TREM2
-
Official Full Name
triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a membrane protein that forms a receptor signaling complex with TYROBP. The encoded;protein may be involved in chronic inflammation by triggering the production of constitutive inflammatory cytokines.;Defects in this gene are a cause of polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy;(PLOSL). -
Synonyms
TREM2;triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2;triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2a;TREM 2;Trem2a;Trem2b;Trem2c;triggering receptor expressed on monocytes 2;TREM-2
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mouse myeloma cell
- Human Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- His
- Avi
- GST
- Fc
- Non
- Strep II
- Myc
- mFc
Background
What is TREM2 Protein?
TREM2, short for Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid cells 2, is a transmembrane receptor protein mainly found in microglia within the central nervous system. Part of the immunoglobulin superfamily, TREM2 plays roles in recognizing various ligands and cell signaling. It’s crucial for microglial survival, activation, and phagocytosis, especially during neuroinflammation. TREM2 also interacts with amyloid beta protein 42, helping microglia to take it up and break it down. Beyond that, it binds with lipoproteins and supports their uptake into microglia. Linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, TREM2 mutations can raise risks, influencing how macrophages respond to inflammation and affecting disease mechanisms. Thus, TREM2 is vital in immune regulation, neurodegeneration, and lipid metabolism.What is the Function of TREM2 Protein?
TREM2 is a receptor mainly found in brain microglial cells and peripheral macrophages. It’s crucial for the life, activation, and phagocytosis of these cells, as well as reducing inflammation. TREM2 binds to things like lipopolysaccharides, apoE, and amyloid beta, linking to DAP12/DAP10 for signaling. It’s also involved in brain lipid metabolism and helping microglial cells adapt in disease contexts. Variations in TREM2 are risk factors for diseases like Alzheimer’s, hinting at the immune system’s role in these conditions. It regulates pathways like ERK and AKT, impacting phagocytosis and inflammation, and influences insulin resistance and inflammation, possibly affecting the blood-brain barrier integrity. Overall, TREM2 is key in immune response, nerve protection, and lipid metabolism, playing a significant part in diseases like Alzheimer’s.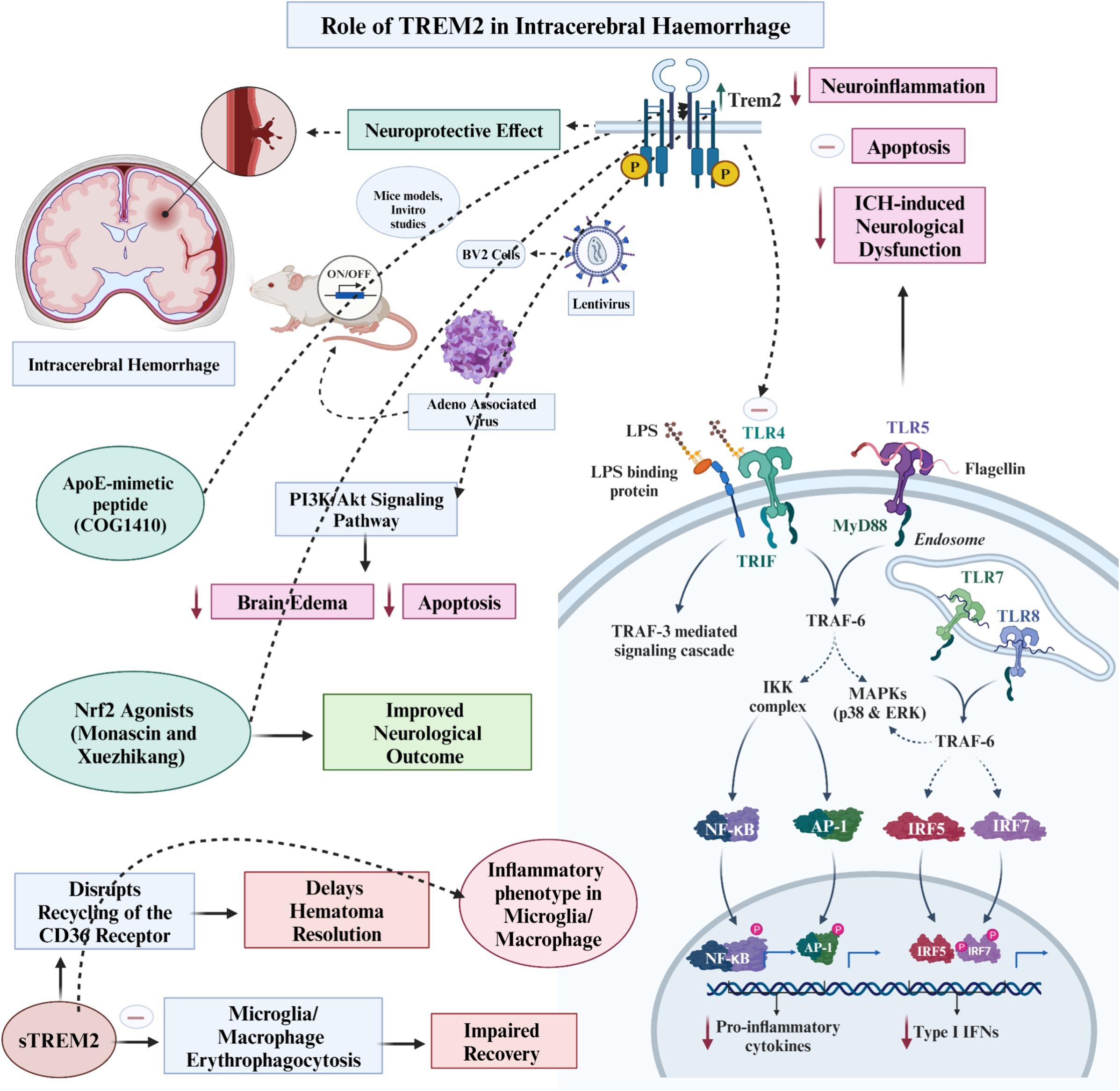
Fig1. The role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in intracerebral haemorrhage. ((Wireko Andrew Awuah, 2024)
TREM2 Related Signaling Pathway
