Active Recombinant Human C2 protein(Met1-Leu752), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | C2-6878H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human complement component 2 (C2) precursor (NP_000054.2) (Met 1-Leu 752) was expressed in HEK293 with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Availability | April 19, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Leu752 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its ability to cleave a colorimetric peptide substrate, N-carbobenzyloxy-Gly-Arg-ThioBenzyl ester (Z-GR-SBzl), in the presence of 5, 5'Dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB). The specific activity is >100 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Molecular Mass : | The single-chain form of recombinant human complement component C2 comprises 743 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 82.5 kDa. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | C2 complement component 2 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | C2 |
| Synonyms | C2; complement component 2; complement C2; C3/C5 convertase; complement component C2; CO2; DKFZp779M0311; |
| Gene ID | 717 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000063 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000054 |
| MIM | 613927 |
| UniProt ID | P06681 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| C2-480M | Recombinant Mouse C2, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C2-598H | Recombinant Human Complement Component 2, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C2-1878C | Active Recombinant Cynomolgus C2 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C2-0620H | Recombinant Human C2 Protein (Ile245-His451), N-His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C2-7265H | Recombinant Human C2 protein, hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| C2-98H | Active Native Human C2 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| C2-001MCL | Recombinant Mouse C2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| C2-3068HCL | Recombinant Human C2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Martini PG, et al. BMC Immunol. 2010
Complement C2 deficiency is the most common genetic issue in the complement system and is linked to diseases like serious infections in kids and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in adults. These links highlight how crucial C2 is for both innate immunity and immune tolerance. While treatments with fresh frozen plasma have shown some success, protein replacement therapy hasn't yet been fully explored. Researchers managed to clone and express human C2 in mammal cells, resulting in a recombinant version (rhC2) with over 95% purity. This rhC2 is stable and active, responding well to C1s cleavage and restoring classical pathway activity in C2-deficient serum. It even boosts C3 fragment deposition on Streptococcus pneumoniae in C2-deficient serum to match normal levels, showing promise for complementing immune function.
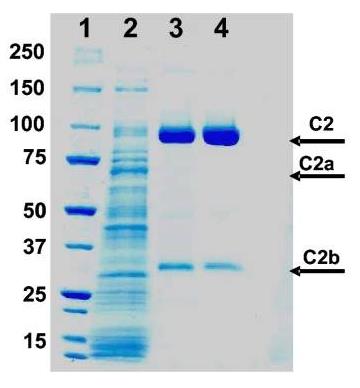
Fig1. Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of rhC2 at different stages of the purification process.
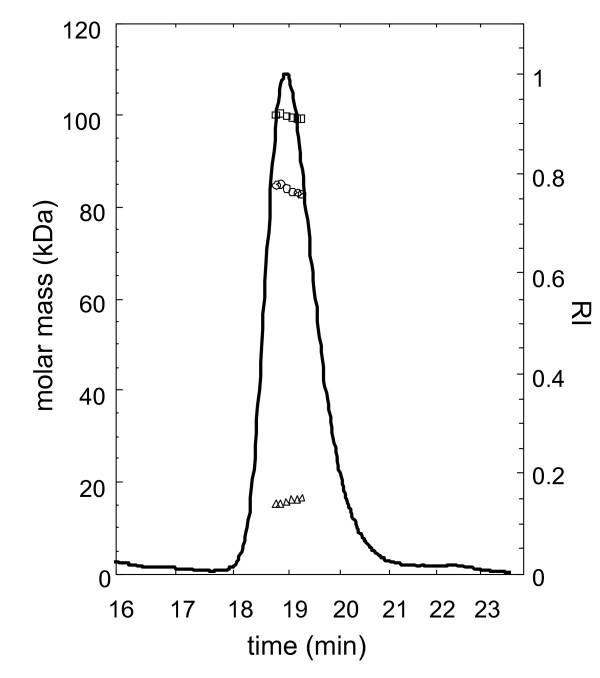
Fig2. Analysis of rhC2 glycosylation by SEC-MALS.
Case 2: Budding K, et al. Eur J Neurol. 2024
Complement factor C2 emerges as a potential target for treating immune-mediated neuropathies. However, some literature hints at the classical complement pathway's ability to proceed to C3 activation even without C2, through a "C2 bypass." This study looked into this bypass mechanism using IgM autoantibodies from patients with multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) or anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein neuropathy (AMN). Utilizing ex vivo models, researchers used C2-depleted (C2D) serum and an anti-C2 antibody. In MMN models, patient-derived IgM antibodies targeted motor neurons and Schwann cells, fixing C3 with fresh serum. This fixation was blocked by anti-C2 and did not occur in C2D serum. In the AMN setting, IgM anti-MAG antibodies also fixed C3 with fresh serum, yet this too was halted without C2 or in the presence of anti-C2.
