F9
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor IX -
Overview
Factor IX (or Christmas factor) (EC 3.4.21.22) is one of the serine proteases of the coagulation system; it belongs to peptidase family S1. Deficiency of this protein causes hemophilia B. It was discovered in 1952 after a young boy named Stephen Christmas was found to be lacking this exact factor, leading to hemophilia. -
Synonyms
coagulation facto;F9;FIX;P19;PTC;HEMB;MGC129641;MGC129642;coagulation factor IX;FIX F9;factor 9;Christmas factor;OTTHUMP00000024154;plasma thromboplastic component
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Bovine
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Cattle
- Rabbit
- Cynomolgus
- VACV
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human
- Plasma
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mouse Plasma
- Human Plasma
- His
- Fc
- Non
- GST
- KSI
- Avi
Background

Fig1. The waterfall / cascade model of coagulation. (Allison P Wheeler, 2016)
What is F9 Protein?
F9 gene (coagulation factor IX) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome X at locus Xq27. This gene encodes vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor IX that circulates in the blood as an inactive zymogen. This factor is converted to an active form by factor XIa, which excises the activation peptide and thus generates a heavy chain and a light chain held together by one or more disulfide bonds. The role of this activated factor IX in the blood coagulation cascade is to activate factor X to its active form through interactions with Ca+2 ions, membrane phospholipids, and factor VIII. Alterations of this gene, including point mutations, insertions and deletions, cause factor IX deficiency, which is a recessive X-linked disorder, also called hemophilia B or Christmas disease. The F9 protein is consisted of 461 amino acids and F9 molecular weight is approximately 51.8 kDa.
What is the Function of F9 Protein?
The protein encoded by the F9 gene circulates in the blood as an inactive zymogen that can be converted to an active form by the activation of factor XIa. Activated factor IX is able to interact with Ca2+ ions, membrane phospholipids, and factor VIII to convert factor X into its active form, thus participating in the blood clotting process. In addition, the expression of F9 gene is regulated by a variety of factors, including miRNAs, such as hsa-miR-4298, hsa-miR-1302, etc. These miRNAs can target F9 gene and thus affect its expression.
F9 Related Signaling Pathway
In terms of signal transduction, the F9 protein is associated with multiple signaling pathways. For example, abnormal expression of the F9 gene is associated with the Wnt signaling pathway, a pathway that plays an important role in various biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis. Activation of the Wnt signaling pathway can promote cell survival, proliferation, inflammatory response, and immune cell development and function. In particular, the expression of F9 gene, as a downstream target of Wnt signaling pathway, is regulated by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, and the high expression of FGF9 is related to the activation of Wnt signaling pathway. In addition, the F9 protein is involved in the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, a key signaling pathway within cells that plays a critical role in multiple biological processes, including cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, and survival. Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway can promote cell proliferation and survival, and inhibit cell apoptosis.
F9 Related Diseases
The F9 protein has been linked to a range of diseases, most notably Hemophilia B, an inherited blood clotting disorder in which a mutation in the F9 gene results in defective or deficient function of factor IX, affecting normal blood clotting. In addition, abnormal expression of the F9 gene has also been associated with the development of certain cancers, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, and downregulation of F9 gene expression may be associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor prognosis. Other studies have pointed out that F9 protein may play a role in the occurrence and development of ovarian cancer, and its high expression may be related to the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. Therefore, abnormal function or expression of F9 protein is closely associated with blood clotting disorders and the development of certain cancers.
