Active Recombinant Human COMP protein(Met1-Ala757), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | COMP-674H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human COMP (NP_000086.2) precusor (Met 1-Ala 757) was expressed in HEK293 with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Ala757 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its ability to induce adhesion of ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cells. When cells are added to COMP-coated plates (0.625 μg/mL and 100 μL/well), approximately >30% cells will adhere specifically after 60 minutes at 37°C. |
| Molecular Mass : | The mature form of human COMP consists of 748 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and predicts a molecular mass of 82.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhCOMP is approximately 120-130 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | COMP cartilage oligomeric matrix protein [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | COMP |
| Synonyms | COMP; cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple) , EDM1, EPD1, PSACH; MED; THBS5; thrombospondin 5; TSP5; thrombospondin-5; pseudoachondroplasia (epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple); cartilage oligomeric matrix protein(pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple); cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (pseudoachondroplasia, epiphyseal dysplasia 1, multiple); EDM1; EPD1; PSACH; MGC131819; MGC149768; |
| Gene ID | 1311 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000095 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000086 |
| MIM | 600310 |
| UniProt ID | P49747 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| COMP-1528R | Recombinant Rat COMP Protein | +Inquiry |
| COMP-01H | Recombinant Human COMP Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| COMP-3658H | Recombinant Human COMP, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| COMP-1185R | Recombinant Rat COMP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Comp-5796R | Recombinant Rat Comp protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| COMP-3031HCL | Recombinant Human COMP cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Maly K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2021
Osteoarthritis slowly breaks down cartilage. Normally inactive chondrocytes reactivate, forming clusters and producing enzymes and proteins like COMP and TSP-4. Researchers studied these proteins using pig chondrocytes and found that COMP attracts cells to damaged areas, aiding repair, while TSP-4 doesn't have this effect. Both proteins, however, encourage the production of certain collagens and proteoglycans, suggesting a role in stabilizing and repairing cartilage.
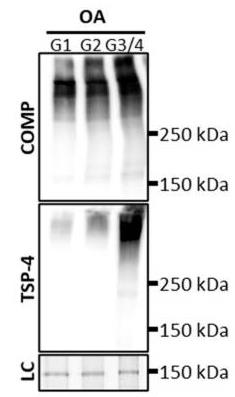
Fig1. Total COMP and TSP-4 content was investigated via immunoblots.
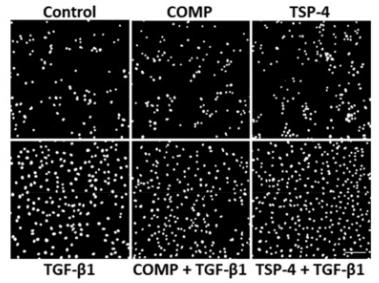
Fig2. Chondrocytes were stimulated with COMP (10 µg/mL) or TSP-4 (10 µg/mL) for seven days. Nuclei were DAPI stained at day 10.
Case 2: Bozó R, et al. J Invest Dermatol. 2020
In psoriasis, the skin's dermal-epidermal junction shows differences from healthy skin. Normally, cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) sits in the papillary dermis, but in psoriatic skin, it extends deeper. In nonlesional psoriatic skin, COMP forms a continuous layer, while in lesions, it's patchy. Researchers found that COMP pairs strongly with β1-integrin where the basement membrane is broken. Lab tests showed that external COMP reduces keratinocyte growth unless α5β1-integrin is blocked, hinting that COMP helps stabilize the epidermis by slowing cell growth. This effect of COMP might be important in other skin conditions with nonhealing wounds and COMP buildup.
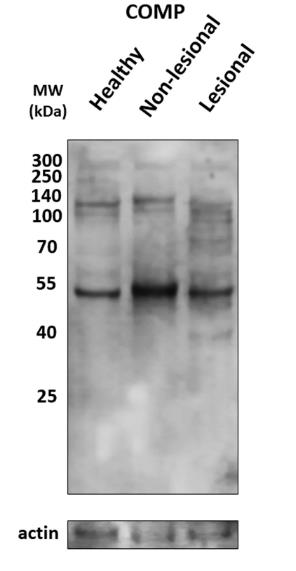
Fig1. COMP protein was detected with western blot analysis from healthy, psoriatic nonlesional, and lesional skin.
