PYY
-
Official Full Name
PYY peptide YY -
Synonyms
PYY;peptide YY;PYY1;PYY-I;peptide tyrosine tyrosine
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Protein Conjugation
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293T
- Yeast
- His
- His&T7
- Non
- GST
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is PYY protein?
PYY gene (growth hormone 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. This gene encodes a member of the neuropeptide Y (NPY) family of peptides. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate two alternative peptide products that differ in length by three amino acids. These peptides, secreted by endocrine cells in the gut, exhibit different binding affinities for each of the neuropeptide Y receptors. Binding of the encoded peptides to these receptors mediates regulation of pancreatic secretion, gut mobility and energy homeostasis. Rare variations in this gene could increase susceptibility to obesity and elevated serum levels of the encoded peptides may be associated with anorexia nervosa. The PYY protein is consisted of 97 amino acids and PYY molecular weight is approximately 11.1 kDa.
What is the function of PYY protein?
PYY is able to reduce food intake and increase satiety through its action in the hypothalamus, and is one of the key factors in regulating appetite and energy balance. PYY has an inhibitory effect on the gastrointestinal tract, which can slow down the rate of gastric emptying and affect the movement and secretion of the gastrointestinal tract. PYY has the effect of constricting blood vessels and may affect blood pressure regulation. The change of PYY level is related to obesity, and the change of plasma concentration may be related to the occurrence and development of obesity and related metabolic diseases. PYY is involved in metabolic regulation throughout the body through its different roles in the gut and brain.
PYY Related Signaling Pathway
Gut-brain axis signaling pathway: PYY is produced in intestinal endocrine cells and can influence the regulation of appetite and energy balance through the gut-brain axis. Interactions with neuropeptide Y (NPY) and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) : PYY belongs to the same family as NPY and PP, and they may interact and signal in appetite regulation and obesity formation. Short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) signaling pathway: SCFA can stimulate the production of PYY, and SCFA activates the signaling pathway through its receptors such as GPR41 and GPR43, which may affect the expression and release of PYY. MAPK signaling pathway: The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation cascade is an important signaling pathway that may be related to the cellular effects of PYY. Interaction with GHSR: PYY binds to its receptor GHSR (growth hormone releasing hormone receptor) and may affect growth hormone release and appetite regulation.
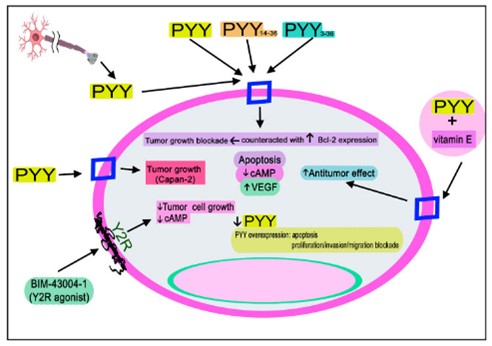
Fig1. Summary of the mechanisms mediated by PYY in tumor cells. (Manuel Lisardo Sánchez, 2023)
PYY Related Diseases
PYY (Peptide YY) is associated with a variety of diseases, especially with metabolic diseases. Its role in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and irritable bowel syndrome has been studied. PYY levels are generally reduced in obese individuals, which is associated with an imbalance in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure. In addition, the expression of PYY in IBS may serve as a diagnostic biomarker to help identify and distinguish different pathological states. PYY may also be associated with metabolic syndrome, a condition that involves multiple metabolic abnormalities, such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, abnormal cholesterol levels, and abdominal obesity.
Bioapplications of PYY
PYY acts as an appetite suppressant hormone, and its increased secretion can reduce food intake, so it has been studied for the treatment of obesity. In type 2 diabetes, PYY has been found to reverse symptoms of hyperglycemia and restore impaired insulin release, providing new ideas for diabetes treatment. In addition, the combination of PYY analogues with other incretin mimics may enhance and maintain long-term efficacy. The combination of PYY3-36 and GLP-1 showed an additive effect on reducing food intake, which opens up the possibility of developing new drugs for weight loss.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiaolun Xu, 2023
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a noteworthy cause of liver diseases, especially cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinomas. However, the interaction between the host and HBV has not been fully elucidated. Peptide YY (PYY) is a 36-amino-acid gastrointestinal hormone that is mainly involved in the regulation of the human digestive system. This study found that PYY expression was reduced in HBV-expressing hepatocytes and HBV patients. Overexpression of PYY could significantly inhibit HBV RNA, DNA levels, and the secretion of HBsAg. In addition, PYY inhibits HBV RNA dependent on transcription through reducing the activities of CP/Enh I/II, SP1 and SP2. Meanwhile, PYY blocks HBV replication independent on core, polymerase protein and ε structure of pregenomic RNA. These results suggest that PYY can impair HBV replication by suppressing viral promoters/enhancers in hepatocytes.
