PNPLA3
-
Official Full Name
patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a triacylglycerol lipase that mediates triacylglycerol hydrolysis in adipocytes. The encoded protein, which appears to be membrane bound, may be involved in the balance of energy usage/storage in adipocytes. -
Synonyms
PNPLA3;patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3;adiponutrin , ADPN, C22orf20, chromosome 22 open reading frame 20;patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3;adiponutrin;dJ796I17.1;FLJ22012;Acylglycerol O acyltransferase;ADPN;C22orf20;Calcium independent phospholipase A2 epsilon;iPLA(2)epsilon;Patatin like phospholipase domain containing 3;iPLA2-epsilon;OTTHUMP00000197822;OTTHUMP00000197823;acylglycerol O-acyltransferase;calcium-independent phospholipase A2-epsilon
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat germ cell free in vitro
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PNPLA3 Protein?
PNPLA3 gene (patatin like phospholipase domain containing 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q13. This is a protein containing a phospholipase domain, which is mainly involved in lipid metabolism. PNPLA3 is highly expressed in the liver, adipose tissue and adrenal cortex, and is localized on lipid droplets in hepatocytes. This protein has the dual functions of triglyceride lipase and acyltransferase, and is involved in the hydrolysis of triglycerides and retinol esters. The role of PNPLA3 in lipid metabolism includes mobilizing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) to support the lipidation of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), which is essential for the secretion of large-sized VLDL by the liver. The PNPLA3 protein is consisted of 481 amino acids and PNPLA3 molecular weight is approximately 52.9 kDa.What is the Function of PNPLA3 Protein?
PNPLA3 protein plays a key role in lipid metabolism, and it is involved in the hydrolysis of triglycerides (TG) and the mobilization of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). PNPLA3 protein has triglyceride lipase activity and is able to hydrolyze triglycerides. In addition to lipase activity, PNPLA3 also has acyltransferase activity, which contributes to the synthesis of phospholipids. In addition, PNPLA3 protein also plays an important role in energy metabolism and fat metabolism. PNPLA3 protein is expressed at the highest level in human hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells, and acts as a lipid droplet regulator. It is a membrane protein that is closely associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplet membranes, and its expression is regulated by insulin through SREBP-1c.
Fig1. A working model for the PNPLA3 function on lipid droplet. (Xiaocheng Charlie Dong, 2019)
PNPLA3 Related Signaling Pathway
The PNPLA3 protein plays a central role in lipid metabolism, especially in the liver. It affects lipid balance in the liver by regulating the synthesis and breakdown of triglycerides. The expression of PNPLA3 is affected by insulin signaling. Insulin affects the activity of PNPLA3 by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which plays a key role in cell proliferation, metabolic regulation, and inhibition of apoptosis. IL-6 affects the expression and function of PNPLA3 by activating the STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby affecting lipid metabolism and inflammatory response in the liver. The expression and function of PNPLA3 may be regulated by the MAPK signaling pathway, affecting lipid metabolism and inflammatory response in the liver.PNPLA3 Related Diseases
The PNPLA3 protein is closely associated with the development of a variety of diseases, especially non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Specific variants of the PNPLA3 gene, such as I148M at the rs738409 site, are associated with an increased risk of NAFLD and may lead to the accumulation of triglycerides and enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids in hepatocytes, thereby increasing the risk of NASH and HCC. In addition, PNPLA3 variants are also associated with cardiovascular disease, mitochondrial dysfunction, and lipid metabolism disorders. The development of these diseases is closely related to metabolic disorders, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammatory responses affected by PNPLA3 gene variants, making PNPLA3 a potential target for the treatment of these diseases.Bioapplications of PNPLA3