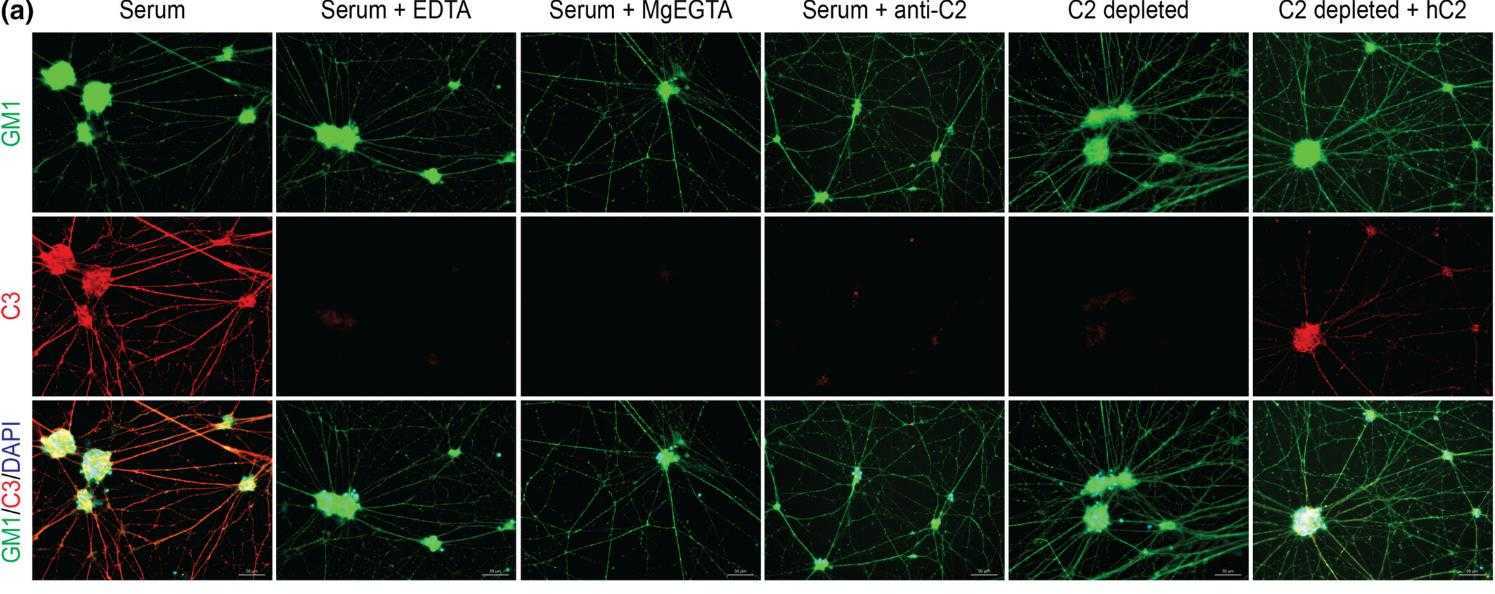
Fig1. Representative images are shown for the complement-activation assays in disease models for MMN.
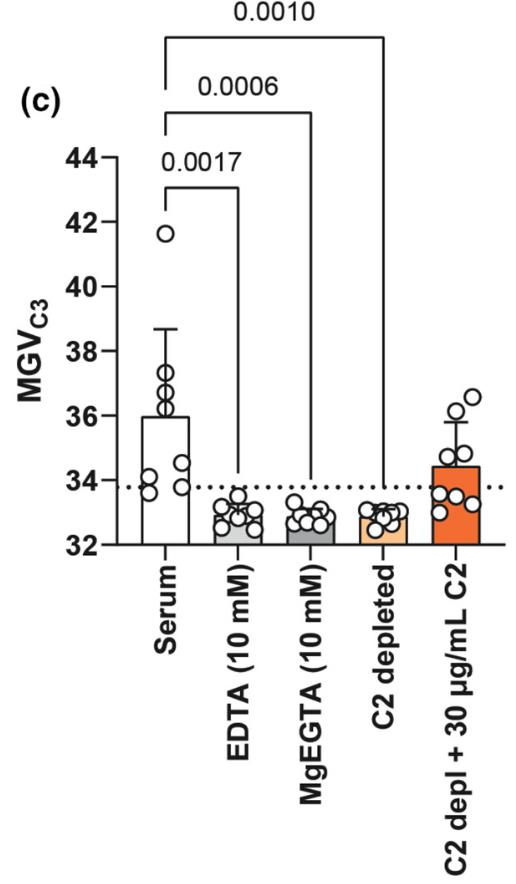
Fig2. 3 fixation is dependent on C2 and does not occur in presence of C2D serum.
Human C2 is a key player in the classical pathway of the complement system, and it's vital for our immune response. Recombinant Human C2 (rhC2) finds its place both in research labs and on an industrial scale due to its important role.
In research settings, rhC2 is mainly used to dive deep into the workings of the classical complement pathway. When activated by factor C1, it's split into C2a and C2b, with C2a pairing up with C4b to crank up the complement cascade. This is crucial for recognizing and clearing immune complexes and fighting off invaders. rhC2 shows up in a variety of immunoassays, like ELISA kits that measure Complement C2 levels in different samples, shedding light on its role in autoimmune disorders and complement-related diseases.
On the industrial front, rhC2 is churned out for drug discovery and developing treatments, especially for those focusing on diseases tied to the complement system. Produced in systems like HEK293 cells, it's handy for creating new therapies and studying how the complement system can be controlled. Plus, it helps spawn standardized research reagents, ensuring experiments stay trustworthy and can be repeated. The production efforts also pave the way for diagnostic tools and antibodies that detect C2 in samples, broadening our understanding of its function and linked health issues.
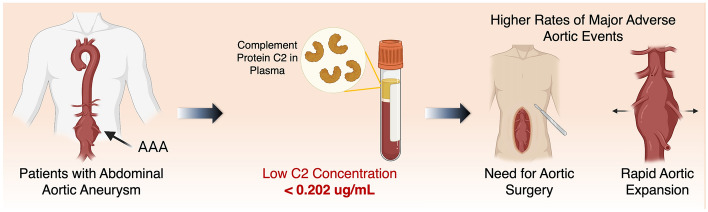
Fig1. The clinical workflow for the use of complement factor 2 (C2) as a prognostic biomarker. (Tiam Feridooni, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All C2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All C2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


