ASPA
-
Official Full Name
aspartoacylase -
Overview
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of N-acetyl_L-aspartic acid (NAA) to aspartate and acetate.;NAA is abundant in the brain where hydrolysis by aspartoacylase is thought to help maintain white matter. This protein;is an NAA scavenger in other tissues. Mutations in this gene cause Canavan disease. Alternatively spliced transcript;variants have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
ASPA;aspartoacylase;aspartoacylase (aminoacylase 2, Canavan disease);ACY2;aminoacylase 2;ASP;Canavan disease;ACY 2;ACY-2;ACY2_HUMAN;Aminoacylase-2;Aminoacylase2;Aspartoacylase (Canavan disease);NUR 7;NUR7;OTTMUSP00000006437;RP23-213I10.1;Small lethargic;OTTHUMP00000115814
Recombinant Proteins
- Bacillus subtilis
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.Coli/Yeast
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Insect Cells
- Yeast
- E.coli
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is ASPA Protein?
ASPA protein, or Aspartoacylase, is a key player in our brain chemistry. It helps break down a specific amino acid called NAA, releasing acetate, which our brain uses to make fatty acids. These fatty acids are crucial because they help build myelin, the protective coating around nerve fibers that ensures smooth and fast communication between brain cells. If the ASPA protein doesn’t work properly due to genetic issues, it leads to a severe condition known as Canavan disease. This disease can cause a range of neurological problems because the neurons can't communicate effectively. So, ASPA protein is vital for healthy brain function, playing a big role in keeping our nervous system running smoothly.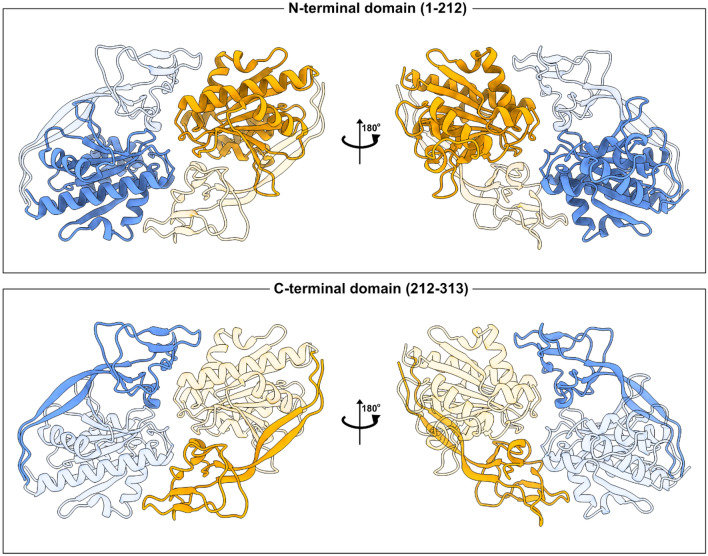
Fig1. The ASPA protein structure. (Martin Grønbæk-Thygesen, 2024)
What is the Function of ASPA Protein?