TREM2 protein is a big player in various pathways, especially when we’re talking about nerve diseases, immune responses, and how our bodies handle fats. When TREM2 teams up with DAP12 and DAP10, it kicks off a chain reaction. This involves activating certain kinases like SYK, and getting PI3K involved when DAP10 gets into the mix. This leads to a cascade where PIP2 transforms, sparking signals that control inflammation and protein creation while keeping cells alive and kicking. TREM2 also recruits SHIP1, which tempers the interaction between DAP12 and SYK, fine-tuning inflammation. In the context of diseases like Alzheimer’s, TREM2 helps break down amyloid plaques and calms brain inflammation, making it vital for immune regulation, nerve health, and fat metabolism, playing crucial roles in managing diseases.TREM2 Related Diseases
TREM2 protein is linked to several diseases, especially neurodegenerative ones. It’s mainly found in microglial cells in the central nervous system. Rare mutations in TREM2, like the R47H mutation, can dramatically increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by up to 4.5 times. Besides AD, TREM2 mutations are associated with disorders like frontotemporal dementia (FTD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). TREM2 responds to ligands like lipids and APOE, playing a role in immune response and disease processes. It also influences conditions related to metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, fatty liver, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Moreover, TREM2 may act as a neuroprotective factor by regulating microglial function after brain injuries. Therefore, TREM2 plays a pivotal role in disease mechanisms and serves as a crucial target for research and therapy in related conditions.Bioapplications of TREM2
Recombinant TREM2 protein finds wide applications in research, industrial production, and medical studies. In the research realm, TREM2 is particularly important for its role in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and in metabolic syndrome research, including obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis. In industry, it’s used in developing bioproducts and drugs, including technologies like biofilm interference and ELISA to study protein interactions with TREM2 ligands. In medical studies, TREM2 is linked to several diseases, offering new targets for immunotherapy in cancer and potential treatments for heart diseases. Overall, recombinant TREM2 protein is crucial for advancing disease mechanism understanding, drug target validation, and innovative treatment development.Case Study
Case Study 1: Schlepckow K. et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2020
TREM2 helps microglia shift from a regular to a disease-associated state. To boost TREM2, we aimed to limit its shedding by enzymes like α-secretase 10/17. We tested various monoclonal antibodies and found that antibody 4D9 could both prevent TREM2 shedding and activate phospho-SYK signaling. It promoted macrophage survival and enhanced microglia’s uptake of debris in lab tests. In Alzheimer’s mouse models, 4D9 decreased amyloid build-up, increased microglial TREM2, and reduced markers, steering microglia toward a protective, disease-associated state.-
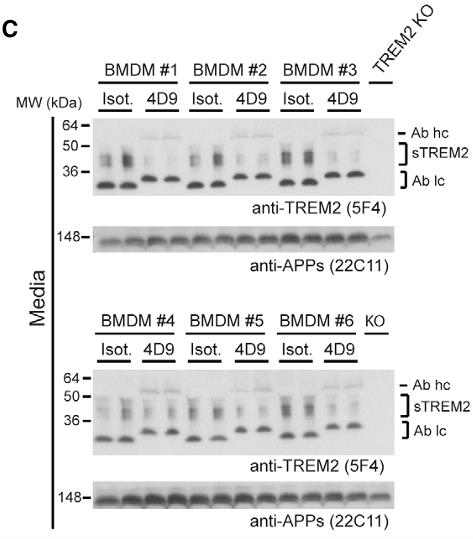 Fig1. Immunoblot analysis of sTREM2 in conditioned media from BMDM upon treatment with 4D9 and isotype antibodies.
