GPLD1
-
Official Full Name
glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 -
Overview
Many proteins are tethered to the extracellular face of eukaryotic plasma membranes by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. The GPI-anchor is a glycolipid found on many blood cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a GPI degrading enzyme. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 hydrolyzes the inositol phosphate linkage in proteins anchored by phosphatidylinositol glycans, thereby releasing the attached protein from the plasma membrane. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
GPLD1;glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1;PLD;GPIPLD;PIGPLD;GPIPLDM;PIGPLD1;phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase D;GPI-PLD;PI-G PLD;GPI-specific phospholipase D;glycoprotein phospholipase D;glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1, isoform 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
Background
What is GPLD1 protein?
GPLD1 gene (glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p22. Many proteins are tethered to the extracellular face of eukaryotic plasma membranes by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. The GPI-anchor is a glycolipid found on many blood cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a GPI degrading enzyme. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase D1 hydrolyzes the inositol phosphate linkage in proteins anchored by phosphatidylinositol glycans, thereby releasing the attached protein from the plasma membrane. The GPLD1 protein is consisted of 840 amino acids and GPLD1 molecular weight is approximately 92.3 kDa.
What is the function of GPLD1 protein?
The GPLD1 protein is a specific enzyme that targets glycosphingomyelin (GPI) anchoring molecules to perform biological functions by cutting membrane-associated GPI molecules. GPLD1 is abundant in serum at concentrations of about 5-10 μg/mL. Studies have shown that GPLD1 plays an important role in the pathogenesis of many chronic diseases, including lipid and glucose metabolism disorders, cancer, and neurological disorders. In addition, there is also research showing that exercise training can restore diabetes-induced changes in circulating GPLD1 levels, suggesting that exercise may have a positive effect on chronic disease by regulating GPLD1 levels.
GPLD1 Related Signaling Pathway
GPLD1 (glycosphingomyelin specific Phospholipase D) is a special enzyme whose primary role is to hydrolyze glycosphingomyelin (GPI) anchoring molecules, which are the anchoring structures of many proteins on cell membranes. The signaling pathways involved in GPLD1 include but are not limited to: the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; The drug alogliptin inhibits hyperglycemy-induced fibrosis of myocardial fibroblasts via the miR-497-5p/GPLD1 signaling pathway. It has also been linked to the neurodevelopmental and cognitive benefits of exercise.
GPLD1 Related Diseases
GPLD1 may be involved in lipid and glucose metabolism disorders, affecting the development of metabolic diseases such as diabetes. Studies have shown that GPLD1 is associated with improved neurodevelopment and cognitive function and may play a role in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. The change of GPLD1 expression level in some cancers may be related to the occurrence and development of tumors, and may affect the proliferation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. GPLD1 may be involved in the function regulation of immune cells and is related to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. GPLD1, as an enzyme abundant in serum, may be involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases, including hepatitis and cirrhosis. In kidney disease, GPLD1 may be involved in the process of kidney damage and fibrosis.
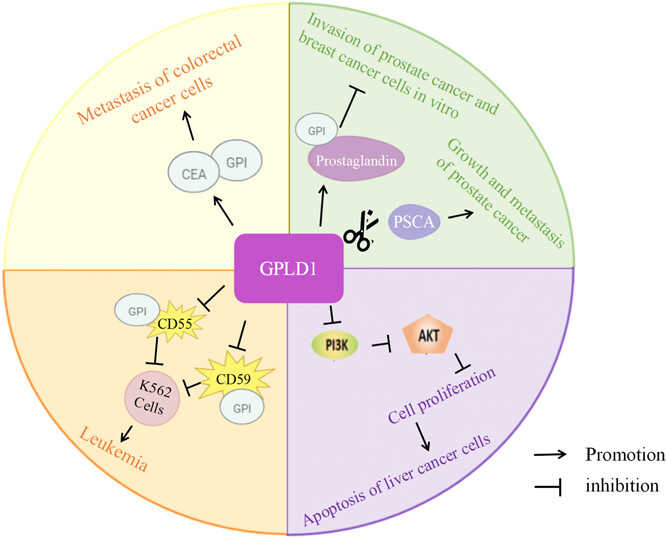
Fig1. The molecular mechanism of GPLD1 involvement in cancers progression. (Jing Cao, 2023)
Bioapplications of GPLD1
The study of the mechanism of action of GPLD1 in a variety of chronic diseases contributes to a deeper understanding of its role in disease development, particularly in metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Due to its critical role in certain pathological processes, GPLD1 is considered a potential drug target. The development of small molecule drugs or biologics that target GPLD1 may help treat related diseases. Changes in the expression level of GPLD1 may be associated with certain diseases, so it can be used as a diagnostic marker for early detection and monitoring of diseases. The role of GPLD1 in cell adhesion and migration may contribute to the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, promoting tissue repair and regeneration.