Bioapplications of F9
The practical application of F9 protein is mainly focused on the treatment of hemophilia B, supplementing or repairing defective clotting factor IX through gene therapy or protein replacement therapy to improve patients' clotting ability, reduce bleeding events, and improve quality of life. In addition, the study of F9 protein also involves the development of new therapeutic strategies, such as the use of gene editing technology to repair F9 gene mutations, as well as exploring its potential applications in cancer therapy, such as by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to inhibit tumor growth and invasion associated with high expression of F9 protein.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Paula Carpintero-Fernández, 2022
Even though cancer cells are arrested after CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment, genes regulating senescence in this context are still unknown limiting their antitumour activity. Here, using a functional genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 genetic screen, several genes that participate in the proliferation arrest induced by CDK4/6 inhibitors. Downregulation of the coagulation factor IX (F9) using sgRNA and shRNA prevents the cell cycle arrest and senescent-like phenotype induced in MCF7 breast tumour cells upon Palbociclib treatment. While F9 knockout prevents the induction of senescence, treatment with a recombinant F9 protein was sufficient to induce a cell cycle arrest and senescence-like state in MCF7 tumour cells. Besides, endogenous F9 is upregulated in different human primary cells cultures undergoing senescence. Importantly, bioinformatics analysis of cancer datasets suggest a role for F9 in human tumours.

Fig1. Representative images for BrdU (red) and p21CIP1 (green) in MCF7 treated twice with 10μg/mL of recombinant F9.
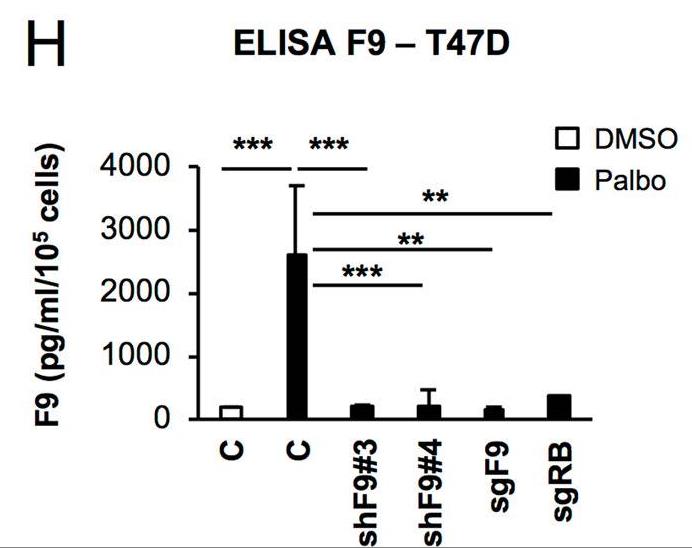
Fig2. ELISA for human F9 released to the conditioned media in T47D cell.
Case Study 2: Mojca Tajnik, 2016
Mutations that result in amino acid changes can affect both pre-mRNA splicing and protein function. Understanding the combined effect is essential for correct diagnosis and for establishing the most appropriate therapeutic strategy at the molecular level. Researchers have identified a series of disease-causing splicing mutations in coagulation factor IX (FIX) exon 5 that are completely recovered by a modified U1snRNP particle, through an SRSF2-dependent enhancement mechanism. Synonymous mutations and missense substitutions associated to a partial FIX secretion defect represent targets for this therapy as the resulting spliced-corrected proteins maintains normal FIX coagulant specific activity. Thus, splicing and protein alterations contribute to define at the molecular level the disease-causing effect of a number of exonic mutations in coagulation FIX exon 5. In addition, our results have a significant impact in the development of splicing-switching therapies in particular for mutations that affect both splicing and protein function where increasing the amount of a correctly spliced protein can circumvent the basic functional defects.
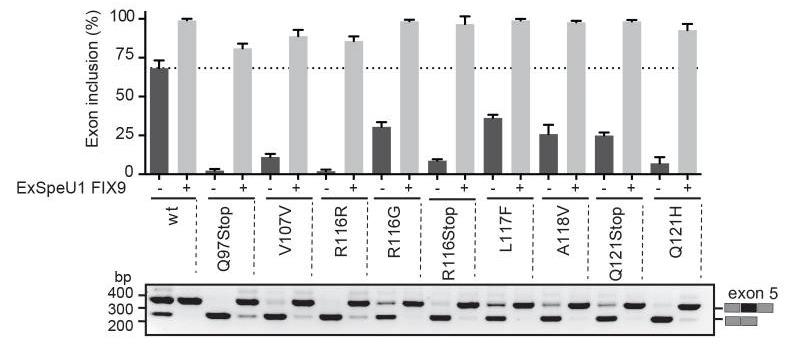
Fig3. Splicing rescue activity mediated by ExSpeU1 FIX9 on exon skipping mutations.
