Recombinant Human RNF43 protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | RNF43-2858H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human RNF43 protein(), fused to His tag, was expressed in E. coli. |
| Availability | April 20, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Form : | The purified protein was Lyophilized from sterile PBS (58mM Na2HPO4,17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH7.4). 5 % trehalose and 5 % mannitol are added as protectant before lyophilization. The elution buffer contain 300mM imidazole. |
| AA Sequence : | GRTGLVLAAAVESERSAEQKAIIRVIPLKMDPTGKLNLTLEGVFAGVAEITPAEGKLMQSHPLYLCNASDDDNLEPGFISIVKLESPRRAPRPCLSLASKARMAGERGASAVLFDITEDRAAAEQLQQPLGLTWPVVLIWGNDAEKLMEFVYKNQKAHVRIELKEPPAWPDY |
| Purity : | 95%, by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. |
| Storage : | Short-term storage: Store at 2-8°C for (1-2 weeks). Long-term storage: Aliquot and store at -20°C to -80°C for up to 3 months, buffer containing 50% glycerol is recommended for reconstitution. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | Reconstitute at 0.25 µg/μl in 200 μl sterile water for short-term storage. Reconstitution with 200 μl 50% glycerol solution is recommended for longer term storage. |
| Gene Name | RNF43 ring finger protein 43 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | RNF43 |
| Synonyms | URCC; RNF124 |
| Gene ID | 54894 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_017763.4 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_060233.3 |
| MIM | 612482 |
| UniProt ID | Q68DV7 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| RNF43-1145H | Recombinant Human RNF43 | +Inquiry |
| RNF43-0655H | Active Recombinant Human RNF43 protein, Fc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| RNF43-3995H | Recombinant Human RNF43 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| RNF43-768H | Recombinant Human RNF43 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| RNF43-2858H | Recombinant Human RNF43 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Hsu SH, et al. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024
RNF43, a RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase crucial for WNT signaling regulation, is mutated in 6-10% of pancreatic cancers. Despite its importance, the downstream effects of RNF43 are not fully understood due to a limited number of known in vivo substrates. This study reveals that pancreatic cancer cells with RNF43 mutations show increased B-RAF/MEK signaling and are particularly responsive to MEK inhibitors. Depletion of RNF43 in normal pancreatic cells increases MEK activity, indicating a regulatory role for RNF43. We demonstrate that RNF43 targets B-RAF for ubiquitination at K499, leading to proteasomal degradation and reduced MEK activity in cancer cells. Conversely, B-RAF phosphorylation at T491 inhibits its ubiquitination by RNF43. B-RAF mutations at K499 are prevalent in multiple cancers. Combined treatment with MEK and WNT inhibitors effectively inhibits the growth of RNF43-mutated pancreatic cancer cells, both in vitro and in vivo.
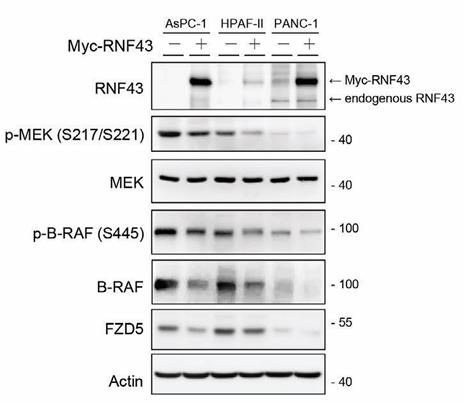
Fig1. The ectopic expression of RNF43 on expression and activation of B-RAF/MEK signaling molecules.
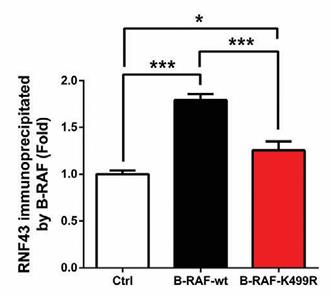
Fig2. Quantification of RNF43 levels immunoprecipitated with B-RAF antibody.
Case 2: Zhu D, et al. Oncol Res. 2022
This study examined the role of RNF43 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), using patient cohorts and various analyses. RNF43 was typically downregulated in ccRCC and associated with poorer prognosis. Overexpressing RNF43 limited ccRCC cell growth and migration, and reduced drug resistance, whereas RNF43 knockdown did the opposite. Mechanistically, RNF43 influenced YAP signaling, affecting YAP phosphorylation and nuclear presence. Restoring RNF43 also sensitized ccRCC to pazopanib. Combining RNF43 and YAP expression with clinical scores improved postoperative prognosis prediction in ccRCC patients.
