Recombinant Cynomolgus FCGR2A protein(Met1-Ile211), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | FCGR2A-4107C |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Cynomolgus CD32a (AAL92096.1) (Met 1-Ile 211) was expressed in HEK293, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Availability | April 21, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Cynomolgus |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-211 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Using the Octet RED System, the affinity constant (Kd) of cynomolgus CD32A-His bound to human IgG was 5.8 μM. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant cynomolgus CD32a consists of 193 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 21.8 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the recombinant protein is approximately 28-33 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| FCGR2A-2964H | Recombinant Human FCGR2A, His & AVI Tagged, Biotinylated, 167 Arg | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-260H | Active Recombinant Human FCGR2A Protein, His-tagged, Biotinylated | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-1962R | Recombinant Rat FCGR2A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-4107C | Recombinant Cynomolgus FCGR2A protein(Met1-Ile211), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-568C | Active Recombinant Cynomolgus FCGR2A protein, His-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| FCGR2A-001HCL | Recombinant Human FCGR2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-1926CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus FCGR2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-1996HCL | Recombinant Human FCGR2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| FCGR2A-678HCL | Recombinant Human FCGR2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Meyer T, et al. Blood. 2015
The CD32a (Fcγ receptor IIa) is a potential therapeutic target for diseases involving IgG immune complexes that cause inflammation, such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. However, IV.3, a well-known CD32a-blocking monoclonal antibody (mAb), has been shown to cause anaphylaxis in "3KO" mice with a human CD32a transgene, which was unexpected as it was believed to lack the ability to trigger cellular activation. This reaction limits IV.3's therapeutic potential. This study investigates the mechanisms behind IV.3-induced anaphylaxis and finds that it, along with two other CD32a-blocking mAbs (AT-10 and MDE-8), also causes severe thrombocytopenia in FCGR2A mice. Here the IgG "Fc" effector function is essential for anaphylaxis and thrombocytopenia induction in these mice. MAbs that cannot activate mouse IgG receptors not only fail to induce these reactions but also protect FCGR2A mice from lethal IgG IC doses.
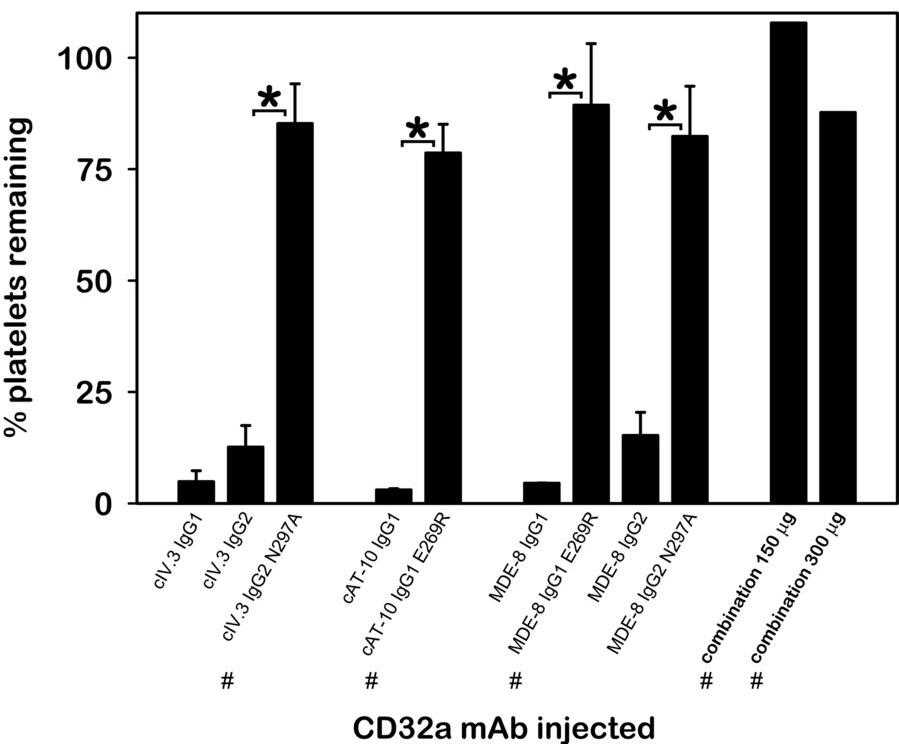
Fig1. Bar chart showing the percentage of platelets remaining in circulation following IV injection of native and effector-deficient CD32a antibodies.

Fig2. Signs of shock in control or CD32a-pretreated FCGR2A mice following M90 IC injection.
