Notch2
-
Official Full Name
notch 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the Notch family. Members of this Type 1 transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple, different domain types. Notch family members play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. The Notch signaling network is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway which regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signaling pathway that plays a key role in development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remain to be determined. This protein is cleaved in the trans-Golgi network, and presented on the cell surface as a heterodimer. This protein functions as a receptor for membrane bound ligands, and may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011] -
Synonyms
NOTCH2;notch 2;hN2;AGS2;HJCYS;neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2;Notch homolog 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- HEK293
- E.coli
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- His
- Fc
- Non
- Avi
- GST
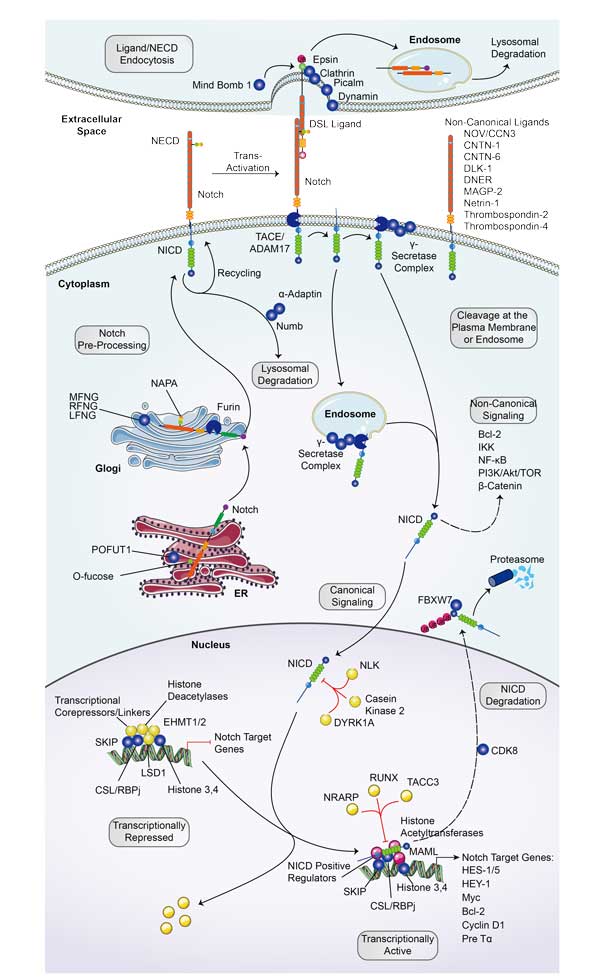
Involved Pathway
Notch2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Notch2 participated on our site, such as Dorso-ventral axis formation,Notch signaling pathway,Thyroid hormone signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Notch2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Dorso-ventral axis formation | GRB2A,CPEB1B,NOTCH1B,ETS2,SPIRE2,NOTCH1A,PIWIL2,CPEB1,ETV7,KRAS |
| Notch signaling pathway | DTX1,CTBP2,KAT2B,RBPJB,DLA,HER6,MFAP5,HER12,DTX2,ADAM12 |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | TTC6,WNT3A,MDM4,ZEB1,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,PRKCG,PRKCA,PRKCE,BMF,CDCA5 |
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | STAT1,PRKCA,PIK3R1,PLCD1,TSC2,RXRB,PLN,SLC9A1,SLCO1C1,NCOA1 |
Protein Function
Notch2 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,protein binding,receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Notch2 itself. We selected most functions Notch2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Notch2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | CALR,CDH16,AIF1,DLB,NECAB2,CANT1A,S100S,PCDHB13,EFCAB2,C1rb |
| protein binding | PLXND1,POLA1,RILP,C3orf52,SUV420H2,NAMPT,GRAP,SEC13,SRP14,KIF3A |
| receptor activity | PROCR,DERL1,NEO1,GUCY1B3,MED12,NOTCH1B,PLXNA1,GRIA3B,VMN1R41,LILRA3 |
Interacting Protein
Notch2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Notch2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Notch2.
ANKRD28;CRKL;IL24;IL13RA2;SMAD1;CST6;ysuR;ITIH5;EPSTI1;FAM84B;MTA3;PSMC3IP;KLK5;ST14;Bmpr1a;RBPJ;Lats2
Notch2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Tumor SuppressorsNotch Pathway
Endothelial Cell Development Molecules
Notch Family
Neural Stem Cell Markers
Neural Crest Cell Markers
Dendritic Cell Development
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Huntzicker, EG; Hotzel, K; et al. Differential Effects of Targeting Notch Receptors in a Mouse Model of Liver Cancer. HEPATOLOGY 61:942-952(2015).
- Minuzzo, S; Agnusdei, V; et al. DLL4 regulates NOTCH signaling and growth of T acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in NOD/SCID mice. CARCINOGENESIS 36:115-121(2015).