Recombinant Human HEY2 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged
| Cat.No. : | HEY2-279H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human HEY2 fused with MYC/DDK tag at C-terminal was expressed in HEK293. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | DDK&Myc |
| Description : | This gene encodes a member of the hairy and enhancer of split-related (HESR) family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type transcription factors. The encoded protein forms homo- or hetero-dimers that localize to the nucleus and interact with a histone deacetylase complex to repress transcription. Expression of this gene is induced by the Notch signal transduction pathway. Two similar and redundant genes in mouse are required for embryonic cardiovascular development, and are also implicated in neurogenesis and somitogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found, but their biological validity has not been determined. |
| Form : | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol. |
| Molecular Mass : | 35.6 kDa |
| Purity : | > 80% as determined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining |
| Concentration : | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Gene Name | HEY2 hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 2 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | HEY2 |
| Synonyms | HEY2; hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 2; hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 2; bHLHb32; HERP1; HRT-2; hCHF1; hHRT2; HESR-2; protein gridlock homolog; HES-related repressor protein 1; HES-related repressor protein 2; hairy-related transcription factor 2; cardiovascular helix-loop-helix factor 1; class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 32; hairy and enhancer of split-related protein 2; cardiovascular basic helix-loop-helix factor 1; GRL; CHF1; HRT2; HESR2; GRIDLOCK; MGC10720; |
| Gene ID | 23493 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_012259 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_036391 |
| MIM | 604674 |
| UniProt ID | Q9UBP5 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| HEY2-2073R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey HEY2 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| HEY2-1894R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque HEY2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| HEY2-279H | Recombinant Human HEY2 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| HEY2-3529HF | Recombinant Full Length Human HEY2 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| HEY2-9160Z | Recombinant Zebrafish HEY2 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| HEY2-5574HCL | Recombinant Human HEY2 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Li H, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019
Researchers hereby formally report the differential plasticity of human skin fibroblasts and lung fibroblasts in the process of transdifferentiation into induced neurons. By sequencing the RNA of homologous and non-homologous human skin and lung fibroblasts for different days during their transformation into neurons, they found that several major regulators in the fibroblast gene regulatory network (TWIST1, TWIST2, PRRX1, and PRRX2) were significantly down-regulated in lung fibroblasts but not in skin fibroblasts. By knocking down these genes, as well as other genes that inhibit neural fate, such as REST, HES1, and HEY2, they found that simultaneously weakening HEY2 and PRRX2 significantly enhanced the transdifferentiation of human skin fibroblasts induced by ASCL1 and p53 shRNA. This new approach, by overexpressing ASCL1 and knocking down p53, HEY2, and PRRX2 (ApH2P2), was able to efficiently transdifferentiate adult skin fibroblasts into MAP2-positive neurons within 14 days. This will be beneficial for a variety of applications that require rapid and efficient acquisition of patient-specific neurons from skin fibroblasts.
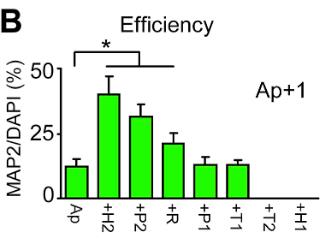
Fig1. Reprogramming efficiency.
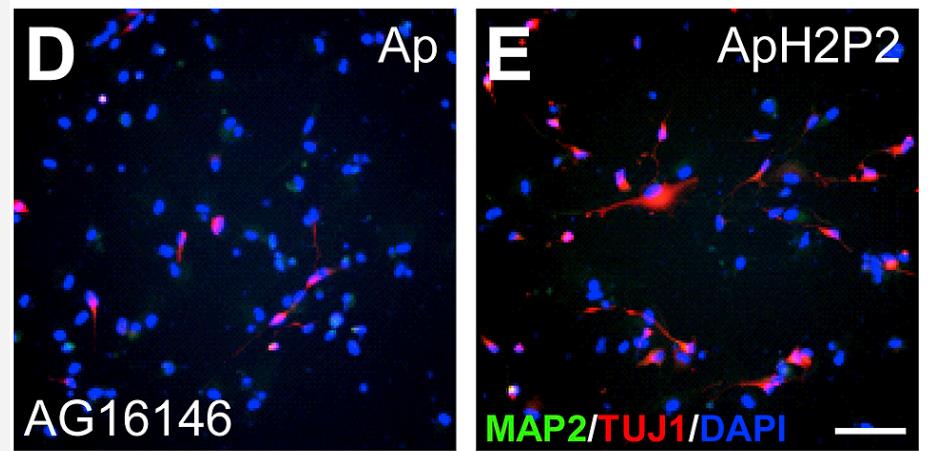
Fig2. GM00731 adult human skin fibroblasts were reprogrammed with ApH2P2.