The ASPA protein, or Aspartoacylase, is vital for brain health. It primarily breaks down N-acetylaspartate (NAA), a compound abundant in the brain, releasing acetate needed to make fatty acids. These fatty acids help form myelin, the protective sheath around nerve fibers, similar to how insulation works for electrical wires. Myelin ensures nerve signals move quickly and smoothly. If ASPA malfunctions, it can disrupt myelin production and lead to neurological issues like Canavan disease. So, ASPA is vital for keeping the nervous system working smoothly by contributing to myelin formation.ASPA Related Signaling Pathway
Let's dive into the ASPA-related signaling pathway. ASPA, or Aspartoacylase, is part of a critical process in the brain that involves breaking down N-acetylaspartate (NAA). This breakdown is crucial because it releases acetate, which then enters various signaling pathways. One key pathway is myelin synthesis, where acetate plays a role in the production of fatty acids necessary for building myelin sheaths. These sheaths insulate nerve fibers, ensuring that nerve signals travel quickly and efficiently. If there's a hiccup in this pathway due to ASPA not doing its job properly, it can lead to problems with myelin production. This disruption might cause nerve signal transmission issues, potentially contributing to neurological disorders like Canavan disease. So, the ASPA signaling pathway is all about maintaining healthy communication between nerve cells by supporting the creation of crucial myelin.ASPA Related Diseases
Problems with the ASPA protein are closely linked to Canavan disease, a rare genetic disorder. This issue occurs when the ASPA enzyme fails to properly break down N-acetylaspartate (NAA) in the brain. As a result, NAA accumulates and there's not enough acetate available, which is crucial for making the fatty acids that form myelin. Myelin acts like insulation for nerve cells, allowing signals to pass smoothly and quickly. Without enough myelin, nerve signals are disrupted, causing the serious neurological symptoms seen in Canavan disease. Babies with this condition might face developmental delays, muscle weakness, and struggle with basic functions. Although this disease is rare and severe, understanding the role of ASPA opens avenues for potential treatments and therapies.Bioapplications of ASPA
ASPA, or Aspartoacylase, has some pretty interesting bioapplications, especially when we look at brain health and genetic research. Scientists are exploring how manipulating ASPA can help in creating therapies for Canavan disease, which is a severe neurological disorder. By understanding ASPA's role in breaking down N-acetylaspartate to produce essential myelin components, researchers are aiming to develop treatments that can address myelin deficiency. Additionally, ASPA's function is being studied to see how it might be used to improve brain metabolism and its protective mechanisms. There's also interest in how ASPA might be applied in neuroprotective strategies, potentially protecting the brain from various types of damage. Overall, ASPA is becoming quite the focus in biomedicine, offering hope for breakthroughs in treating certain brain disorders.Case Study
Case Study 1: Han Y. et al. BMC Cancer. 2023
ASPA is key in cancer metabolism, but its role in gastric cancer (GC) needs clarity. Studies found lower ASPA in GC tissues, affecting prognosis and immune cell presence. Techniques showed altering ASPA levels changes GC cell growth and invasion, highlighting its role in cancer dynamics.-
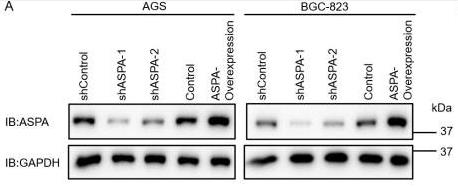 Fig1. Knockdown and overexpression of ASPA using lenti-virus in AGS and BGC-823 cells.
Fig1. Knockdown and overexpression of ASPA using lenti-virus in AGS and BGC-823 cells. -
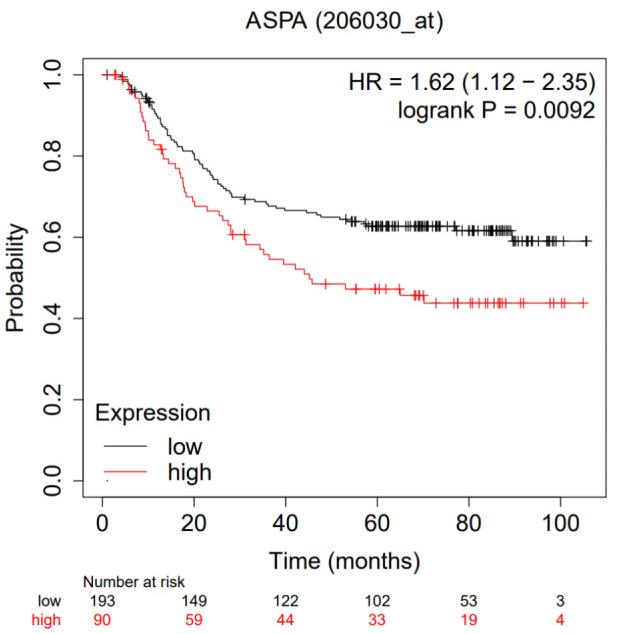 Fig2. Patients with low expressed ASPA had significantly longer overall survival.