Case Study
Case Study 1: M A Deeg, 2001
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D (GPI-PLD) is abundant in serum and associates with high density lipoproteins (HDL). Researchers have characterized the distribution of GPI-PLD among lipoproteins in human plasma. Apolipoprotein (apo)-specific lipoproteins containing apoB (Lp[B]), apoA-I and A-II (Lp[A-I, A-II]), or apoA-I only (Lp[A-I]) were isolated using dextran sulfate and immunoaffinity chromatography. Further characterization of the GPI-PLD-containing lipoproteins by gel-filtration chromatography and nondenaturing polyacrylamide and agarose gel electrophoresis revealed that these apoA-I-containing particles/complexes were small (8 nm) and migrated with pre-beta particles on agarose electrophoresis. Immunoprecipitation of GPI-PLD with a monoclonal antibody to GPI-PLD co-precipitated apoA-I and apoA-IV but little or no apoA-II, apoC-II, apoC-III, apoD, or apoE. In vitro, apoA-I but not apoA-IV or bovine serum albumin interacted directly with GPI-PLD, but did not stimulate GPI-PLD-mediated cleavage of a cell surface GPI-anchored protein.
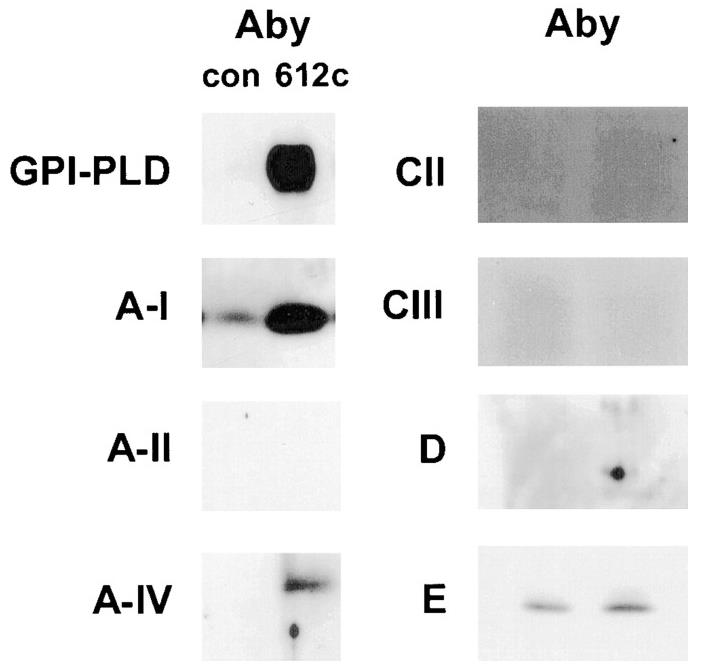
Fig1. Immunoprecipitation of GPI-PLD complexes from human plasma.