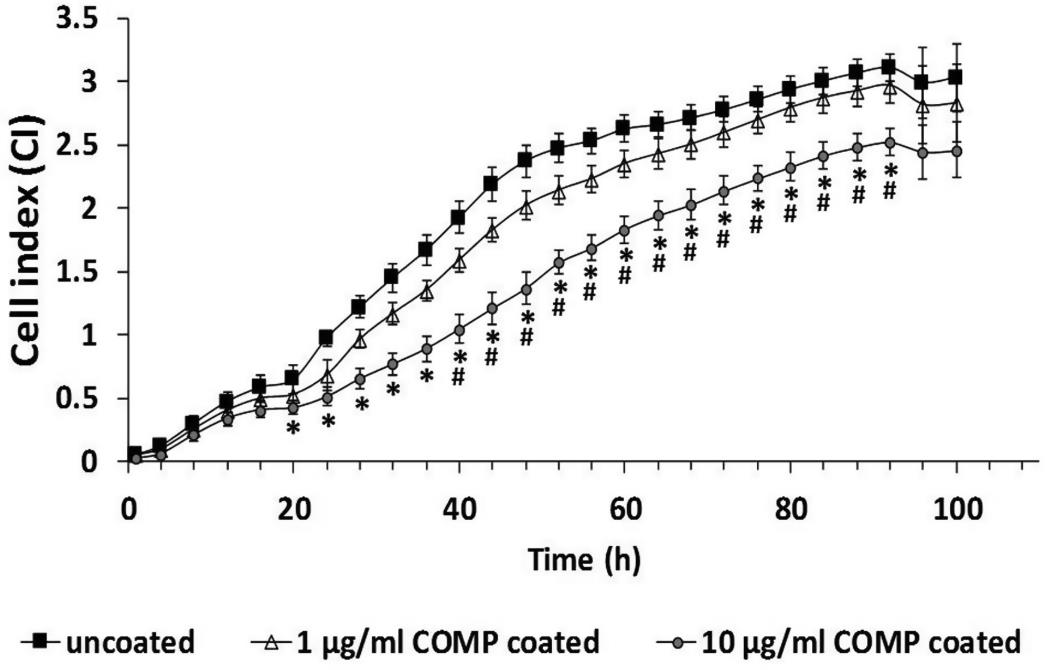
Fig2. CI measurement of HPV-KER cells cultured on surfaces that were uncoated or coated with rhCOMP.
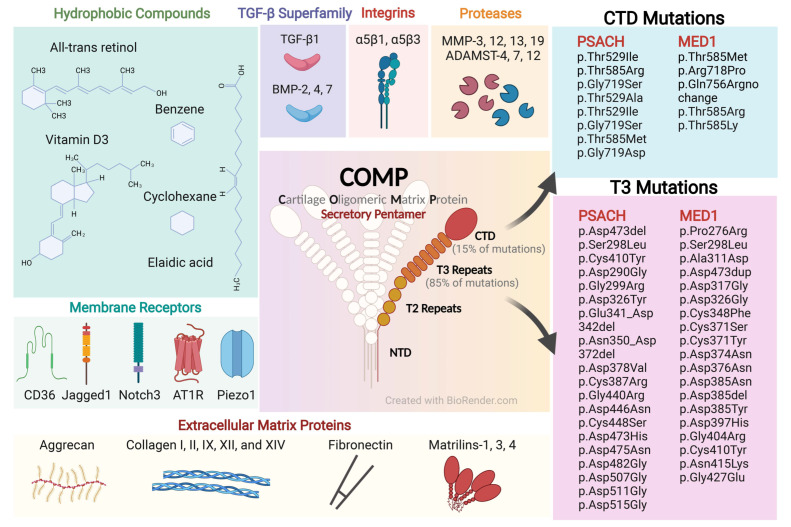
Fig1. The structure, binding molecules, and mutations of COMP. (Jiarui Cui, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All COMP Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All COMP Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