In medical research, PNPLA3 gene variation is closely associated with susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which provides important information for genetic research and personalized treatment of NAFLD. In addition, the role of PNPLA3 in regulating liver lipid metabolism makes it a potential target for drug development. For example, inhibiting PNPLA3 expression by activating the AMPK pathway may help reduce liver fat accumulation and provide a new strategy for the treatment of NAFLD. In scientific research, functional studies of PNPLA3 help understand the mechanism of liver secretion of very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and its role in lipid metabolism, which is crucial for the development of new therapies for metabolic diseases. In addition, research on PNPLA3 also involves multi-omics analysis, which helps to reveal key molecular roles, pathways and interactions in complex biological systems, thereby playing a role in cancer research, drug discovery, personalized medicine and systems biology.Case Study
Case Study 1: Scott M Johnson, 2024
The PNPLA3 I148M variant has a strong link with fatty liver disease. Recent research suggests that this mutant version acts as a blocker for the lipolysis process led by PNPLA2/ATGL, leaving the normal role of PNPLA3 still unclear. Even though lab studies show that PNPLA3 can break down triglycerides, it hasn’t been proven to work as a lipase in living organisms yet. This study points out that PNPLA3 specifically breaks down polyunsaturated triglycerides, helping to release polyunsaturated fatty acids for phospholipid desaturation and boosting the liver’s release of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. When conditions are ripe for fat production, mice that have a liver-specific removal or a sudden reduction of PNPLA3 show worsened fatty liver and lowered levels of VLDL-triglycerides in the blood. In the same way, mice with the I148M mutation show less liver triglyceride release when exposed to factors that encourage fat production.-
 Fig1. EM analysis of lipoprotein particles from control and PNPLA3 ASO mice +T09.
Fig1. EM analysis of lipoprotein particles from control and PNPLA3 ASO mice +T09. -
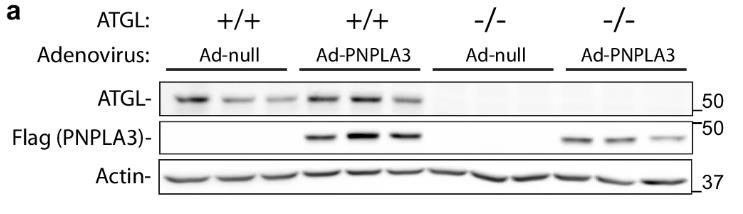 Fig2. Immunoblotting analysis of ATGL and FLAG-PNPLA3 expression in the liver.
Fig2. Immunoblotting analysis of ATGL and FLAG-PNPLA3 expression in the liver.
Case Study 2: Carlo Pirazzi, 2014
Retinoids are important dietary components that are stored in the form of retinyl esters within both the retina and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). These HSCs are integral to the process of fibrogenesis seen in chronic liver diseases. Up to now, the exact enzyme that facilitates the breakdown and subsequent release of retinyl esters from HSCs remains unidentified, and the connection between retinoid metabolism and liver disease has yet to be clearly defined. Researchers propose that the protein known as patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 (PNPLA3) could play a role in the metabolism of retinol within HSCs. To investigate, we looked into this both with primary human HSCs and in a study involving 146 people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Here’s what we found: PNPLA3 is highly present in human HSCs, and its levels change based on retinol availability and insulin levels. When there’s more PNPLA3, the lipid droplet content in HSCs decreases. PNPLA3 helps HSCs release retinol when insulin is present. Also wild-type PNPLA3 can break down retinyl palmitate into retinol and palmitic acid. However, this capability drops significantly in the PNPLA3 148M mutation, a common variant linked to liver fibrosis and the development of liver cancer. Furthermore, the PNPLA3 I148M mutation is an independent factor influencing levels of retinol-binding protein 4 in the bloodstream, which is a good indicator of retinol levels in humans.-
 Fig3. Immunoblot showing PNPLA3 and PNPLA2 protein expression in pHSCs.
