ULBP1
-
Official Full Name
UL16 binding protein 1 -
Overview
UL16-binding proteins (ULBP) or retinoic acid early transcripts-1 (RAET1) are ligands to the activating receptor, NKG2D. Ten members of the human ULBP/RAET1 gene family have been identified to encode for potentially functional proteins, and have tissue-s -
Synonyms
ULBP1;UL16 binding protein 1;NKG2D ligand 1;UL16-binding protein-like transcript 1;MULT1;A430108B07Rik;RAET1I
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- S.frugiperda
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Non
Background
What is ULBP1 Protein?
ULBP1 gene (UL16 binding protein 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6q25. The protein encoded by this gene is a ligand of natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D), an immune system-activating receptor on NK cells and T-cells. Binding of the encoded ligand to NKG2D leads to activation of several signal transduction pathways, including those of JAK2, STAT5, ERK and PI3K kinase/Akt. Also, in cytomegalovirus-infected cells, this ligand binds the UL16 glycoprotein and is prevented from activating the immune system. The ULBP1 protein is consisted of 244 amino acids and ULBP1 molecular weight is approximately 28.0 kDa.
What is the Function of ULBP1 Protein?
ULBP1 is a ligand that activates the NKG2D receptor on natural killer (NK) cells and T cells. The binding of ULBP1 to NKG2D activates several signaling pathways, such as JAK2, STAT5, ERK, and PI3K kinase /Akt, thereby promoting cytotoxicity of NK cells. In tumor immunotherapy, ULBP1 expression levels correlate with patient survival, suggesting its potential as a prognostic biomarker. In addition, ULBP1 expression is regulated by specific transcription factors, such as Sp1, Sp3, and AP-2α, which may play an important role in immune surveillance. Due to the high expression of ULBP1 in a variety of tumors, it has become a potential target for immunotherapy, such as NKG2D receptor-based CAR T cell therapy, of which CYAD-01 is a CAR T therapy targeting ULBP1 in clinical trials.
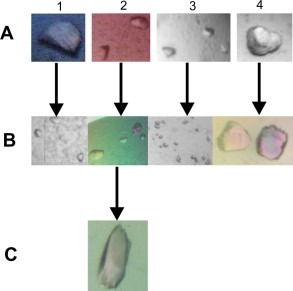
Fig1. Crystals of recombinant human ULBP1. (Aleksandra A Watson, 2011)
ULBP1 Related Signaling Pathway
The NKG2D receptor is an immune-activating receptor that is mainly expressed on NK cells and T cells. When ULBP1 binds to the NKG2D receptor, it activates a variety of signal transduction pathways including JAK2, STAT5, ERK, and PI3K kinase /Akt. Activation of these signaling pathways results in immune cells being able to recognize and kill infected cells or tumor cells. In addition, in cytomegalovirus (CMV) -infected cells, ULBP1 binds to the UL16 glycoprotein, preventing immune system activation, a mechanism by which the virus evades the host immune response.
ULBP1 Related Diseases
ULBP1 is a glycoprotein, composed of 16 amino acids, widely distributed on the cell surface and involved in biological processes including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, apoptosis and immune response. ULBP1 expression has been found to be elevated in many types of cancer, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, breast cancer, colon cancer, glioblastoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma, and may be associated with disease prognosis and treatment response. Particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma, elevated serum levels of ULBP1 are significantly associated with reduced survival in patients, suggesting its potential as a prognostic marker as well as a potential therapeutic target. In addition, the expression of ULBP1 in colorectal cancer also shows its value in diagnosis and prognosis, with increased expression levels associated with poorer prognosis. In the field of tumor immunotherapy, ULBP1, as one of the NKG2D ligands, is involved in the process of immune surveillance and clearance of tumor cells by activating NK cells and T cells.
Bioapplications of ULBP1
ULBP1, as a widely distributed glycoprotein on the surface of various cell types, has important biological functions and clinical application potential. It plays a role in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis, and is involved in immune responses, especially in the activation of natural killer (NK) cells and immune surveillance of T cells. In terms of clinical application, ULBP1 expression levels are elevated in a variety of cancers, making it a potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and therapeutic response monitoring. In addition, ULBP1 is also a promising target for drug development and immunotherapy due to its role in tumor immune escape, for example, NKG2D receptor-based CAR T cell therapies utilize ULBP1 as a target to enhance immune response against tumor cells.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Benjamin G Gowen, 2015
Recognition and elimination of tumor cells by the immune system is crucial for limiting tumor growth. Natural killer (NK) cells become activated when the receptor NKG2D is engaged by ligands that are frequently upregulated in primary tumors and on cancer cell lines. However, the molecular mechanisms driving NKG2D ligand expression on tumor cells are not well defined. Using a forward genetic screen in a tumor-derived human cell line, researchers identified several novel factors supporting expression of the NKG2D ligand ULBP1. The results show stepwise contributions of independent pathways working at multiple stages of ULBP1 biogenesis. Deeper investigation of selected hits from the screen showed that the transcription factor ATF4 drives ULBP1 gene expression in cancer cell lines, while the RNA-binding protein RBM4 supports ULBP1 expression by suppressing a novel alternatively spliced isoform of ULBP1 mRNA.
