Recombinant Human CAMK1D protein(Met1-Lys385), GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CAMK1D-780H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CAMK1D (NP_705718.1) (Met 1-Lys 385) was expressed in Insect Cells, fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Availability | April 21, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | 1-385 a.a. |
| Form : | Supplied as sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM Reduced Glutathione, pH 8.0. |
| Bio-activity : | The specific activity was determined to be 70 nmol/min/mg using Autocamtide-2 synthetic peptide (KKALRRQETVDAL-amide) as substrate. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CAMK1D/GST chimera consists of 610 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 69 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 60 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CAMK1D calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CAMK1D |
| Synonyms | CAMK1D; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase ID; calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1D; CKLiK; caMKI delta; caM-KI delta; CaM kinase ID; caM kinase I delta; CamKI-like protein kinase; CaM-K1; CaMKID; |
| Gene ID | 57118 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_020397 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_065130 |
| MIM | 607957 |
| UniProt ID | Q8IU85 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CAMK1D-5442HF | Active Recombinant Full Length Human CAMK1D Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK1D-0180H | Recombinant Human CAMK1D Protein (A2-K385), GST tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK1D-1975H | Recombinant Human CAMK1D Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| CAMK1D-404H | Recombinant Human CAMK1D Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMK1D-780H | Recombinant Human CAMK1D protein(Met1-Lys385), GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CAMK1D-7882HCL | Recombinant Human CAMK1D 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Bergamaschi A, et al. Mol Oncol. 2008
Breast cancer is diverse, both clinically and molecularly, with five key molecular subtypes identified. The basal-like subtype is particularly aggressive, lacking ER, PR, and HER2 but showing high DNA alterations and specific chromosome gains like those on 10p, often leading to a poor prognosis. To pinpoint key drivers in this subtype, we explored genomic data from 172 breast tumors, focusing on a small region at 10p13 housing seven genes, notably CAMK1D. Though traditionally involved in cell signaling, CAMK1D hadn't been tied to cancer before. Our findings showed that CAMK1D is overexpressed when amplified, especially noticeable in invasive breast cancers. Moreover, when we overexpressed CAMK1D in normal breast cells, it prompted faster growth and signs of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, including weakened cell adhesion and increased movement, hinting at its potential role in cancer progression.
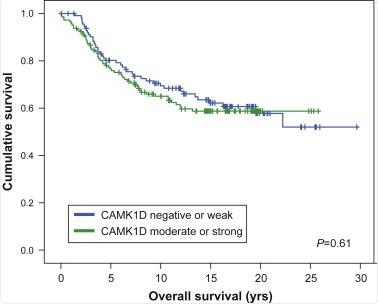
Fig1. CAMK1D expression and patient outcome.
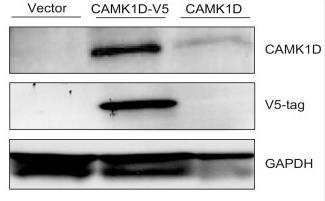
Fig2. Western blot analysis confirming CAMK1D expression (43kD) in MCF10A cells.
Case 2: Volpin V, et al. Cancer Immunol Res. 2020
Cancer immunotherapy often struggles due to resistance mechanisms against immune checkpoint blockers. In our genetic screening of anti-PD-L1 resistant tumors, we pinpointed a significant player—calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1D (CAMK1D). This gene, which is active in tumors resistant to PD-L1/PD-1 therapies and usually signals a poor outlook, gets switched on by CTLs via Fas-receptor prompting. CAMK1D then connects with and phosphorylates caspases -3, -6, and -7, putting a halt to their usual activity. Interestingly, when CAMK1D was blocked pharmacologically, cancer cells became more susceptible to Fas-ligand, shedding light on how CAMK1D might bolster immune resistance in certain cancers.
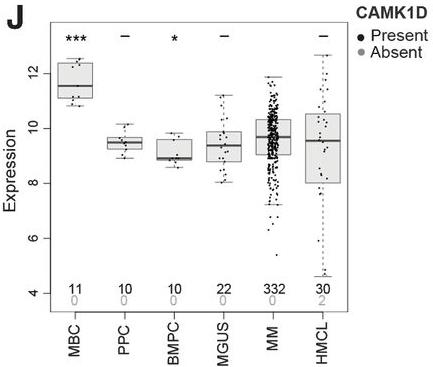
Fig1. CAMK1D expression by gene expression profiling in human MBC, PPC, BMPC, MGUS, multiple myeloma (MM), and HMCL.
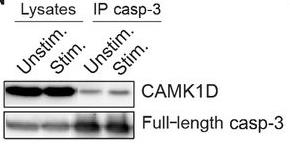
Fig2. Representative blots showing coimmunoprecipitation of CAMK1D with caspase-3.
Human CAMK1D is a type of serine/threonine kinase that's a part of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase 1 family, playing a key role in several cell functions.
In the research world, scientists use recombinant Human CAMK1D to delve into its role in things like how granulocytes function, how certain genes get transcribed, and the process of apoptosis in specific cell types. It's also looked at for its part in the signaling pathways of chemokines and how neurons undergo apoptosis. Researchers focus on its enzymatic functions using various assays, attempting to block its interaction with other proteins to understand more about its activity.
Industrially, this recombinant protein is produced for drug discovery, especially aimed at cancer treatment. Made in systems like E. coli or through insect cells, it helps in crafting new therapies and provides a basis for researching cellular signaling modulation. Producing rhCAMK1D ensures consistency in experiments and helps develop diagnostic tools and antibodies, crucial for studying its role and potential in treating diseases.
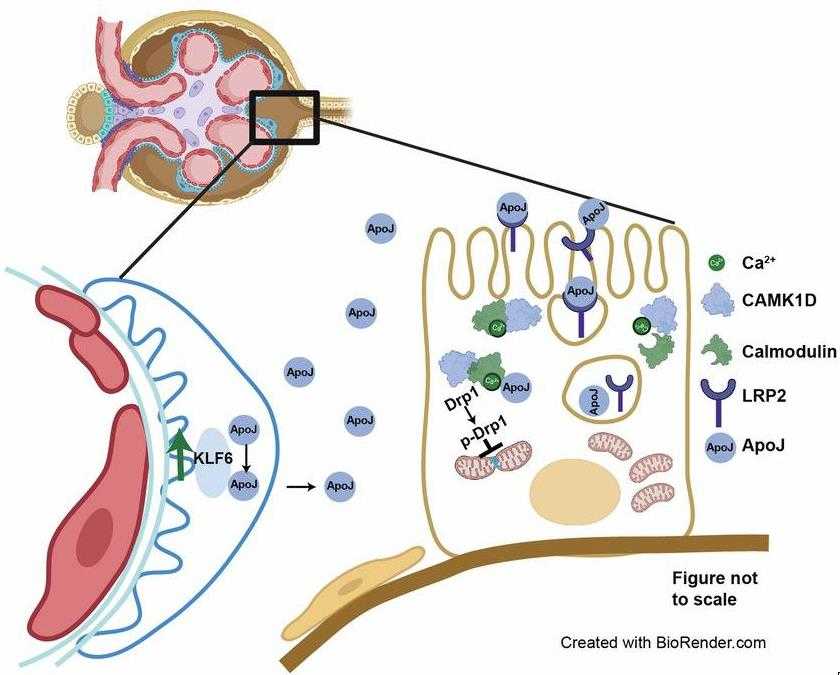
Fig1. Proposed schematic of potential KLF6-ApoJ-CaMK1D signaling between podocytes and PT cells. (Nehaben A Gujarati, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CAMK1D Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CAMK1D Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


