S100A9
-
Official Full Name
S100 calcium binding protein A9 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in the inhibition of casein kinase and altered expression of this protein is associated with the disease cystic fibrosis. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
S100A9;S100 calcium binding protein A9;MIF;NIF;P14;CAGB;CFAG;CGLB;L1AG;LIAG;MRP14;60B8AG;MAC387;protein S100-A9;MRP-14;calgranulin B;calgranulin-B;calprotectin L1H subunit;leukocyte L1 complex heavy chain;migration inhibitory factor-related protein 14;S100 calcium-binding protein A9 (calgranulin B)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Cattle
- Mouse
- Dog
- Bovine
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Insect Cell
- Human Cell
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293 cells
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293
- E. coli
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- His&SUMO
- His&T7
- StrepII
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
- His&Myc&SUMO
- GST
- His&Myc&B2M
Background
What is S100A9 protein?
S100A9 gene (S100 calcium binding protein A9) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. This protein may function in the inhibition of casein kinase and altered expression of this protein is associated with the disease cystic fibrosis. This antimicrobial protein exhibits antifungal and antibacterial activity. The S100A9 protein is consisted of 114 amino acids and S100A9 molecular weight is approximately 13.2 kDa.
What is the function of S100A9 protein?
The S100A9 protein, also known as calgranulin B or MRP14, is a small calcium-binding protein that belongs to the S100 family of proteins. It primarily functions in the regulation of inflammatory responses and cellular differentiation. S100A9 often forms homodimers or heterodimers with S100A8 (calgranulin A or MRP8) to exert its biological activities. These dimers are involved in the modulation of cytoskeletal dynamics, cell motility, and the activation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. They play a role in host defense mechanisms against pathogens and are implicated in various inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and certain cancers. The expression of S100A9 is upregulated during inflammation and can be detected in neutrophils and keratinocytes, highlighting its involvement in immune response and tissue remodeling processes.
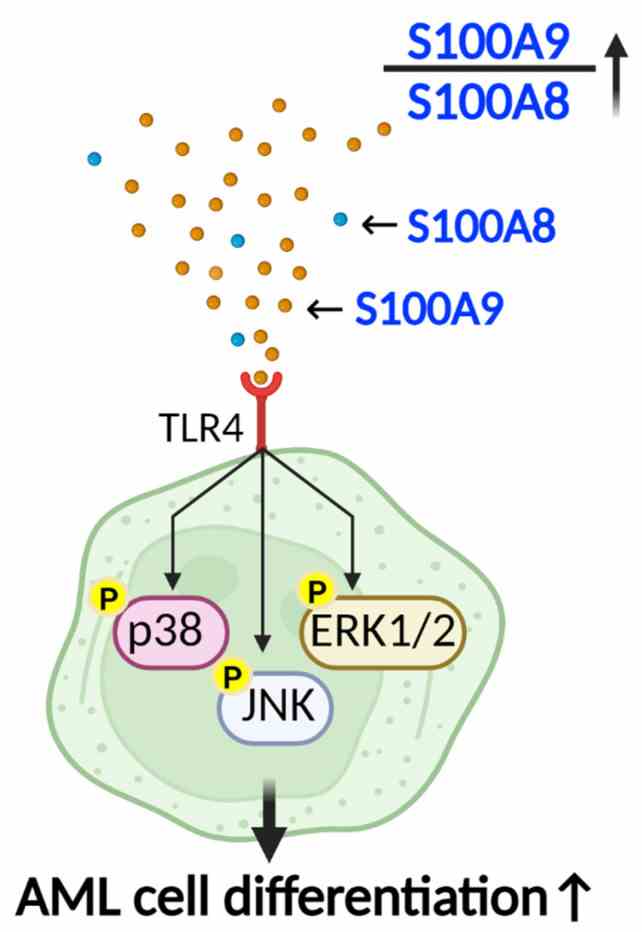
Fig1. AML cell differentiation by S100A9. (Farnaz Razmkhah, 2023)
S100A9 related signaling pathway
S100A9 is a calcium-binding protein that plays a significant role in immune responses and inflammation. It is involved in the modulation of leukocyte recruitment and cytokine secretion during inflammation by interacting with pattern recognition receptors such as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). S100A9 has been implicated in acute lung injury, where it can exacerbate inflammation by promoting M1 macrophage polarization and pyroptosis via the TLR4/MyD88/NFκB signaling pathway. Additionally, S100A9 is involved in the pathogenesis of tendinopathy, a condition characterized by chronic inflammation and impaired tissue repair, where it may participate in a positive feedback mechanism that perpetuates inflammation.
S100A9 related diseases
S100A9 is a member of the S100 family of proteins, which usually form a heterodimer with S100A8 called calprotectin. This protein plays a role in a variety of inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and certain types of cancer such as breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer. The expression level of S100A9 may serve as a biomarker to monitor disease activity in these diseases. In addition, S100A9 may promote chronic inflammation, tumor growth, and metastasis during tumor development. In animal models of autoimmune diseases, blocking S100A8/A9 activity may have beneficial effects on disease activity.
Bioapplications of S100A9
S100A9 is usually produced by activated mononuclear macrophages, neutrophils, and glial cells during inflammation and is involved in the regulation of inflammatory and immune responses. In oncology, S100A9 expression levels are associated with the development of a variety of cancers, including breast, lung, and prostate cancers, making it a potential target for cancer treatment. In addition, S100A9 also plays a role in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, and its inhibitors may help control disease activity. S100A9 is also considered a potential biomarker in cardiovascular disease to help predict the risk of heart failure after acute myocardial infarction. In diabetes treatment, S100A9 has been found to regulate blood sugar, lipids and ketone bodies, offering a potential non-insulin-dependent treatment approach. These advances indicate that S100A9 has important value in biomedical research and clinical applications.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yan Le, 2024
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition marked by redness and pimples due to inflammation. S100A9, known for its role in inflammatory diseases, has been linked to rosacea, with higher levels found in the skin lesions and blood of affected patients and in an animal model. This increase correlates with disease severity and inflammation. This research indicates that S100A9 triggers inflammation in skin cells via the toll-like receptor 4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Blocking S100A9 reduced inflammation in the animal model, suggesting it plays a key role in rosacea pathogenesis by enhancing this signaling pathway and promoting skin inflammation.