Fig3. Immunoblot showing PNPLA3 and PNPLA2 protein expression in pHSCs. -
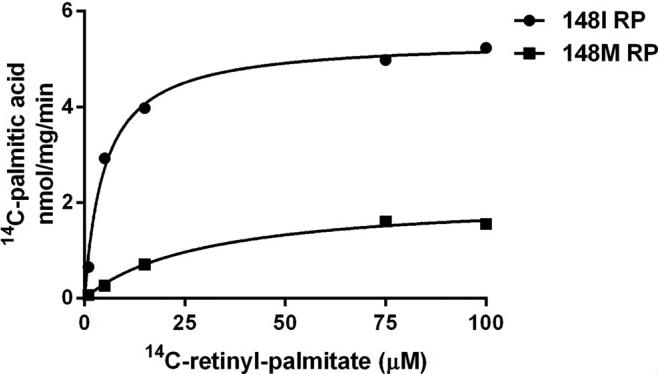 Fig4. PNPLA3 148I and 148M purified proteins were incubated with increasing concentrations of radiolabeled retinyl palmitate.
Fig4. PNPLA3 148I and 148M purified proteins were incubated with increasing concentrations of radiolabeled retinyl palmitate.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PNPLA3-367H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PNPLA3-367H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PNPLA3-26H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PNPLA3-26H)
Involved Pathway
PNPLA3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PNPLA3 participated on our site, such as Glycerolipid metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PNPLA3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glycerolipid metabolism | CELL,GLYCTK,Cel,ALDH2,CEL.1,LIPCA,ALDH3A2,PNLIPRP2,AGPAT5,PPAP2A |
| Metabolic pathways | COX5A,ACSBG2,PTGES3A,ADH4,GALCB,CD38,FASN,DHRS3B,FBP2,SMPD2A |
-
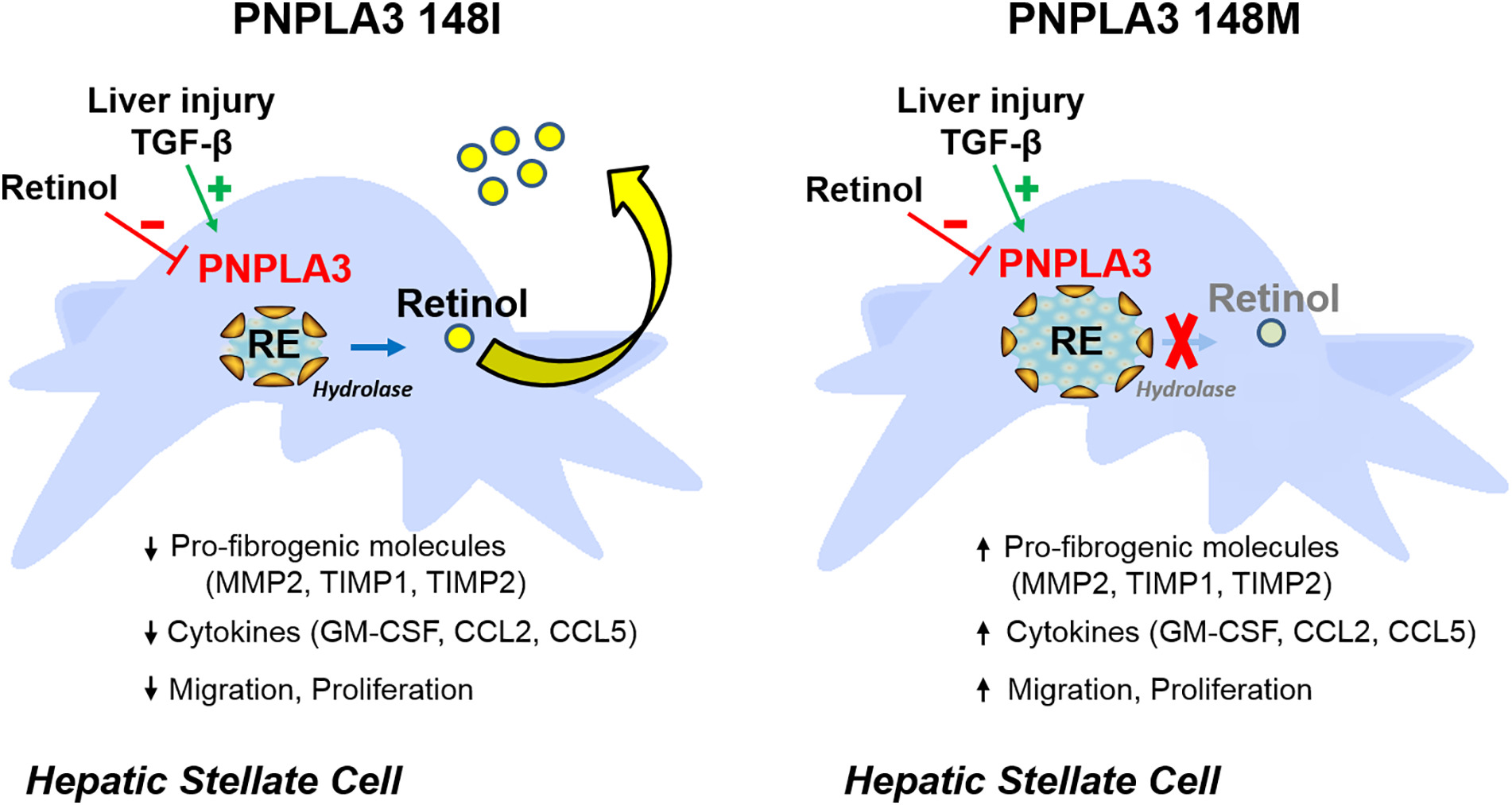 Fig1. Role of PNPLA3 in hepatic stellate cells. (Piero Pingitore, 2018)
Fig1. Role of PNPLA3 in hepatic stellate cells. (Piero Pingitore, 2018)
-
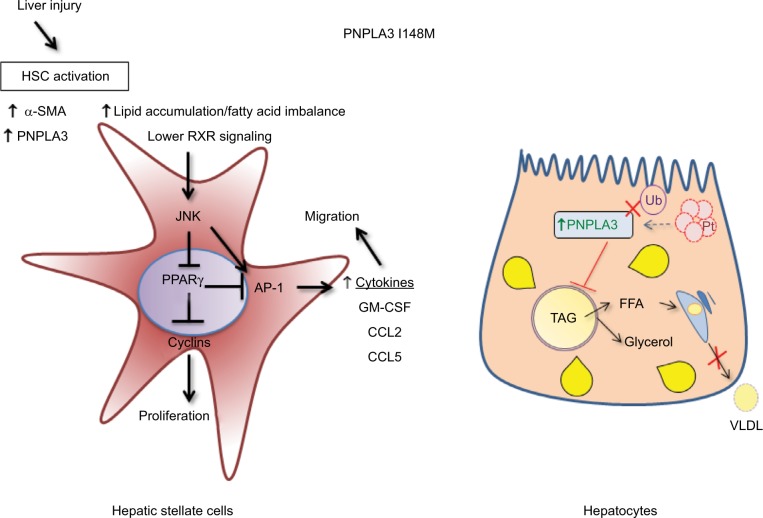 Fig2. Differential molecular mechanisms of PNPLA3 I148M in HSCs and hepatocytes. (Francesca Virginia Bruschi, 2017)
Fig2. Differential molecular mechanisms of PNPLA3 I148M in HSCs and hepatocytes. (Francesca Virginia Bruschi, 2017)
Protein Function
PNPLA3 has several biochemical functions, for example, diolein transacylation activity,mono-olein transacylation activity,phospholipase A2 activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PNPLA3 itself. We selected most functions PNPLA3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PNPLA3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| triglyceride lipase activity | LIPE,CEL.1,CES3,CES1D,Cel,PNLIPRP3,PNLIP,PNPLA4,AADAC,PNLIPRP2 |
| phospholipase A2 activity | PLA2G2E,OC90,ABHD3,PLA2G4AA,RARRES3,PLA2G10,LCAT,PLA2G16,PLA2G2A,PLA2G2F |
Interacting Protein
PNPLA3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PNPLA3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PNPLA3.
AKT2;SNX27
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Huang, CF; Dai, CY; et al. Association of diabetes and PNPLA3 genetic variants with disease severity of patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY 62:512-518(2015).
- Zhou, Y; Llaurado, G; et al. Circulating triacylglycerol signatures and insulin sensitivity in NAFLD associated with the E167K variant in TM6SF2. JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY 62:657-663(2015).


