FXN expression in indicated FXN knockdown and control HT-1080 cells. Tom20 was served as internal loading control.
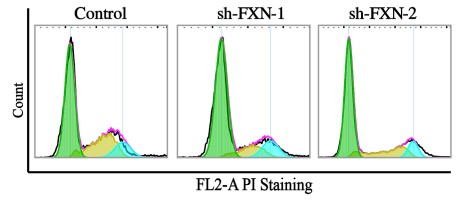
Fig2. Effects of FXN suppression in HT-1080 cells on the proliferation capacity were measured by plate clone formation assay.
Case 2: Agrò M, Díaz-Nido J. Int J Mol Sci. 2020.
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by recessive mutations in the frataxin gene that lead to a deficiency of the mitochondrial frataxin (FXN) protein. The study transduced two human cell lines of patient and healthy subjects with lentiviral vectors overexpressing the mitochondrial or the cytosolic FXN isoforms and studied their effect on the mitochondrial network and metabolism. Accordingly, increases of mitochondrial respiration were detected after transduction with FXN I or FXN II in both cellular models.
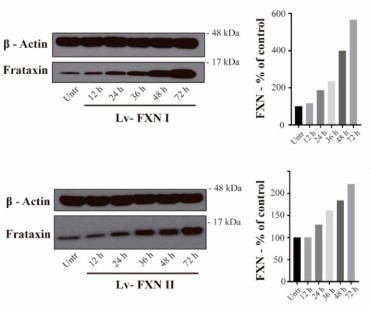
Fig1. Intracellular localization of frataxin isoform I and II in FRDA-derived OE-MSCs. OE-MSCs from FRDA patient transduced for 48 h before cell fractionation with either Lv-FXN I or Lv-FXN II.
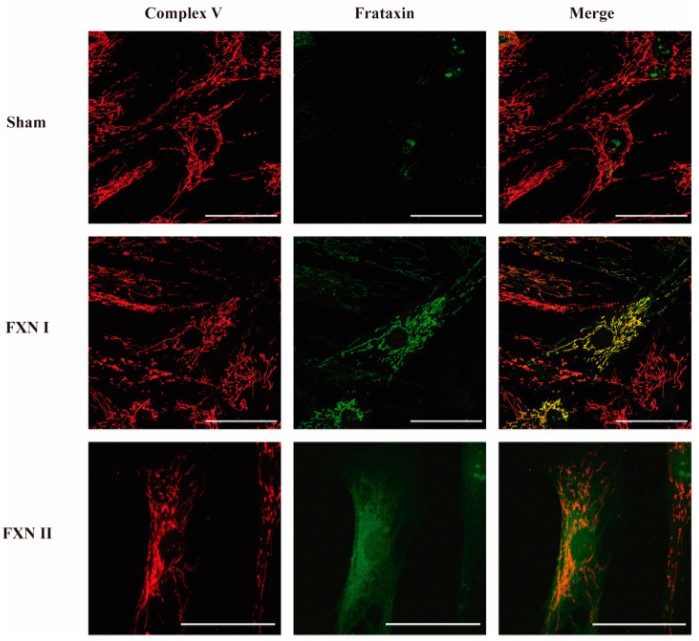
Fig2. Intracellular localization of frataxin isoform I and II in fibroblasts from FRDA patients. Representative confocal photomicrographs showing FRDA-derived fibroblasts either untreated, transduced with Lv-FXN I or Lv-FXN II, and stained with antibodies against Complex V (Red) and frataxin (Green). The merged panels show mitochondrial co-localization between frataxin isoform I and Complex V, and the cytosolic localization of frataxin isoform II.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
FXN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FXN participated on our site, such as Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FXN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism | UGT1A6B,GUSB,BLVRB,HCCSB,COX15,UROD,HMOX1,P22,UGT1AB,UGT1A4 |
Protein Function
FXN has several biochemical functions, for example, 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding,ferric iron binding,ferrous iron binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FXN itself. We selected most functions FXN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FXN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ferroxidase activity | FTH1,HEPHL1,CP,HEPH,FTMT |
| ferrous iron binding | SERPINB1A,HEPH,TH,TRR1,ALKBH3,DNAJC24,ISCA2,FTO,Trf,BCO1 |
| ferric iron binding | FTH1A,TH,FTMT,FTHL17,FTH1B,Trf,ACP5,TF,FTH1,MIOX |
| protein binding | UBE2D3,ANK2,TRPM8,DZIP1,C10orf28,TBKBP1,TAGLN,SLMAP,GSTO1,MSTN |
| 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding | AOX3L1,ISCU,AOX4,CISD1,CISD3,RFESD,GLRX5,UQCRFS1,SDHB,ISCUB |
| iron-sulfur cluster binding | NDUFS1,GLRX3,AOX3L1,REV3L,DPYDB,AIFM4,NFS1,CISD3,AOX4,RSAD1 |
Interacting Protein
FXN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FXN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FXN.
PASK;SDHB;SDHA;ACTN1;PICK1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References