Fig2. Patients with low expressed ASPA had significantly longer overall survival.
Case Study 2: Wang Q. et al. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014
Aspartoacylase breaks down a crucial brain amino acid, releasing acetate for fatty acids. Faulty aspartoacylase causes Canavan disease, a serious brain disorder. While studies hinted at a glycan needed for its stability, new research shows human aspartoacylase isn't glycosylated but still works fine, even when made in bacteria. This clears up past confusion about its structure and function.-
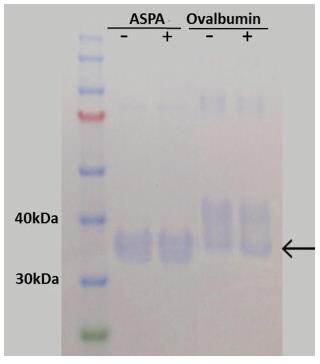 Fig3. SDS–PAGE of PNGase F-treated (+) and untreated (−) aspartoacylase (ASPA).
Fig3. SDS–PAGE of PNGase F-treated (+) and untreated (−) aspartoacylase (ASPA). -
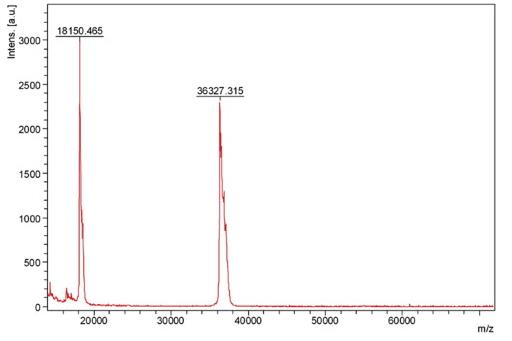 Fig4. MALDI-MS of intact, untreated aspartoacylase showing the +2 and +1 molecular ions at the expected m/z values for the non-glycosylated protein.
Fig4. MALDI-MS of intact, untreated aspartoacylase showing the +2 and +1 molecular ions at the expected m/z values for the non-glycosylated protein.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ASPA-916H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ASPA-916H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ASPA-2438H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ASPA-2438H)
Involved Pathway
ASPA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ASPA participated on our site, such as Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism,Histidine metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ASPA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism | AGXTA,CPS1,GOT2A,ADSSL1,ABAT,AGXTB,GOT2,GLUD1B,GPT2L,DDO |
