PPARG
-
Official Full Name
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPARs form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and these heterodimers regulate transcription of various genes. Three subtypes of PPARs are known: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-delta, and PPAR-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene is PPAR-gamma and is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. Additionally, PPAR-gamma has been implicated in the pathology of numerous diseases including obesity, diabetes, atherosclerosis and cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different isoforms have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
PPARG;peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma;GLM1;CIMT1;NR1C3;PPARG1;PPARG2;PPARgamma;PPAR gamma;PPAR-gamma;nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3;peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 1;peroxisome proliferator-activated nuclear receptor gamma variant 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cattle
- Rabbit
- Cynomolgus
- Zebrafish
- African clawed frog
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- Non
- MBP
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
What is PPARG protein?
PPARG gene (peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p25. This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPARs form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and these heterodimers regulate transcription of various genes. Three subtypes of PPARs are known: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-delta, and PPAR-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene is PPAR-gamma and is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation. The PPARG protein is consisted of 505 amino acids and PPARG molecular weight is approximately 57.6 kDa.
What is the function of PPARG protein?
PPARG protein, also known as PPARγ, is an important nuclear receptor that plays a variety of roles in the body, mainly including promoting the differentiation and maturation of fat cells, regulating lipid and sugar metabolism, controlling energy balance and appetite, participating in the regulation of inflammatory responses and immune cell function, and in some cases inhibiting or promoting tumor development. In addition, PPARγ also plays a role in the skeletal and cardiovascular systems and affects the thermogenic function of brown adipose tissue, and is a key molecule in maintaining metabolic health and immune homeostasis.
PPARG related signaling pathway
The PPARG-related signaling pathway is a critical component of cellular metabolism and differentiation, primarily mediated by the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma (PPARG). This nuclear receptor plays a pivotal role in adipogenesis, lipid storage, glucose homeostasis, and inflammation regulation. Upon activation by ligands such as thiazolidinediones or endogenous fatty acids, PPARG forms heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR) and binds to specific DNA response elements within the promoter regions of target genes. This interaction modulates gene transcription, leading to increased expression of proteins involved in insulin sensitivity enhancement, fatty acid uptake and storage, and adipocyte differentiation. Additionally, PPARG has an anti-inflammatory effect by repressing pro-inflammatory cytokine production through interference with nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) signaling pathways. Dysregulation of PPARG signaling is implicated in metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases, highlighting its importance as a therapeutic target for these conditions.
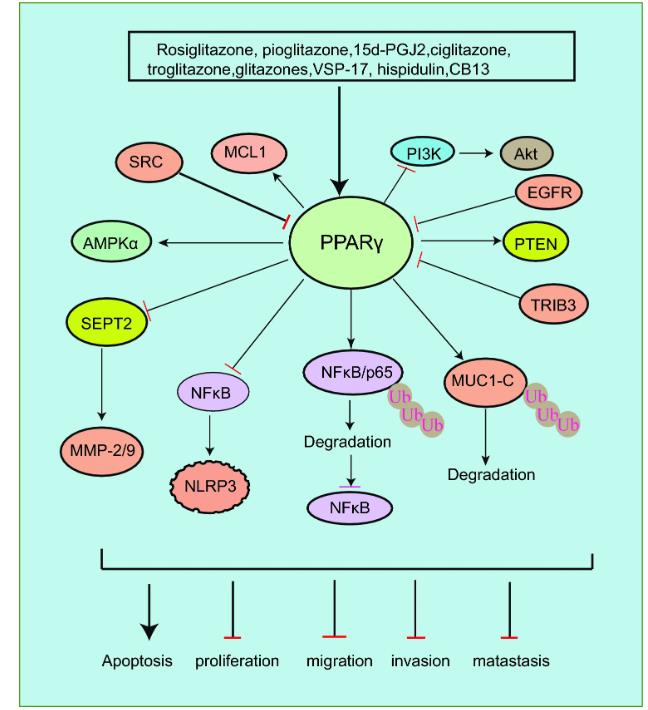
Fig1. Activation of PPARγ inhibits tumor progression. (Mingjun Chen, 2024)
PPARG related diseases
Mutations or imbalances in PPARG activity can lead to various disorders. Type 2 diabetes mellitus stands out as a prominent condition linked to PPARG dysfunction, where reduced insulin sensitivity and impaired glucose metabolism are central features. Obesity is another closely related disease, characterized by excessive fat accumulation due to abnormal adipocyte differentiation and lipid handling. Cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis and hypertension, often result from the pro-atherogenic lipid profiles and inflammatory states induced by PPARG dysregulation. Additionally, certain cancers, such as colorectal and breast cancer, have been associated with altered PPARG expression, influencing cell proliferation and survival mechanisms. Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease also show connections to PPARG, given its role in suppressing immune system overactivity.