Fig1. mRNA levels of IL6, IL1β, and TNFα in HaCaT cells from the control group, rS100A9-treated group, rS100A9 + TLR4-IN-C34–treated group, and rS100A9 + BMS-345541–treated group.

Fig2. Correlation between serum S100A9 and RSSs in patients with PPR.
Case Study 2: Lanfang Yang, 2024
This study explored how HNRNPL influences ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its underlying mechanisms. HNRNPL and S100A9 were overexpressed in HCC. Knocking down HNRNPL decreased cell activity and key ferroptosis proteins while increasing oxidative stress markers. The pro-ferroptotic effect of HNRNPL was counteracted by overexpressing S100A9 or using the ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1. Mechanistically, HNRNPL enhanced S100A9 mRNA stability. In vivo, reduced HNRNPL expression slowed tumor growth and altered the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins.

Fig3. RIP assay was adopted to detect the specificity of HNRNPL and S100A9.

Fig4. Expression of HNRNPL or S100A9 protein detected western blot.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (S100A9-12HFL)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (S100A9-6221H)
Involved Pathway
S100A9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways S100A9 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with S100A9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
S100A9 has several biochemical functions, for example, RAGE receptor binding,Toll-like receptor 4 binding,antioxidant activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by S100A9 itself. We selected most functions S100A9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with S100A9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | SDF4,CALML4A,CD69,PRRG3,PNLIPRP1,DLL4,SYT7,EDEM2,PCDH2AB6,MEX3B |
| arachidonic acid binding | ALOX5AP,S100A8,PPARG,CYP4F14,STX3,CYP4A14 |
| microtubule binding | MTAP4,CLIP3,NDE1,PRC1,MTAP1B,KIF11,DPYSL5,KIF7,CCDC87,POLB |
| antioxidant activity | APOA4,HP,PRDX5,PRDX6,MT3,APOM,UBIAD1,APOE,TP53INP1,FAM213AA |
| protein binding | TRIB3,SPRY2,SVIL,NUP153,ALCAM,TBXA2R,HIST4H4,C1GALT1C1,WT1,Raet1a |
| Toll-like receptor 4 binding | S100A8,TIRAP,SAA3 |
| signal transducer activity | TAS2R201.1,GPR30,MAPKAPK2,CCR12A,DRD7,PTK2,PLCD3,PRLH2R,OPN1MW1,TRAF3 |
| zinc ion binding | GATA2,EWSR1A,BTR12,GRIN2A,MMP9,ZDHHC13,MT1M,TGFB1I1,AMZ2,ADAM2 |
| RAGE receptor binding | S100A13,S100B,S100A12,S100A8,S100A4,S100P,FPR1,S100A7,HMGB2,HMGB1 |
Interacting Protein
S100A9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with S100A9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of S100A9.
S100A8;ARRB2;ARRB1;NOS2;40031146;NUAK1
Resources
Research Area
Granulocyte MarkersCalcium-binding Proteins and Related Molecules
CD Antigen (Granulocyte Markers)
Monocyte Markers
MDSC Cytokines and Growth Factors
Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Obry, A; Lequerre, T; et al. Identification of S100A9 as Biomarker of Responsiveness to the Methotrexate/Etanercept Combination in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using a Proteomic Approach. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Lapeire, L; Hendrix, A; et al. Cancer-Associated Adipose Tissue Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Paracrine Oncostatin M and Jak/STAT3 Signaling. CANCER RESEARCH 74:6806-6819(2014).


