FN1
-
Official Full Name
fibronectin 1 -
Overview
Fibronectin (FN) is a major component of the extracellular matrix and blood plasma, and is a specific ligand for several integrin adhesion receptors. Fibronectin plays an important role not only in cell adhesion and wound healing but also in embryogenesis and hematopoiesis. Fibronectin is over-expressed in cardiovascular disease states such as atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction. Reduced levels of Fibronectin have been reported in patients with Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) and low concentrations appear to correlate with a poor prognosis. -
Synonyms
Fn1;fibronectin 1;fn-1;FIBNEC;fibronectin;FN
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Bovine
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Pig
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Rat Plasma
- C-His
- Bovine Plasma
- Mammalian Cell
- Human Cell
- CHO-K1
- Human blood/plasma
- Oryza Sativa
- Human plasma
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mouse Plasma
- Human Foreskin Fibroblasts
- HEK293F
- His
- GST
- Non
- His&T7
- His&Fc&Avi
- N-His&C-Myc
- His&Avi
Background
What is FN1 Protein?
FN1 gene (fibronectin 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q35. This gene encodes fibronectin, a glycoprotein present in a soluble dimeric form in plasma, and in a dimeric or multimeric form at the cell surface and in extracellular matrix. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protein. Fibronectin is involved in cell adhesion and migration processes including embryogenesis, wound healing, blood coagulation, host defense, and metastasis. The FN1 protein is consisted of 2477 amino acids and FN1 molecular weight is approximately 272.3 kDa.
What is the Function of FN1 Protein?
FN1 protein is a multifunctional glycoprotein that plays a key role in the extracellular matrix. It is involved in a variety of biological processes, including cell adhesion, cell migration, tissue repair, embryonic development, blood clotting, and tumor progression. FN1 binds to a variety of components on the cell surface and in the extracellular matrix, such as collagen, fibrin, heparin, DNA, and actin. FN1 exists as a soluble dimer in plasma and is synthesized by liver cells. On the cell surface and in the extracellular matrix, it exists as dimers or polymers and is produced by resident cells including connective tissue, bone and periodontal tissue.
FN1 Related Signaling Pathway
FN1 promotes chondrocyte differentiation and collagen production in fracture healing by activating the TGF-β/ PI3K/Akt pathway. Studies have shown that upregulation of FN1 can improve TGF-β, c-Caspase-9 / t-Caspase-9 ratio and NF-κBp65 protein expression, and reduce p-PI3K/PI3K and p-AKT/AKT ratios. Thus, the TGF-β/ PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is positively regulated. FN1 promotes proliferation and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Specifically, high expression of FN1 is associated with tumor diameter and lymph node metastasis in thyroid cancer patients, and FN1 promotes expression levels of proteins associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway and activates the NF-κB signaling pathway.
FN1 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of FN1 protein is associated with a variety of diseases, especially closely related to tumor development, including breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and thyroid cancer, and plays a key role in the proliferation, migration, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. In addition, FN1 also plays a role in tissue repair, wound healing, fibrosis, and certain autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Abnormalities in FN1 are also associated with certain genetic disorders, such as fibronectin glomerulopathy caused by mutations in the FN1 gene, leading to progressive kidney disease. Therefore, the regulation of FN1 expression under pathological conditions has an important impact on disease progression and treatment response.