Bioapplications of PPARG
PPARγ is a nuclear receptor capable of regulating gene expression by binding to specific ligands, affecting a variety of cellular functions and metabolic pathways. In clinical studies, rhPPARγ and its agonists are used to treat type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancers. For example, PPARγ agonists can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels while protecting vascular health through anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects in cardiovascular disease. In addition, the development of selective PPARγ modulators (SPPARMs) provides new strategies for reducing adverse reactions associated with PPARγ activation, which may reduce side effects such as weight gain and edema while preserving therapeutic effects. These advances indicate that rhPPARγ has important value in biomedical research and clinical therapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kristina Kraus, 2018
This study reveals that a fragment of the mouse cell adhesion molecule L1, produced by proteolytic cleavage, can enter the nucleus and interact with nuclear receptors like estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), PPARγ, and RXRβ, through specific LXXLL and FXXLF motifs. Disrupting these motifs with mutations hinders this interaction and leads to deficits in motor coordination, learning, memory, and cerebellar synaptic connectivity when introduced into mouse embryos, resembling the effects of L1 deficiency.
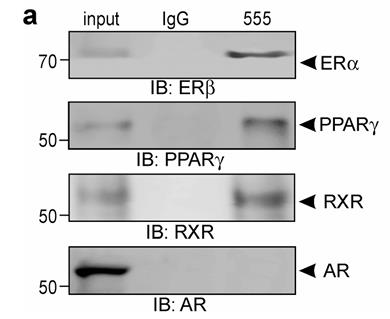
Fig1. The immunoprecipitates were probed by Western blot analysis with antibodies against ERβ, RXR, PPARγ, and AR.
Fig2. Nuclear L1 interacts with nuclear receptors after treated with recombinant PPARγ.
Case Study 2: Hannah Harris, 2023
DEHP, a common plasticizer, and its metabolite MEHP are endocrine disruptors that may affect health by interacting with nuclear hormone receptors like PPARs. The toxicity of their stereoisomers hasn't been extensively studied. Researchers synthesized these molecules' enantiomers and tested their PPARγ binding affinity using thermal shift assay (TSA). Enantiomerically pure primary alcohols were obtained through enzymatic resolution and then esterified to produce MEHP and DEHP enantiomers. Secondary metabolites were also synthesized. Preliminary TSA results indicated the need for further optimization to accurately assess PPARγ binding.
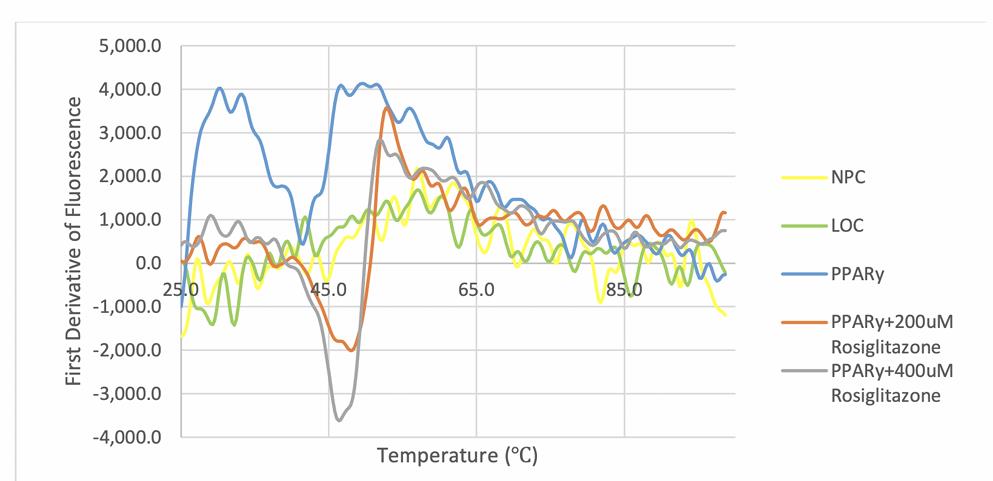
Fig3. Both PPARγ + rosiglitazone plots show a rightward shift of fluorescence maxima,
corresponding to a higher TM.
