Recombinant Human APOA1 protein(Met1-Gln267), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | APOA1-33H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human APOA1 (CAA26097.1) (Met 1-Gln 267) was expressed in HEK293, fused with Fc region of Human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Availability | April 18, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | 1-267 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM Glycine, 10mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized Human ApoAI at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human SCARB1, The EC50 of biotinylated human SCARB1 is 0.37 μg/mL. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human APOA1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein.The reduced monomer consists of 481 amino acids migrates as approximately 55 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions as predicted. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | APOA1 apolipoprotein A-I [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | APOA1 |
| Synonyms | APOA1; apolipoprotein A-I; apo-AI; apoA-I; MGC117399; |
| Gene ID | 335 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000039 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000030 |
| MIM | 107680 |
| UniProt ID | P02647 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| APOA1-373R | Recombinant Rat APOA1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Apoa1-631M | Recombinant Mouse Apoa1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-26120TH | Recombinant Human APOA1, Protein A-tagged | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-33H | Recombinant Human APOA1 protein(Met1-Gln267), hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-1060H | Recombinant Human ApoA1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| APOA1-5301H | Native Human Apolipoprotein A-I | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-26121TH | Native Human APOA1, Protein A-tagged | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-23D | Native Dog Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) Protein | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-8344H | Native Human APOA1 | +Inquiry |
| ApoA-I-3554H | Native Human ApoA-I | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| APOA1-1497MCL | Recombinant Mouse APOA1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| APOA1-3088HCL | Recombinant Human APOA1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Sarkar S, et al. J Lipid Res. 2024
HDL's ability to clear cholesterol from cells is a better heart health indicator than just having high HDL cholesterol. Earlier, we saw that HDL with both APOA1 and APOA2 ramps up cholesterol removal through the ABCA1 transporter. In our latest study, by adding pure, lipid-free APOA2 to human plasma, we saw a clear increase in the whole plasma's ability to remove cholesterol, depending on the dose. APOA2 also boosted cholesterol removal in isolated HDL, especially when APOA1 and APOA2 were present in equal amounts. More tests confirmed that having both APOA1 and APOA2 is crucial for this effect. By looking at the protein structure, we saw that APOA2 changes the shape of APOA1. Our findings suggest that APOA2 shifts the C-terminal helix of APOA1 from the HDL's surface, allowing it to interact with ABCA1, similar to its action in lipid-poor APOA1.
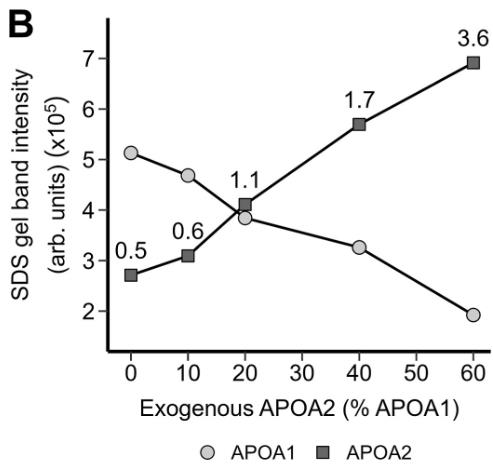
Fig1. SDS-PAGE-based densitometry analysis of HDL-bound fractions shows the change in APOA1 and APOA2 content with increasing addition of exogenous APOA2.
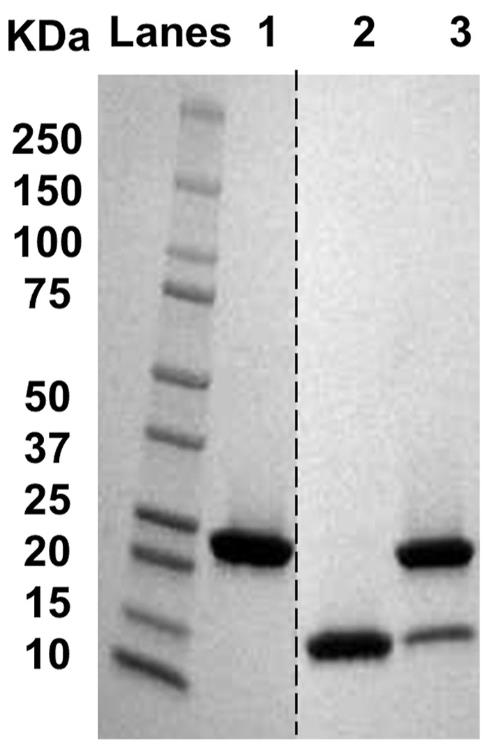
Fig2. SDS-PAGE analysis (nonreducing) of the rHDL particles showing APOA1 and/or APOA2.