Fig1. Schematic diagram for the regulatory mechanism of tumor-suppressing action of Lrp5-overexpressing osteoblasts. (Xun Sun, 2022)
Bioapplications of FN1
FN1 protein has become an important target for biomedical research and clinical applications due to its central role in cell adhesion, migration and tissue repair. Currently, FN1 related applications are focused on the development of therapeutic strategies targeting FN1, including antibodies, small molecule drugs, and extracellular matrix mimics for promoting wound healing, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine. In addition, FN1 is also used as a biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis assessment, especially in epithelial cancers, where changes in its expression level can reflect tumor aggressiveness and patient response to treatment. In cell culture and biomaterial design, FN1 is also used as a key component to improve cell-scaffold material interactions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chen Chen, 2023
It is known that Fibronectin 1 (FN1) drives the occurrence and development of a variety of cancers through metabolic reprogramming. Aspartic acid is considered to be an important substrate for nucleotide synthesis. However, the regulatory mechanism between FN1 and aspartate metabolism is currently unclear. MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were used to explore the effects of FN1-regulated aspartic acid metabolism on cell survival, invasion, migration and tumor growth. Researchers used PCR, Western blot, immunocytochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques to study it. In vivo and in vitro experiments showed that silencing FN1 inhibits the activation of the YAP1/Hippo pathway by enhancing YAP1 phosphorylation, down-regulates SLC1A3-mediated aspartate uptake and utilization by tumor cells, inhibits BC cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes apoptosis. In addition, inhibition of FN1 combined with the YAP1 inhibitor or SLC1A3 inhibitor can effectively inhibit tumor growth, of which inhibition of FN1 combined with the YAP1 inhibitor is more effective.

Fig1. Correlation between FN1 and SLC1A3 were determined by IHC.
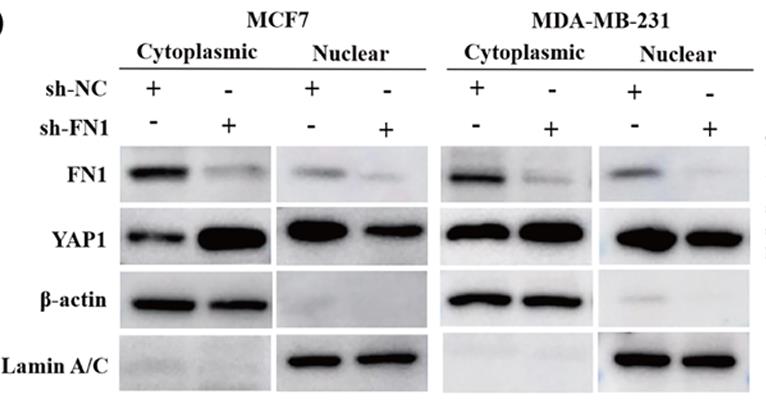
Fig2. The nucleocytoplasmic separation experiment measured the expression of FN1 and YAP1 in the cytoplasm and nucleus.
Case Study 2: Chengliang Yang, 2020
Osteoporosis (OP) is a systemic skeletal disease leading to fragility fractures and is a major health issue globally. WNT/β-catenin signaling regulates bone-remodeling processes and plays vital roles in OP development. However, the underlying regulatory mechanisms behind WNT/β-catenin signaling in OP requires clarification, as further studies are required to identify novel alternate therapeutic agents to improve OP. In this study, fibronectin 1 (FN-1) promoted differentiation and mineralization of osteoblasts by activating WNT/β-catenin pathway, in cultured pre-osteoblasts. FN-1 accumulated in osteoblasts in bone samples from OP patients and age-related OP mice compared to control group. In addition, integrin β1 (ITGB1) acts as an indispensable signaling molecule for the interplay between FN-1 and β-catenin, and that FN-1 expression increased, but ITGB1 expression decreased in osteoblasts during OP progression.
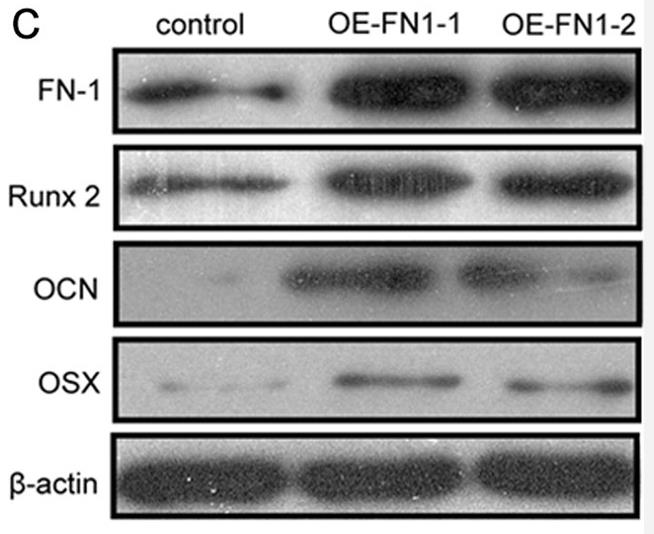
Fig3. WB of MC3T3-E1 cells were transfected with controls or two FN-1 encoding plasmids.