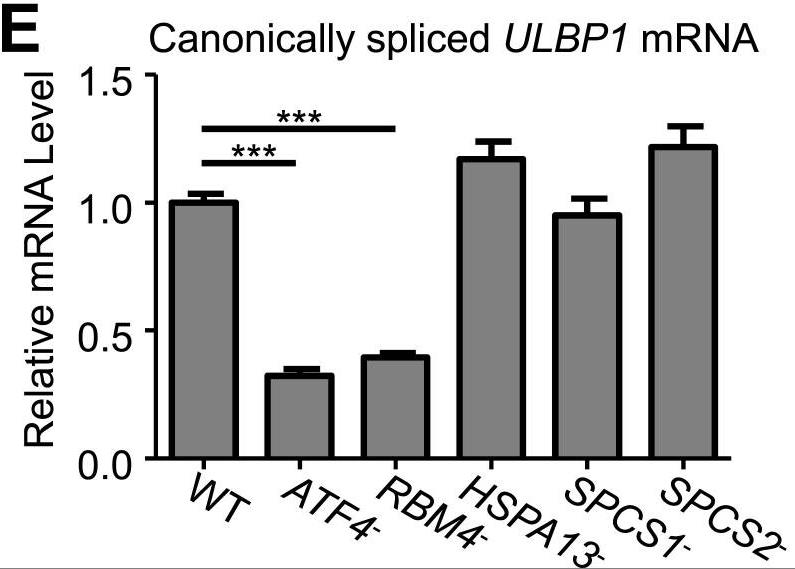
Fig1. RT-qPCR analysis of canonically spliced ULBP1 mRNA expression levels.
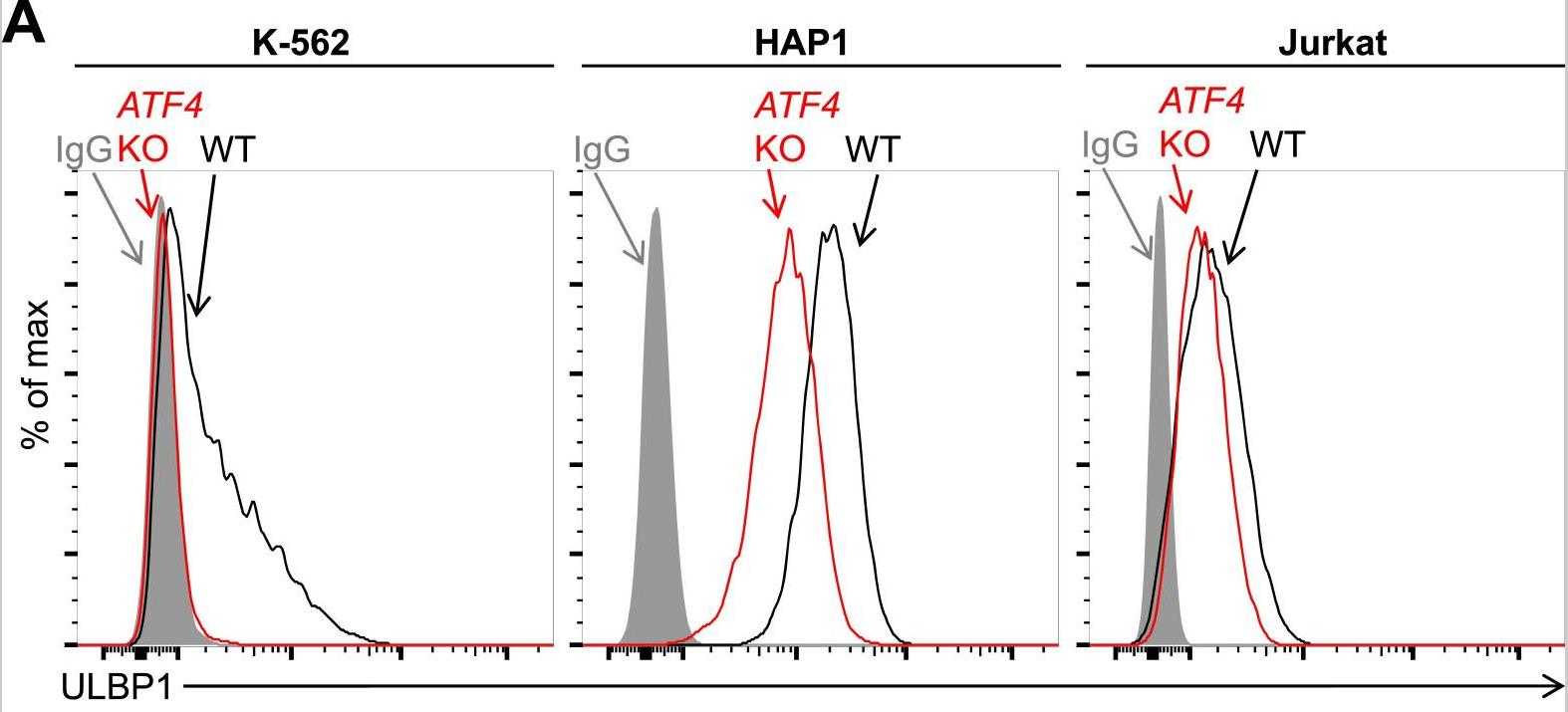
Fig2. Flow cytometric analysis of ULBP1 expression.
Case Study 2: Hiromichi Dansako, 2018
Natural killer (NK) cells through their NK group 2 member D (NKG2D) receptors recognize NKG2D ligands such as UL16-binding proteins (ULBPs) on virus-infected cells and subsequently trigger the host innate immune response. In the present study, researchers demonstrated that hepatitis C virus (HCV) induced the cell surface expression of ULBP1 in human immortalized hepatocyte PH5CH8 cells and human hepatoma HuH-7 cell-derived RSc cells. Interestingly, NK cell line NK-92 induced cytotoxicity and interferon-γ mRNA expression and subsequently reduced the levels of HCV RNA replication during co-culture with HCV-infected RSc cells. From these results, ULBP1 is a target of the NK cell-mediated innate immune response in HCV-infected human hepatocytes.
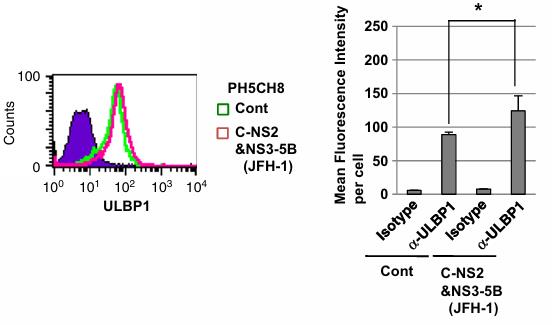
Fig3. Flow cytometric analysis of intracellular ULBP1.
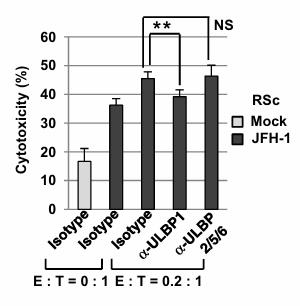
Fig4. Functional analysis of ULBP1 on NK-92-mediated cytotoxicity towards JFH-1-RSc cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ULBP1-12H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ULBP1-05H)
Involved Pathway
ULBP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ULBP1 participated on our site, such as Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ULBP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | PPP3CC,TNFRSF10C,PTPN6,KIR2DS2,SOS1,IFNGR2,LCP2,PPP3R2,IFNAR2,RAC2 |
Protein Function
ULBP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, natural killer cell lectin-like receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ULBP1 itself. We selected most functions ULBP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ULBP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| natural killer cell lectin-like receptor binding | ULBP2,ULBP3,CLEC2G,Mill2,HLA-E,RAET1G,RAET1E,RAET1D,CLEC2H,SAMD3 |
Interacting Protein
ULBP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ULBP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ULBP1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Fujita, H; Hatanaka, Y; et al. Immunohistochemical Validation and Expression Profiling of NKG2D Ligands in a Wide Spectrum of Human Epithelial Neoplasms. JOURNAL OF HISTOCHEMISTRY & CYTOCHEMISTRY 63:217-227(2015).
- Seidel, E; Le, VTK; et al. Dynamic Co-evolution of Host and Pathogen: HCMV Downregulates the Prevalent Allele MICA*008 to Escape Elimination by NK Cells. CELL REPORTS 10:968-982(2015).