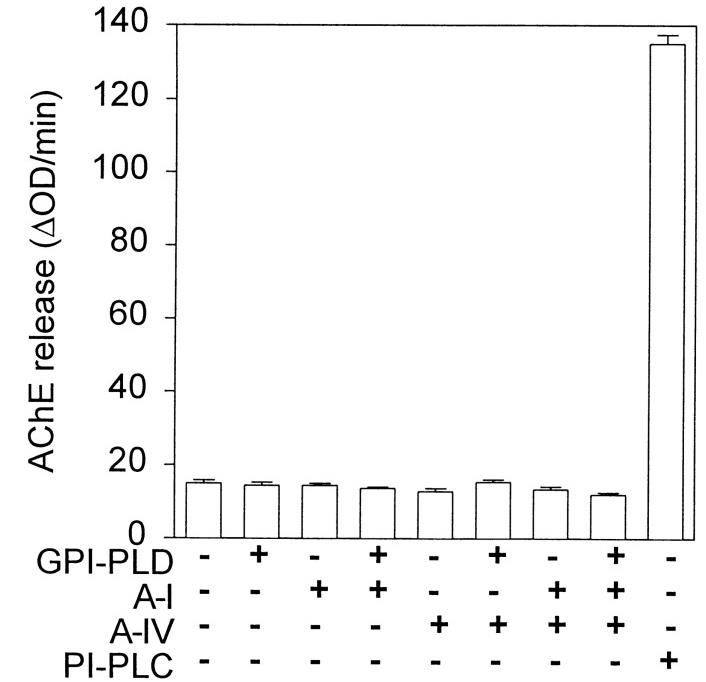
Fig2. Effect of GPI-PLD on release of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) from porcine erythrocytes.
Case Study 2: Shigeki Masuda, 2019
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D (GPI-PLD) is an enzyme that specifically cleaves GPI anchors. Previous human studies suggested the relationship of GPI-PLD to insulin resistance, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, GPI-PLD mRNA was most highly expressed in the liver, and the hepatic mRNA level and circulating concentration of GPI-PLD were significantly augmented in diabetic mice. To investigate in vivo functions of GPI-PLD, researchers generated GPI-PLD knockout (GP-KO) mice. Mice lacking GPI-PLD exhibited the amelioration of glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis under high-fat and high-sucrose diet. Furthermore, diacylglycerol (DAG) content was significantly decreased, and PKCε activity was suppressed in the livers of GP-KO mice. In vitro knockdown and overexpression experiments of GPI-PLD using rat primary hepatocytes showed the GPI-PLD-dependent regulation of intracellular DAG content.

Fig3. Effect of glucose on GPI-PLD mRNA level in rat primary hepatocytes.
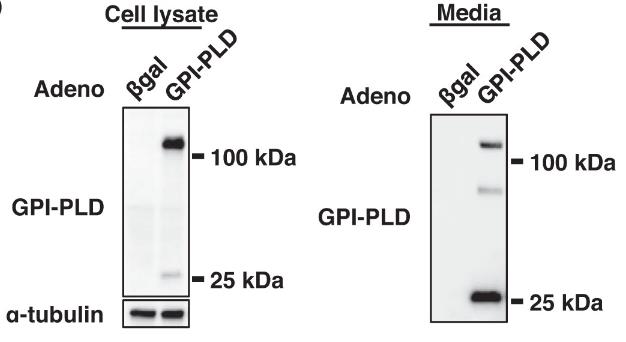
Fig4. Immunoblots for GPI-PLD from cell lysates and culture media after 24 h of infection.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GPLD1-2251H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GPLD1-5160H)
Involved Pathway
GPLD1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GPLD1 participated on our site, such as Glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GPLD1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Glycosylphosphatidylinositol(GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | PIGH,PIGS,PIGO,GPAA1,PIGX,PIGW,PIGC,PIGM,PIGB,PIGQ |
Protein Function
GPLD1 has several biochemical functions, for example, glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase D activity,phospholipase D activity,sodium channel regulator activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GPLD1 itself. We selected most functions GPLD1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GPLD1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| sodium channel regulator activity | SCN3B,SCN1BA,SGK2B,PKP2,FXYD2,TMPRSS3,SGK2,FXYD7,SCN1BB,FGF13 |
| phospholipase D activity | PLD3,PLD1A,PLD4,HMOX1,PLD1,PLD2 |
Interacting Protein
GPLD1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GPLD1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GPLD1.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sanjabi, B; Dashty, M; et al. Lipid droplets hypertrophy: a crucial determining factor in insulin regulation by adipocytes. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 5:-(2015).
- Deeg, MA; Xuei, XL; et al. Genetic variation of GPLD1 associates with serum GPI-PLD levels: A preliminary study. BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-MOLECULAR AND CELL BIOLOGY OF LIPIDS 1821:381-385(2012).



