Recombinant Human CD82 protein(Gly111-Leu228), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CD82-3969H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CD82 (P27701-1) (Gly 111-Leu 228) was expressed in HEK293, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus and a signal peptide at the N-terminus. |
| Availability | April 18, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 111-228 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The secreted recombinant human CD82 consists of 129 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 15 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 25-33 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CD82 CD82 antigen (R2 leukocyte antigen, antigen detected by monoclonal [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CD82 |
| Synonyms | CD82; CD82 antigen (R2 leukocyte antigen, antigen detected; CD82 antigen (R2 leukocyte antigen, antigen detected by monoclonal; SAR2; |
| Gene ID | 8052 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CD82-3970H | Recombinant Human CD82(Gly103-Gln225) Protein, N-Fc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD82-3969H | Recombinant Human CD82 protein(Gly111-Leu228), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD82-127H | Recombinant Human CD82 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD82-67HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CD82 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CD82-3111M | Recombinant Mouse CD82 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CD82-1960HCL | Recombinant Human CD82 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Ordas L, et al. Cells. 2021
The plasma membrane plays a big role in cell movement, affecting migration and caveolae integrity. Proteins like caveolin-1 trigger processes that involve actin and focal adhesions, influencing cell movement through YAP. CD82, or KAI-1, is a membrane protein known to suppress metastasis and is often missing in cancers like breast cancer. It significantly inhibits cell migration, though the exact method was unclear. Here CD82 affects cell movement by regulating stress fibers, focal adhesions, membrane tension, caveolae levels, and YAP's movement to the nucleus, all in a caveolin-1-dependent way. This means CD82 controls 2D cell migration through membrane mechanics involving caveolin and the YAP pathway.
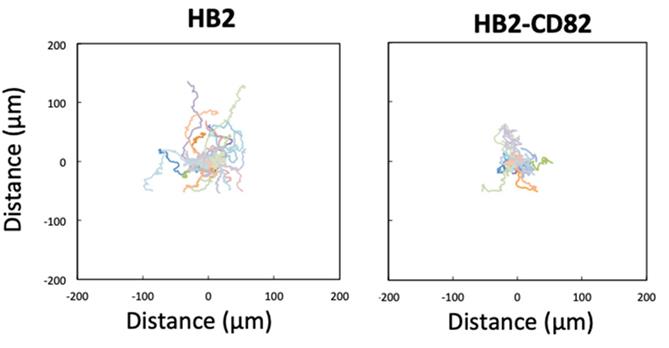
Fig1. Trajectories of the 10 EGF-stimulated single HB2 or HB2-CD82 cells.
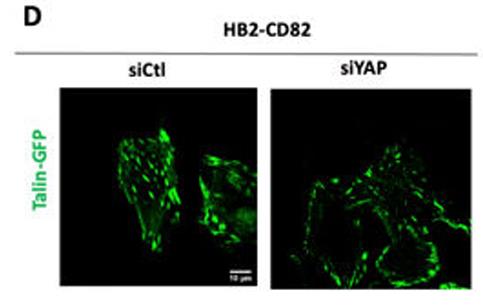
Fig2. Talin-GFP labelling in HB2-CD82 cells transfected with Si Ctl or Si YAP.
Case 2: Watanabe A, et al. Sci Rep. 2021
Creating pancreatic β cells from pluripotent stem cells is essential for treating insulin-dependent diabetes, but the process is complicated and can be unstable due to many differentiation steps. It’s important to remove undifferentiated cells to prevent tumor risks. We identified CD82, part of the tetraspanin family, as helpful for isolating β cell precursors from late-stage pancreatic progenitor cells, leading to more efficient differentiation into endocrine cells. CD82+ cells secreted insulin better than CD82- cells, and reducing CD82 hindered β cell function, highlighting its role in maturing these progenitor cells into insulin-producing β cells.
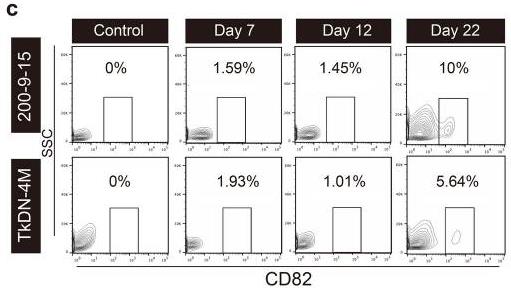
Fig1. Flow cytometric analysis of CD82-expressing cells in day 7, day 12, and day 22 cells.
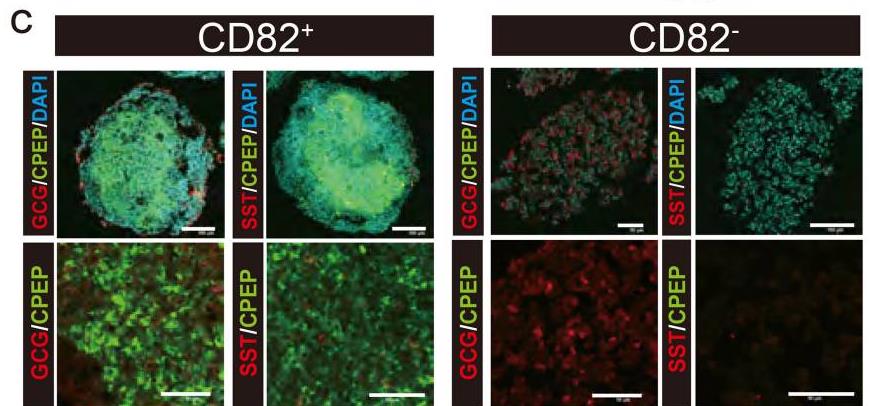
Fig2. Immunofluorescence staining of the clusters derived from CD82− and CD82+ cells.
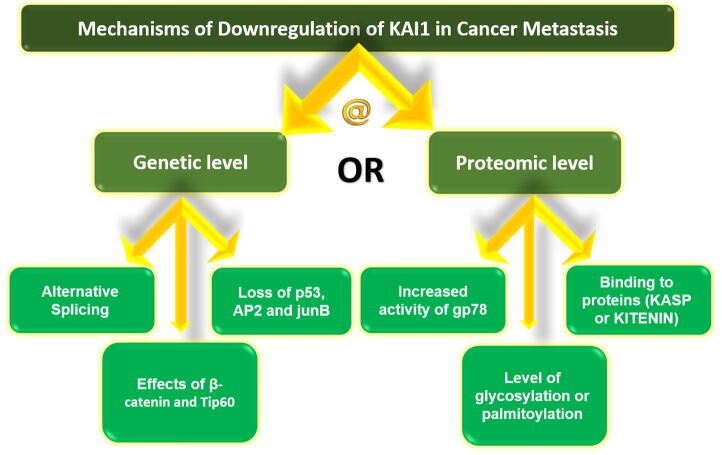
Fig1. Summary of the main mechanisms of KAI1 downregulation in metastasis. (Khulood M Al-Khater, 2021)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CD82 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CD82 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