Fig1. Immunoblot analysis of sTREM2 in conditioned media from BMDM upon treatment with 4D9 and isotype antibodies. -
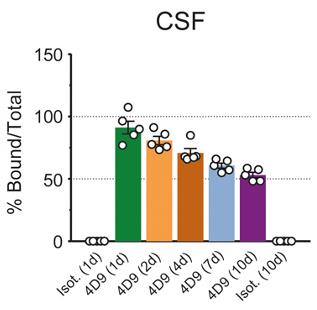 Fig2. Target engagement time course demonstrated near 100% 4D9‐bound sTREM2 in CSF of wild‐type mice at 24 h post‐dose.
Fig2. Target engagement time course demonstrated near 100% 4D9‐bound sTREM2 in CSF of wild‐type mice at 24 h post‐dose.
Case Study 2: Xiang X. et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2016
Immunotherapy is leading the charge in treating Alzheimer’s these days. It uses antibodies to latch onto amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) in the brain, clearing it out with the help of microglia cells. If microglia aren’t doing their job well, this process can hit a snag. Recently, some genetic tweaks in TREM2, crucial for microglia action, have been tied to a higher chance of getting Alzheimer’s. When TREM2 is lacking, microglia struggle to clear Aβ. We’ve dug into whether this affects how well these treatments work. Our findings suggest that anti-Aβ antibodies help clear amyloid plaques in a dose-dependent way, regardless of TREM2. But when TREM2 is missing, microglia and macrophages find it hard to take up the antibody-bound Aβ, leading to less plaque clearance. However, bumping up the antibody levels can offset this inefficiency in cells without TREM2.-
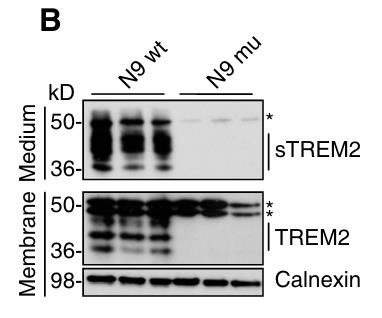 Fig3. Western blot analysis of lysates and media from wt and mutant N9 cells.
Fig3. Western blot analysis of lysates and media from wt and mutant N9 cells. -
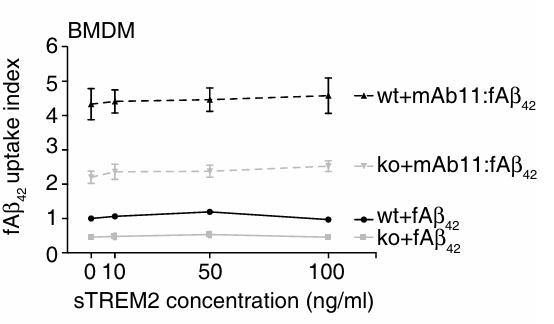 Fig4. Recombinant mouse sTREM2 does not rescue fAβ42 uptake in Trem2‐deficient BMDM.