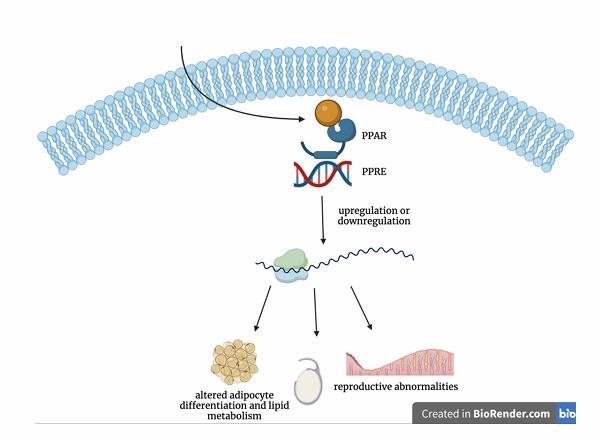
Fig4. Overview of the mechanism of action of transcriptional regulation by PPARγ-ligand (orange sphere) complexes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PPARG-6217H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PPARG-5941H)
Involved Pathway
PPARG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PPARG participated on our site, such as PPAR signaling pathway,AMPK signaling pathway,Osteoclast differentiation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PPARG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Osteoclast differentiation | MITF,LILRB4,NFKB1,FOSB,TYK2,NOX1,IFNAR2,FYN,MAP3K14,TGFB2 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | TMPRSS2,HIST1H3G,REL,ITGB7,PLAU,PROM1,ETV4,ETV5,SIX1,MMP3 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | SLC27A4,ACAA1,ADIPOQ,ACSBG2,FADS2,ACADL,APOA1,RXRAA,CYP7A1A,FABP4 |
| Thyroid cancer | MAP2K2,CDH1,CCND1,TRP53,MAP2K1,RET,CCDC6,RXRA,NCOA4,NRAS |
| Pathways in cancer | HIF1A,PTGS2,LPAR4,RET,PIK3R2,SOS1,PLCB4,AKT1,PLCB3,RXRG |
| Huntingtons disease | MT-ATP6,CREB3L2,COX6B1,NDUFA4L2,NDUFA8,SDHB,CREB3L3,COX6C,DCTN2,COX8C |
| AMPK signaling pathway | RHEB,PIK3CA,FASN,LEPR,HNF4A,RAB2A,CAB39L,RAB10,LEP,SCD5 |
Protein Function
PPARG has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA polymerase II regulatory region DNA binding,RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, ligand-activated sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PPARG itself. We selected most functions PPARG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PPARG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific binding | STAT3,BARHL2,BHLHA15,AIRE,ARID3A,SOHLH2,CREB3L3,GRHL3,NR1I3,CSRNP2 |
| metal ion binding | CYP1C2,SOD3A,ZDHHC24,PCGF5A,CLCA2,ZNF592,HBAE3,EFCAB11,EBF1,BCL6A |
| WW domain binding | SHISA5,SCNN1G,DNM2,ATCAY,CDC25C,TRAF4,TCEAL1,TRP63,TNK2,FAM189B |
| arachidonic acid binding | S100A8,ALOX5AP,STX3,S100A9,CYP4F14,CYP4A14 |
| contributes_to sequence-specific DNA binding | EPAS1,FIGLA,HDAC4,HNRNPAB,TRIM28,ARNT,SMAD4,HIF1A,NEUROD1,TCF3 |
| drug binding | PDE10A,HTR1B,PYGB,NAMPT,PPARA,DHFR,P2RX4,FASN,PPARD,GSTP2 |
| protein phosphatase binding | GRB2,NEK2,TRAF2,MAP3K5,HSF4,PPP1R3C,ANAPC7,DLG3,PPP6R1,VCP |
| protein binding | ILF2,SPN,RHOG,NR1H2,AGPAT4,MALT1,TXK,CMTM2A,RORB,SCAMP1 |
| core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | SIRT1,SP1,PDX1,ESR2,TRP53,CREM,H2AFY,SOX1,SOHLH2,KLF10 |
Interacting Protein
PPARG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PPARG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PPARG.
Sirt1;MED1;SIRT1;Prdm16;ucp1_mouse_gene
Resources
Research Area
Tumor SuppressorsAdipocytokines
Transcription Regulators in VSMC
Alzheimer's Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Therapeutic Targets
Macrophage Markers
Adipogenesis Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Schneider, C; Nobs, SP; et al. Alveolar Macrophages Are Essential for Protection from Respiratory Failure and Associated Morbidity following Influenza Virus Infection. PLOS PATHOGENS 10:-(2014).
- Oysyannikova, IG; White, SJ; et al. Leptin and leptin-related gene polymorphisms, obesity, and influenza A/H1N1 vaccine-induced immune responses in older individuals. VACCINE 32:881-887(2014).