Case 2: Anderson DJ, et al. Nat Commun. 2018
Congenital heart defects can be caused by mutations in genes that guide the formation of heart lineages. Here, researchers show that deletion of NKX2-5, a key component of the cardiac gene regulatory network, in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) results in impaired cardiomyogenesis, failure to activate VCAM1, and reduced expression of the precursor marker PDGFRα. In addition, NKX2-5 deficient cardiomyocytes had abnormal physiological features, including out-of-sync contractions and altered action potentials. Molecular analysis and genetic rescue experiments showed that HEY2, the basic helix-loop-helix protein, is the key mediator for NKX2-5 to play a role in human cardiogenesis. These findings confirm HEY2 as a novel component of the NKX2-5 cardiac transcription network and provide conclusive evidence that the hESC model is capable of interpreting the complex pathways that regulate early development of the human heart.
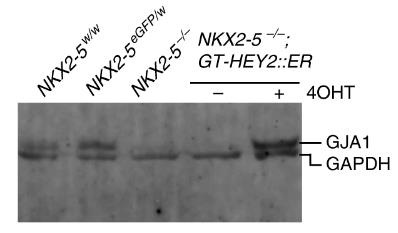
Fig1. Western blot showing restoration of GJA1 (connexin 43) levels.
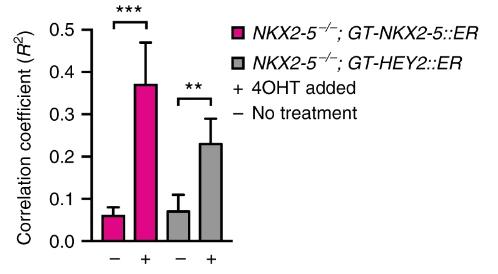
Fig2. Correlation coefficient between contractile areas improves when both NKX2-5 and HEY2 are induced.
The HEY2 protein is a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) type transcription factor and a member of the Hair Enhancement Division Associated (HESR) family. This protein can form a homologous or heterodimer, localize to the nucleus, and interact with the histone deacetylase complex to inhibit transcription. The expression of HEY2 gene is induced by Notch signaling pathway.
Recombinant HEY2 protein plays an important role in basic science research. For example, it is being used to explore its specific role in heart development, angiogenesis, and cell fate determination.
Recombinant HEY2 protein and its Matched Antibody Pair can be used in a variety of immunoassay platforms, such as sandwich ELISA and multi-bead array analysis. These applications help improve the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tools to better serve the early detection and research of diseases such as cardiovascular disease and developmental abnormalities.
Because of HEY2's role in heart development and disease, recombinant human HEY2 protein could be used for drug screening, especially when developing drugs that may affect heart function.
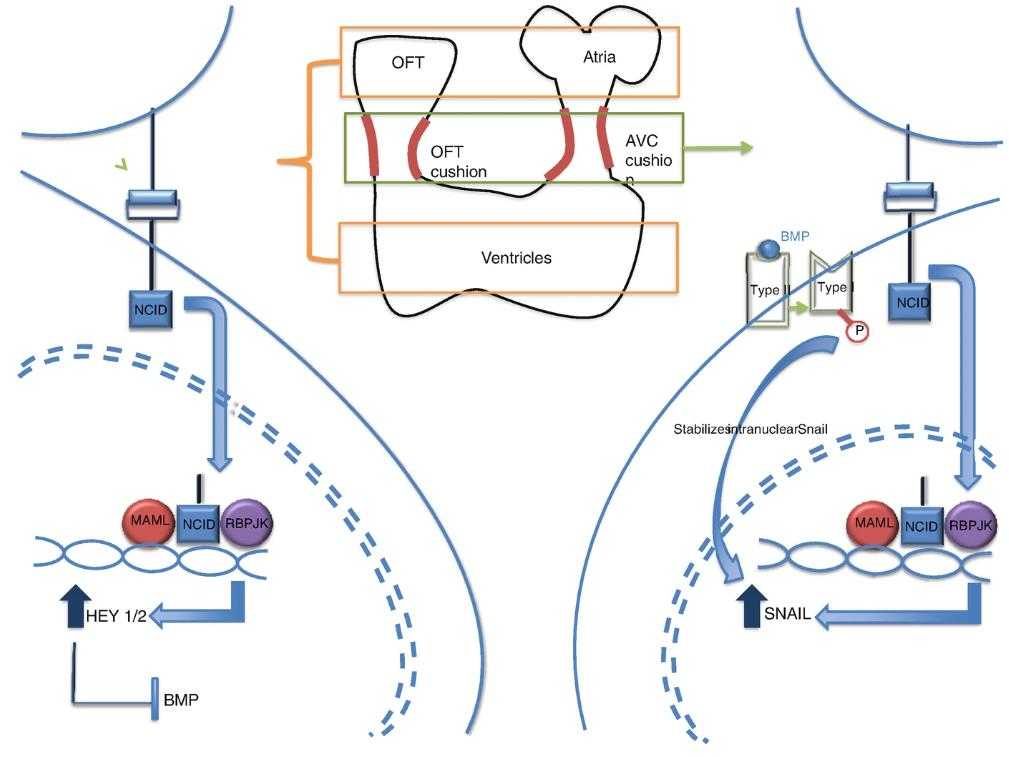
Fig1. The Notch-Hey2 Pathway. (Kamel Shibbani, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All HEY2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All HEY2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