Fig4. Recombinant mouse sTREM2 does not rescue fAβ42 uptake in Trem2‐deficient BMDM.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TREM2-3111H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TREM2-3111H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TREM2-1933H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TREM2-1933H)
Involved Pathway
TREM2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TREM2 participated on our site, such as Osteoclast differentiation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TREM2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Osteoclast differentiation | IL1R1,STAT2,MAPK1,NFKB1,GAB2,RAC1,LILRA4,TNFRSF11B,MAPK10,PIK3R1 |
-
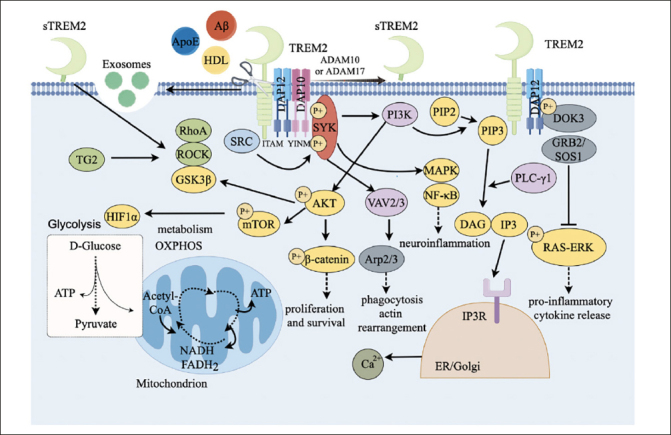 Fig1. TREM2 signaling pathway. (M Lin, 2024)
Fig1. TREM2 signaling pathway. (M Lin, 2024) -
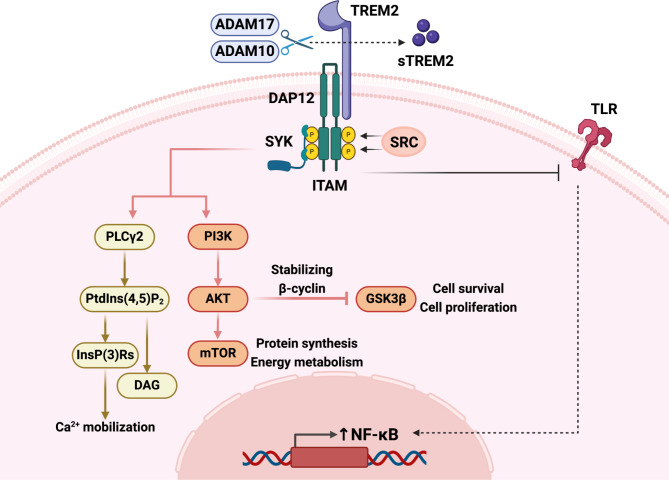 Fig2. Structural features and basic functions of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2). (Botao Zhu, 2024)
Fig2. Structural features and basic functions of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2). (Botao Zhu, 2024)
Protein Function
TREM2 has several biochemical functions, for example, lipopolysaccharide binding,lipoteichoic acid binding,peptidoglycan binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TREM2 itself. We selected most functions TREM2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TREM2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| scaffold protein binding | KCNH2,NLGN3,ATP2B4,CHRNA7,KRT5,GRIN2A,CACNA1G,P2RY1,CIT,SHANK3 |
| receptor activity | CADM2A,PAQR3B,OGFRL2,NLGN1,CUBN,GRIK3,TLR2,LDLR,UBXN6,GRIA3B |
| lipopolysaccharide binding | P2RX7,SCARB1,PTAFR,CD6,KIAA0644,DROSHA,SPON2,TLR2,LBP,TRIL |
| peptidoglycan binding | TLR2,PGLYRP1,RNASE7,PGLYRP3,PGLYRP4,NLRP3,NOD1,PGLYRP2 |
| lipoteichoic acid binding | CD14,CD6,LBP,TLR2 |
Interacting Protein
TREM2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TREM2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TREM2.
Resources
Research Area
Natural Killer Cell (NK Cell)Semaphorins, Plexin Receptors, and Related Molecules
Macrophage Markers
Monocyte Markers
Dendritic Cell Activation
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Satoh, J; Kawana, N; et al. A survey of TREM2 antibodies reveals neuronal but not microglial staining in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded postmortem Alzheimer's brain tissues. ALZHEIMERS RESEARCH & THERAPY 5:-(2013).
- Satoh, J; Tabunoki, H; et al. Immunohistochemical characterization of microglia in Nasu-Hakola disease brains. NEUROPATHOLOGY 31:363-375(2011).