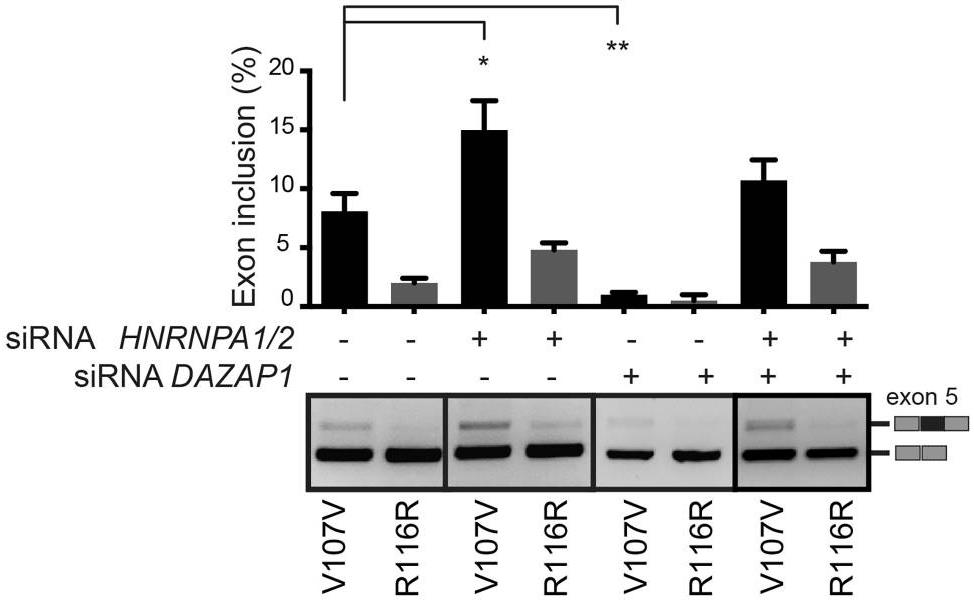
Fig4. FIX exon 5 inclusion levels upon silencing of HNRNPA1/2 and DAZAP1, in V107V and R116R mutated minigenes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F9-3626H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F9-7807H)
Involved Pathway
F9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F9 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | A2M,CFB,CFD,PLG,C5,VWF,MASP2,PLAU,SERPINE1,SERPIND1 |
Protein Function
F9 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,endopeptidase activity,serine-type endopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F9 itself. We selected most functions F9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| endopeptidase activity | MME,PSMA6,KLK1B1,Ren1,TPP2,ECE1,KLK1B8,NCSTN,FURIN,MMP12 |
| calcium ion binding | SWAP70B,CDK5R1,HPCA,LRP2A,CD93,RHOT2,PCDH10B,BNIP2,ANXA1A,DSG2 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | PLAT,KEX2,PRSS30,APEH,CFB,F7I,PRSS57,TMPRSS5,HTRA3A,GZMH |
Interacting Protein
F9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F9.
GAMMAHV.ORF33
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Anderson, DR; Cameron, AC; et al. WASP-20b and WASP-28b: a hot Saturn and a hot Jupiter in near-aligned orbits around solar-type stars. ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS 575:-(2015).
- Almenara, JM; Damiani, C; et al. SOPHIE velocimetry of Kepler transit candidates XV. KOI-614b, KOI-206b, and KOI-680b: a massive warm Jupiter orbiting a G0 metallic dwarf and two highly inflated planets with a distant companion around evolved F-type stars. ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS 575:-(2015).