Fig4. ITGB1 is essential for FN-1 in promoting osteogenesis via β-catenin signaling.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FN1-10H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FN1-649H)
Involved Pathway
FN1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FN1 participated on our site, such as PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Focal adhesion,ECM-receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FN1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | MAP2K1,TP53,ITGAV,ERBB4,HSPG2,PTPN6,ANK2,RPS6,SRC,ARHGEF1 |
| Amoebiasis | COL4A1,CD14,C8A,SERPINB6,LAMB2,RAB5C,ACTN3,ITGB2,LAMC2,PRKCA |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | ITGAL,PIK3R5,ITGB1A,DIAPH1,FGF12A,ARPC5A,MYLPFA,GNG12,LIMK1,ITGB7 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | DNM3,DNM2,SHC4,ARPC5,WASL,PIK3CD,DOCK1,CTNNA1,CRK,PTK2 |
| Focal adhesion | PAK7,MAPK3,FYNB,COL5A2,THBS3A,ROCK2,ROCK2A,GSK3AA,MYL12.1,RAPGEF1 |
| Pathways in cancer | CBLB,FH,BID,PTK2,FLT3LG,ITGAV,AHA-1,FZD6,GNAQ,PIK3R1 |
| Small cell lung cancer | CCNE1,LAMB3,RXRB,LAMA5,PIK3R2,LAMC2,PIK3CB,APAF1,SKP2,NFKB1 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | NR4A1,PKN3,CREB5,MAP2K1,MAPK1,NGFR,CRTC2,IFNA7,RAC1,PDGFB |
| ECM-receptor interaction | THBS3,Npnt,ITGB6,COL6A5,COMP,VTNB,ITGB1A,LAMC1,GP6,ITGA2 |
Protein Function
FN1 has several biochemical functions, for example, collagen binding,heparin binding,integrin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FN1 itself. We selected most functions FN1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FN1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| collagen binding | TGFBI,ASPN,GP6,LRRC15,PCOLCE2,CCBE1,ACHE,C1QTNF1,ITGA10,GPR56 |
| protein binding | WBP1L,TRIM27,PARP1,FSD2,DERL2,RAMP3,KLK13,TFIP11,APC2,TBC1D2 |
| heparin binding | RSPO3,NAV2,THBS1,APLP1,LTBP2,CCL2,NDNF,TGFBR3,COL13A1,AZU1 |
| integrin binding | TSPAN8,WISP1A,COL16A1,CYR61L1,S1PR2,LYN,ADAMTS13,ESM1,SEMA7A,LAMA5 |
| protease binding | SERPINA1E,SERPINB13,FLOT2,SERPINF2,CRADD,SERPINA1A,CFLAR,INS2,CSTA,TIMP2 |
| peptidase activator activity | FBLN1,PSME4,MMP14,PCOLCE,PCOLCE2,PSME4B,CAV1,PINK1,APP,CLPX |
Interacting Protein
FN1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FN1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FN1.
fnbB;heparin
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Xie, BX; Chen, DX; et al. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human liver FN1 proteins. JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 28:788-788(2013).
- Liszka, L; et al. DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE PANCREAS USUALLY RETAINED SMAD4 AND p53 PROTEIN STATUS AS WELL AS EXPRESSION OF EPITHELIAL-TO-MESENCHYMAL TRANSITION MARKERS AND CELL CYCLE REGULATORS AT THE STAGE OF LIVER METASTASIS. POLISH JOURNAL OF PATHOLOGY 65:100-112(2014).