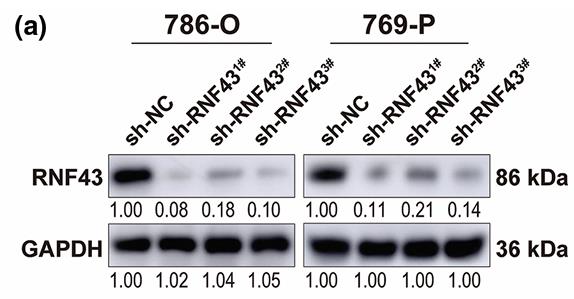
Fig1. Western blot assays were performed to examine the expression of RNF43 in 786-O or 769-P cells with or without RNF43 knockdown.
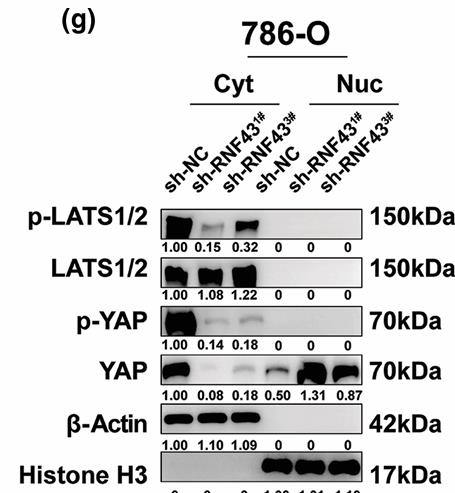
Fig2. Western blot analysis of p-LATS1/2, LATS1/2, p-YAP, and YAP in cytoplasmic (Cyt) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions of 786-O cells without or with RNF43 knockdown.
Recombinant Human RNF43 protein, also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF43 or RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase RNF43, is a protein that plays a crucial role in the negative regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway. This pathway is involved in various cellular processes including cell fate determination, tissue homeostasis, and has been implicated in cancer development. RNF43 functions by mediating the ubiquitination, endocytosis, and subsequent degradation of Wnt receptor complex components, particularly the Frizzled receptors, thus acting as a tumor suppressor.
In the context of cancer research, RNF43 has been found to be mutated in various types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer. The loss of function of RNF43 can lead to increased Wnt signaling, which may promote tumor growth and progression. The study of recombinant RNF43 protein can help researchers understand the mechanisms by which it regulates Wnt signaling and how its dysfunction contributes to cancer development.
The recombinant protein is produced in a controlled laboratory setting, often using expression systems such as HEK 293 cells or E. coli, and is purified for use in various experimental applications. It can be utilized in functional studies, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), and other biochemical and cell-based assays to investigate its role in cellular processes and its potential as a therapeutic target.
In the clinical setting, understanding the role of RNF43 and its mutations can inform the development of personalized medicine strategies. For instance, certain mutations in RNF43 have been found to predict response to specific anti-cancer therapies, such as anti-BRAF/EGFR combinatory therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. This suggests that testing for RNF43 mutations could help guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
In summary, recombinant Human RNF43 protein is a valuable tool for research into the molecular mechanisms of Wnt signaling and cancer development, and may have implications for the development of targeted therapies and predictive biomarkers in cancer treatment.
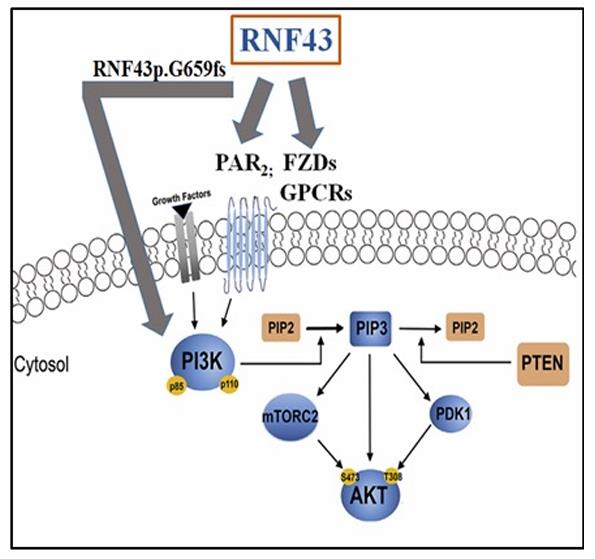
Fig1. Targets of RNF43. (Jeetendra Kumar Nag, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All RNF43 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All RNF43 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