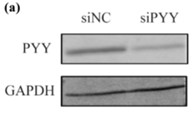
Fig1. PYY protein expressions were measured by western blot analysis.

Fig2. Huh7 cells were transfected with pCMV-Fluc and EGFP-PYY or EGFP.
Case Study 2: Andres Acosta, 2011
Peptide YY(3-36) is a satiation hormone released postprandially into the bloodstream from L-endocrine cells in the gut epithelia. In the current report, researchers demonstrate PYY(3-36) is also present in murine as well as in human saliva. In mice, salivary PYY(3-36) derives from plasma and is also synthesized in the taste cells in taste buds of the tongue. Moreover, the cognate receptor Y2R is abundantly expressed in the basal layer of the progenitor cells of the tongue epithelia and von Ebner's gland. The acute augmentation of salivary PYY(3-36) induced stronger satiation as demonstrated in feeding behavioral studies. The effect is mediated through the activation of the specific Y2 receptor expressed in the lingual epithelial cells. In a long-term study involving diet-induced obese (DIO) mice, a sustained increase in PYY(3-36) was achieved using viral vector-mediated gene delivery targeting salivary glands. The chronic increase in salivary PYY(3-36) resulted in a significant long-term reduction in food intake (FI) and body weight (BW).
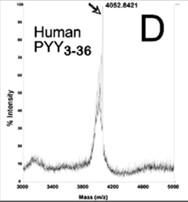
Fig3. Validation of synthetic PYY3-36 by MALDI-TOF .

Fig4. Effect of PYY3-36 on 1 hour FI after 24 hours fasting compared to control oral spray.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PYY-2831H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PYY-370H)
Involved Pathway
PYY involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PYY participated on our site, such as Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors),G alpha (i) signalling events,GPCR downstream signaling, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PYY were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Peptide ligand-binding receptors | NMBB,PROKR2,PROKR1A,APLN,EDN3,QRFPR,PENKA,NPFF,CXCL11.8,TRH |
| GPCR downstream signaling | FGD4A,OPN1SW1,CXCR6,OPN5,PYYA,GPRC6A,MGLL,PNOCB,NPFF,PENK |
| G alpha (i) signalling events | OXGR1A.1,RHOL,RGS21,CCR6,DRD3,TAS2R16,CCL19A.2,SOUL4,RLN3A,CCL35.1 |
| GPCR ligand binding | RAMP2,PPY,LPAR5A,S1PR3,EMR3,OPN4,OPN1SW,CASR,RGS1,OPN1MW2 |
| Signaling by GPCR | PNOC,RGS7,GPR120,ARHGEF18A,GPR37L1,ANXA1B,PENK,RGS1,OR4D2,ZFPM2B |
| Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | OXTRL,SST1.1,CCBP2,CCL35.2,APLN,NMB,GPR17,INSL5,OPN1LW1,GPR77 |
| Signal Transduction | SDR16C5,PTHRP2,ARAP1,KLHL12,GPR55A,BBS13,PROK1,RGS14,DISP2,NF2A |
Protein Function
PYY has several biochemical functions, for example, G-protein coupled receptor binding,hormone activity,neuropeptide hormone activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PYY itself. We selected most functions PYY had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PYY. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| G-protein coupled receptor binding | PSAPL1,UCN3L,PPY,NPFF,GNAI2A,HAND2,CORT,SFTPBB,RSPO3,PACRG |
| neuropeptide hormone activity | PYYA,POMCA,UCN,QRFP,NPFFL,CCK,GRP,NPFF,CORT,ADCYAP1 |
| hormone activity | LEPA,CSH2,ADCYAP1B,FNDC5B,GPHA2,UCN2,FSHB,RLN3,TTR,PRL7A1 |
| protein binding | VSNL1,PLG,CTPS2,CDK6,NKX2-1,C12orf5,KLF11,ATP1A2,XPO5,TOR1AIP2 |
Interacting Protein
PYY has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PYY here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PYY.
DPP4;FAP;NPY1R;NPY2R
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Nagatake, T; Fujita, H; et al. Enteroendocrine Cells Are Specifically Marked by Cell Surface Expression of Claudin-4 in Mouse Small Intestine. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Hoffmann, E; Konkar, A; et al. PK modulation of haptenylated peptides via non-covalent antibody complexation. JOURNAL OF CONTROLLED RELEASE 171:48-56(2013).