Case 2: El Mdawar MB, et al. Blood Adv. 2021
Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is a significant cause of death from transfusions, and the role of human Fcγ receptors in antibody-mediated TRALI is not fully understood. Human platelets uniquely express the FcγRIIA/CD32A receptor, which is not present in mice, suggesting that current murine models do not fully represent human immunology. With a humanized mouse model with the FcγRIIA/CD32A receptor, these mice had increased alveolar edema and mortality when exposed to a chimeric human immunoglobulin G1/mouse anti-major histocompatibility complex class I monoclonal antibody. In these mice, monocytes/macrophages played a role in initiating TRALI, and platelet activation was significantly higher, leading to their consumption and release of granule contents. Platelet depletion mitigated TRALI in CD32A+ mice but not in wild-type mice. Blocking platelet serotonin uptake with fluoxetine reduced TRALI severity in CD32A+ mice, and inhibiting the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A serotonin receptor with sarpogrelate prevented lung edema aggravation in these mice.
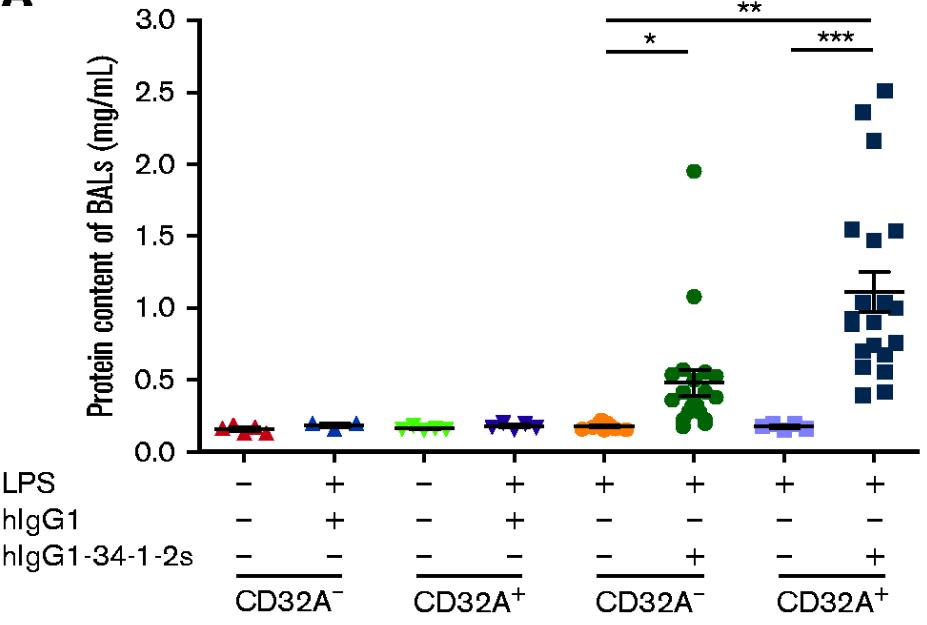
Fig1. Protein concentrations in BALs were measured 15 minutes after injection of hIgG1-34-1-2S or in negative controls.
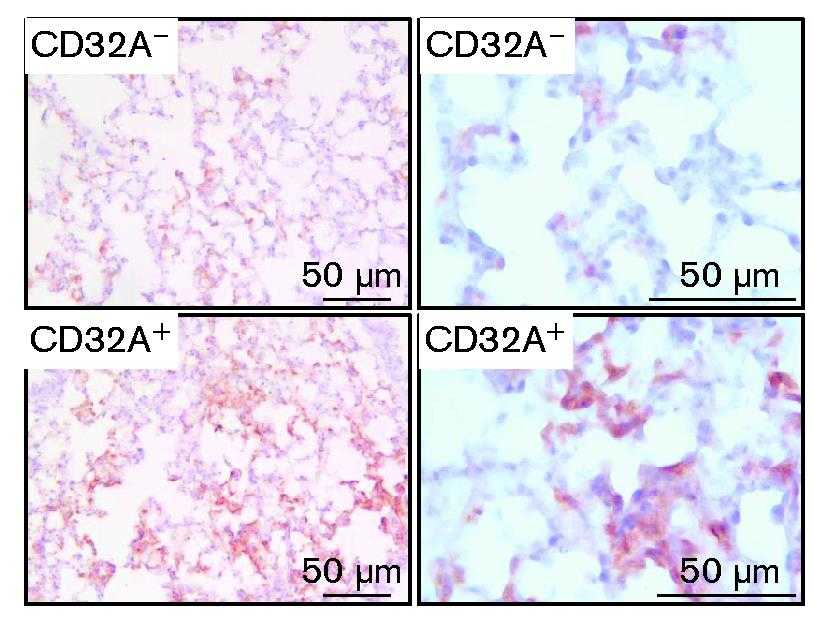
Fig2. Representative lung sections from CD32A– and CD32A+ mice immunolabeled with the anti-neutrophil mAb 1A8.