| Histidine metabolism | HAL,AOC1,ALDH2,ALDH2.1,CNDP2,ALDH3B1,FTCD,CNDP1,ALDH7A1,ALDH3B2 |
| Metabolic pathways | HMGCR,OXSM,TGDS,POLR1B,ALDH7A1,PLCD1B,ATP6V0B,THA1,ALDH1B1,MTMR14 |
-
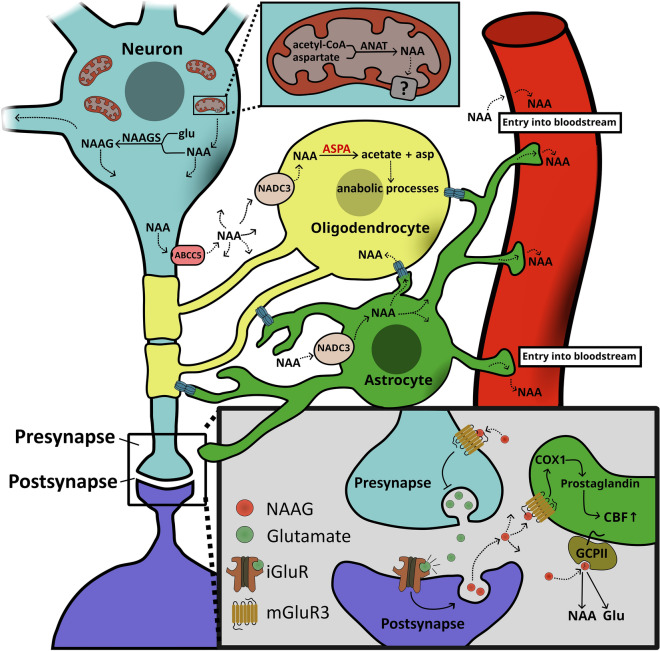 Fig1. Overview of the NAA cycle. (Martin Grønbæk-Thygesen, 2024)
Fig1. Overview of the NAA cycle. (Martin Grønbæk-Thygesen, 2024) -
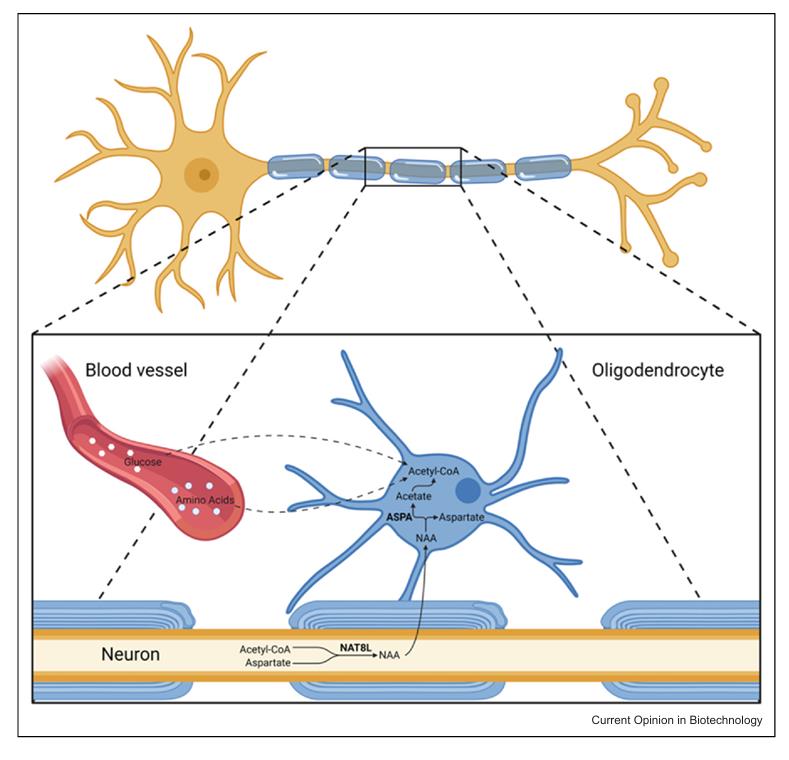 Fig2. Acetyl-aspartate (NAA) metabolism in the vertebrate brain. (Nils Krause, 2024)
Fig2. Acetyl-aspartate (NAA) metabolism in the vertebrate brain. (Nils Krause, 2024)
Protein Function
ASPA has several biochemical functions, for example, aminoacylase activity,aspartoacylase activity,hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ASPA itself. We selected most functions ASPA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ASPA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| aminoacylase activity | CAT,ACY1,DARS,ACY3 |
| hydrolase activity, acting on ester bonds | APMAP,C11orf54,ACY3.1,PGAP3,LIPK,PTER,ENDOU2,IAH1,ESD,LIPM |
| protein binding | ELK3,RUNX1T1,N4BP2L2,MEGF6,BCOR,pab1,IL1RL1,ZNF266,HBD,POLR1B |
| metal ion binding | ATP2B1,ZSCAN4,COL18A1,TRIM35-28,PGCP,B3GNT1,ZNF654,TNNC1,ZNF362A,ALOX5A |
Interacting Protein
ASPA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ASPA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ASPA.
ACY3
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chang, Z; Lu, M; et al. Production of disulfide bond-rich peptides by fusion expression using small transmembrane proteins of Escherichia coli. AMINO ACIDS 47:579-587(2015).
- Abad, FX; Busquets, N; et al. Serological and virological surveys of the influenza A viruses in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic penguins. ANTARCTIC SCIENCE 25:339-344(2013).


