GPNMB
-
Official Full Name
glycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb -
Overview
Transmembrane glycoprotein NMB is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPNMB gene. The mouse and rat orthologues of GPNMB are known as DC-HIL and Osteoactivin (OA), respectively. Two transcript variants encoding 560 and 572 amino acid isoforms have been characterized for this gene in humans. GPNMB is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein which shows homology to the pmel17 precursor, a melanocyte-specific protein. GPNMB has been reported to be expressed in various cell types, including: melanocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts, dendritic cells, and it is overexpressed in various cancer types. In melanocytic cells and osteoclasts the GPNMB gene is transcritionally regulated by Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. In osteoblast progenitor cells, Osteoactivin works as a positive regulator of osteoblast differentiation during later stages of matrix maturation and mineralization that is mediated at least in part by BMP-2 in a SMAD1 dependent manner to promote osteoblast differentiation. In addition, using a rat fracture model, Osteoactivin (OA) enhances the repairing process in bone fracture, demonstrated by its high expression during chondrogenesis (soft callus) and osteogenesis (hard callus) compared to the intact femurs that is why Osteoactivin (OA) could be a novel therapeutic agent used to treat generalized osteoporosis or localized osteopenia during fracture repair by stimulating bone growth and regeneration. Similarly, Osteoactivin expression increases during osteoclast differentiation and it is functionally implicated in this process, possibly by promoting the fusion of osteoclast progenitor cells. -
Synonyms
GPNMB;HGFIN;NMB;glycoprotein (transmembrane) nmb;dendritic cell-associated heparin sulfate proteoglycan-dependent integrin ligand;dendritic cell-associated transmembrane protein;iris pigment dispersion;osteoactivin;transmembrane glycoprotein NMB
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Monkey
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian cells
- NS0
- CHO
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- Human Cell
- Human cells
- HEK293T
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Fc
- C-mIgG2a
- C-Fc&Avi
- Non
- His&Fc
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is GPNMB protein?
GPNMB gene (glycoprotein nmb) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 7 at locus7p15. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein which shows homology to the pMEL17 precursor, a melanocyte-specific protein. GPNMB shows expression in the lowly metastatic human melanoma cell lines and xenografts but does not show expression in the highly metastatic cell lines. GPNMB may be involved in growth delay and reduction of metastatic potential. The GPNMB protein is consisted of 572 amino acids and GPNMB molecular weight is approximately 63.9 kDa.
What is the function of GPNMB protein?
GPNMB is expressed in immune cells such as macrophages and microglia, which are involved in innate immune responses in the peripheral and brain, respectively. GPNMB can interact with a variety of receptors, proteins, and other cell membrane molecules to activate intracellular signaling pathways that lead to changes in the expression of other proteins, thereby affecting cellular responses. GPNMB plays a role in tissue repair and regeneration and may be related to the interaction of extracellular matrix. Under certain conditions, GPNMB may contribute to neuroprotection by activating specific signaling pathways, such as the ERK/MEK and AKT/PI3K pathways. GPNMB may play a role in cell adhesion and migration, influencing the interaction between cells.
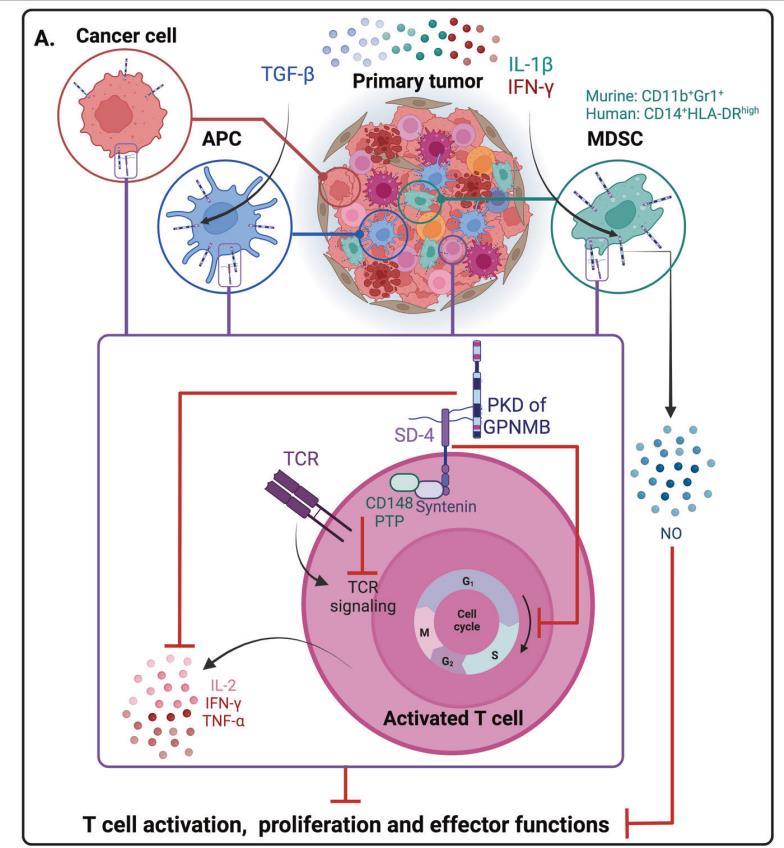
Fig1. Inhibition of T cell responses. (Anna-Maria Lazaratos, 2022)
GPNMB Related Signaling Pathway
GPNMB may play a role in ameliorating neuroinflammation and brain edema by modulating the AMPK/NFκB signaling pathway, which has been investigated in subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) models. In the context of glioblastoma (GBM), GPNMB is produced by macrophages and plays an important role in the cell state transition from PN (proneural) to MES (mesenchymal) through the interaction between immune cells and tumor cells. GPNMB expression is associated with the development and metastasis of various tumors, and may participate in the malignant progression of tumors by regulating the proliferation, invasion and drug resistance of tumor cells.