Recombinant Cynomolgus FCGR2A protein, also known as the Fc gamma receptor IIa, plays a significant role in immune system research and has a range of applications in various fields. This protein is crucial for studying antibody-mediated cellular toxicity reactions and is involved in the regulation of immune responses in conditions such as autoimmunity, infections, and cancer. It is used in the analysis of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by conducting in vitro experiments to assess the potency of monoclonal antibodies, as FCGR2A participates in this antibody-dependent cell killing process. Additionally, it aids in the search for potential biomarkers associated with immune-related diseases, contributing to the development of diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies.
The FCGR2A protein is also important in drug development, particularly in the design of antibodies for targeted therapies. It is expressed on immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils and is involved in phagocytosis and clearance of immune complexes. The recombinant protein is used to understand the binding characteristics of IgG and FcγR, which is vital for the development of antibodies with specific effector functions. Furthermore, FCGR2A has been implicated as a prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), correlating with immune infiltration and tumor-immune interactions, which suggests its potential role in cancer prognosis and treatment response.
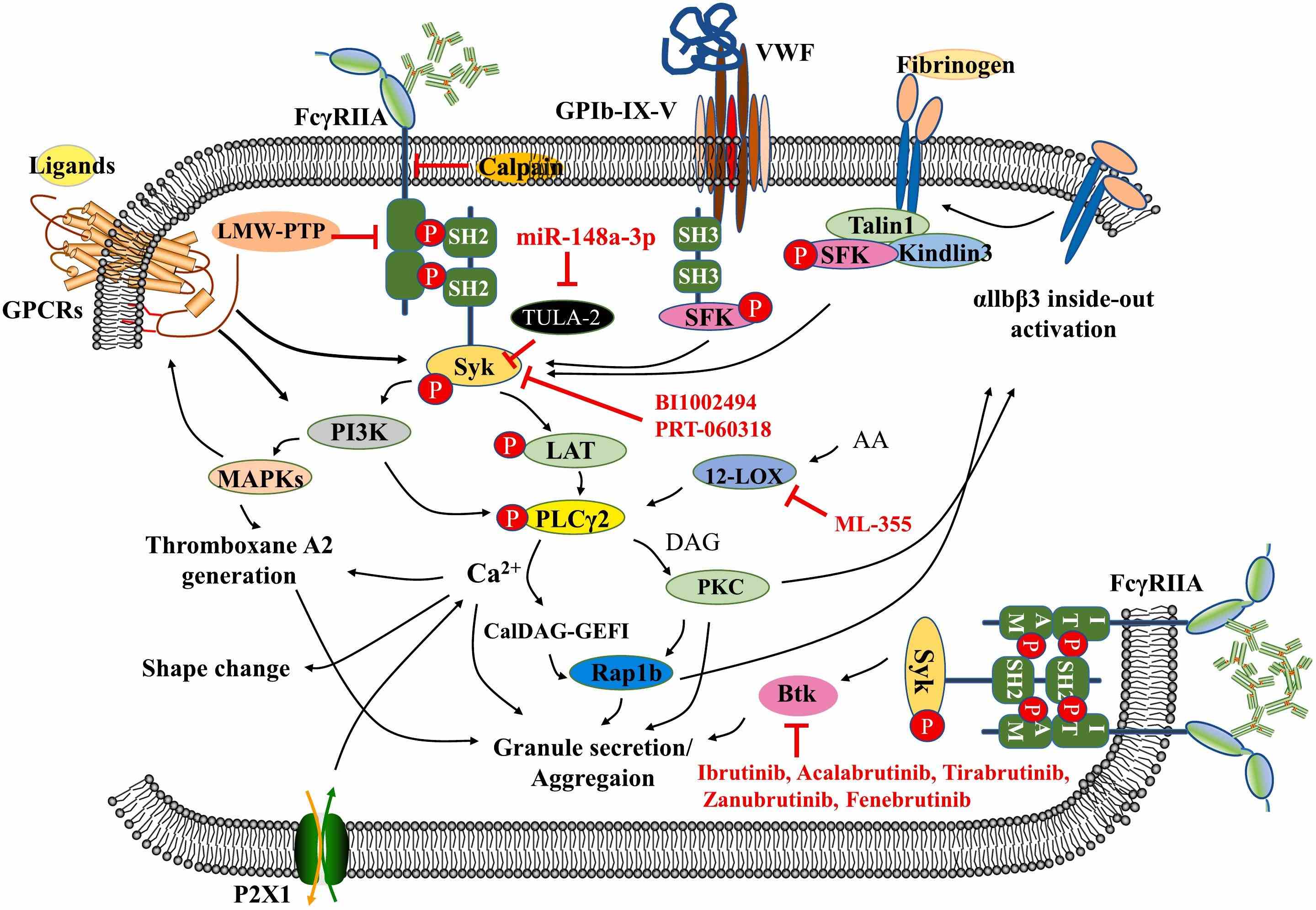
Fig1. Platelet FcγRIIA signal transduction. (Qingsong Zhang, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All FCGR2A Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All FCGR2A Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