Case 2: Fung KYY, et al. J Lipid Res. 2024
Atherosclerosis happens when LDL builds up and oxidizes in the arterial space, causing blockages due to immune cell infiltration. This process kicks off when LDL gets shuttled across blood vessel linings via endothelial cells, thanks to connections with receptors like SR-B1. HDL plays a protective role by clearing extra cholesterol and serving as an antioxidant. Notably, apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) in HDL can tie up with SR-B1, suggesting it might outcompete LDL for SR-B1 attachment, limiting LDL's buildup. Experiments showed that raising HDL or even just APOA1 in mice led to less LDL deposit in certain areas of the aorta, with the APOA1-Milano variant being particularly effective at this.
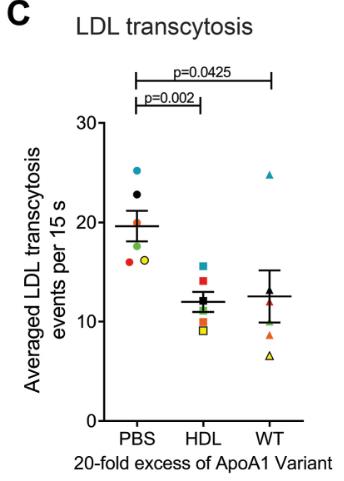
Fig1. Inhibition of DiI-LDL transcytosis by 20x excess unlabeled commercially purchased human purified HDL and also by 20x excess unlabeled APOA1-WT as measured using TIRF microscopy.
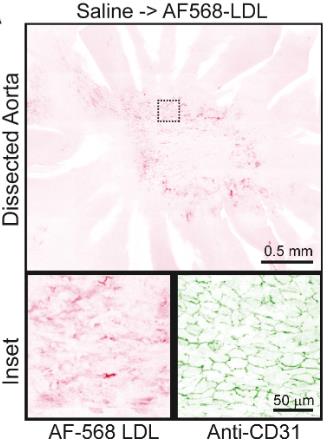
Fig2. Representative images of en face staining of the isolated aortas from mice perfused with PBS or 0.4 mg of APOA1-WT or APOA1-Milano.
In the realms of industrial production and biomedical research, Recombinant Human APOA1 is being utilized to develop HDL analogs. These analogs are crafted in vitro and are evaluated for their potential to lessen coronary atherosclerosis and provide clinical benefits. This utilization holds promise not only for advancing cardiovascular disease treatment but also showcases the significant potential and importance of APOA1 in biomedical innovation.
In the industrial and biomedical fields, Recombinant Human APOA1 is used to create HDL-like particles. These are made in vitro to explore their potential in reducing atherosclerotic burden in coronary arteries and offering clinical benefits. Such applications are advancing cardiovascular disease treatment research and showcasing the significance and potential of APOA1 in the biomedical sphere.
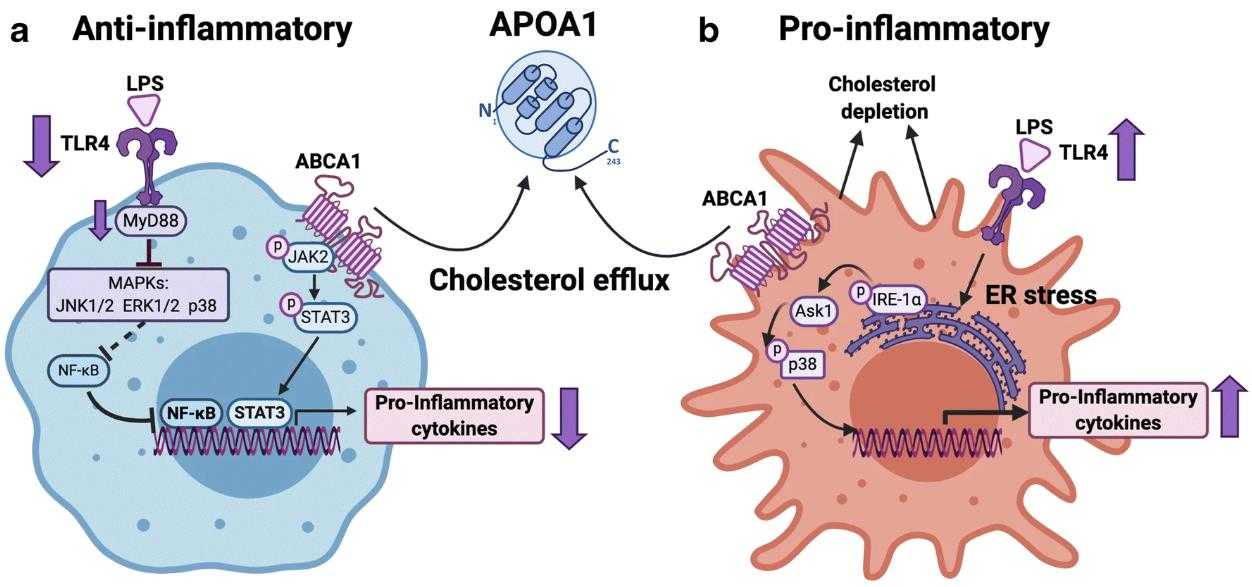
Fig1. APOA1 has pro-and anti-inflammatory effects in macrophages. (Blake J. Cochran, 2021)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All APOA1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All APOA1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