GPNMB Related Diseases
GPNMB protein has been implicated in a variety of diseases, especially in pathological conditions such as tumors, neurodegenerative diseases, obesity, and inflammation. In terms of tumors, GPNMB is overexpressed in a variety of solid tumors and is associated with tumor cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis, such as in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), where high GPNMB expression is associated with disease severity. In neurodegenerative diseases, GPNMB may be involved in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD), and its plasma level can be used as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease. In addition, GPNMB plays a role in obesity and its related diseases, with studies finding that it is increased in adipose tissue of obese individuals and may contribute to obesity development by promoting lipid synthesis and exacerbating insulin resistance. GPNMB is also emerging as a novel marker in inflammatory diseases, where its levels rise under pro-inflammatory conditions, such as LPS treatment.
Bioapplications of GPNMB
In the field of GPNMB cancer, GPNMB is a target for immunotherapy, and its specific antibody drug conjugate (ADC) such as glembatumumab vedotin (Glemba) is being developed for the treatment of GPNMB overexpressed triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In addition, GPNMB expression levels are elevated in Parkinson's disease (PD) and may serve as a biomarker and therapeutic target for early diagnosis. In obesity and its related diseases, GPNMB is a potential therapeutic target by affecting lipid synthesis and energy expenditure in adipose tissue, and antibody neutralization of GPNMB may help improve obesity and diabetes. GPNMB is also emerging as a novel biomarker in inflammatory diseases, and its expression levels increase under pro-inflammatory conditions, which may help in the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Erin Gibbons, 2024
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, progressive cystic lung disease affecting almost exclusively female-sexed individuals. The cysts represent regions of lung destruction caused by smooth muscle tumors containing mutations in one of the two tuberous sclerosis (TSC) genes. mTORC1 inhibition slows but does not stop LAM advancement. Furthermore, monitoring disease progression is hindered by insufficient biomarkers. Therefore, new treatment options and biomarkers are needed. LAM cells express melanocytic markers, including glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma protein B (GPNMB). The function of GPNMB in LAM is currently unknown; however, GPNMB's unique cell surface expression on tumor versus benign cells makes GPNMB a potential therapeutic target, and persistent release of its extracellular ectodomain suggests potential as a serum biomarker. Here, researchers establish that GPNMB expression is dependent on mTORC1 signaling, and that GPNMB regulates TSC2-null tumor cell invasion in vitro.
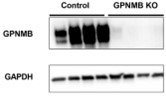
Fig1. Western blot analysis of protein from tumors.
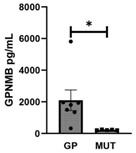
Fig2. GPNMB ELISA for GPNMB ectodomain levels in serum.
Case Study 2: Fatih Yalcin, 2024
Tumor-associated microglia and blood-derived macrophages (TAMs) play a central role in modulating the immune suppressive microenvironment in glioma. Here, researchers show that GPNMB is predominantly expressed by TAMs in human glioblastoma multiforme and the murine RCAS-PDGFb high grade glioma model. Loss of GPNMB in the in vivo tumor microenvironment results in significantly smaller tumor volumes and generates a pro-inflammatory innate and adaptive immune cell microenvironment. The impact of host-derived GPNMB on tumor growth was confirmed in two distinct murine glioma cell lines in organotypic brain slices from GPNMB-KO and control mice. Using published data bases of human glioma, the elevated levels in TAMs could be confirmed and the GPNMB expression correlated with a poorer survival.
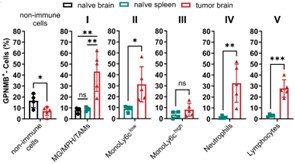
Fig3. Quantification of GPNMB expression in non-immune cells.

Fig4. Western Blot of total GPNMB protein.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GPNMB-3783H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GPNMB-5162H)
Involved Pathway
GPNMB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GPNMB participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GPNMB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
GPNMB has several biochemical functions, for example, heparin binding,integrin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GPNMB itself. We selected most functions GPNMB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GPNMB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| integrin binding | ADAM17,LAMA5,TIMP2,ADAM2,MMP14,EMP2,ITGA5,CD151,PXN,NIPAL1 |
| heparin binding | WISP3,RSPO4,LIPI,CTGFB,ADAMTS1,BMP7,FBLN7,FMODA,KAL1,CCL7 |
Interacting Protein
GPNMB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GPNMB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GPNMB.
SMAD4
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Torres, C; Linares, A; et al. The Potential Role of the Glycoprotein Osteoactivin/Glycoprotein Nonmetastatic Melanoma Protein B in Pancreatic Cancer. PANCREAS 44:302-310(2015).


