PCNA
-
Official Full Name
proliferating cell nuclear antigen -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is found in the nucleus and is a cofactor of DNA polymerase delta. The encoded protein acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. In response to DNA damage, this protein is ubiquitinated and is involved in the RAD6-dependent DNA repair pathway. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. Pseudogenes of this gene have been described on chromosome 4 and on the X chromosome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
PCNA;proliferating cell nuclear antigen;cyclin;DNA polymerase delta auxiliary protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Yeast
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Sf9 Insect Cells
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- Insect Cell
- Human
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293T
- His
- Non
- GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
- Myc&DDK
Involved Pathway
PCNA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PCNA participated on our site, such as DNA replication,Base excision repair,Nucleotide excision repair, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PCNA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis B | TBK1,MAP3K1,IFNA6,ATP6AP1,BAX,Ifna15,IFNA5,CREB5,EGR2,IL-8 |
| HTLV-I infection | TLN1,VAC14,BUB3,HLA-B,MAP3K14,LTA,PIK3R1,XBP1,SLC2A1,POLE3 |
| Nucleotide Excision Repair | GTF2H2,ZNF830,KIAA1530,XPC,GTF2H4,MCRS1,NFRKB,POLE3,COPS4,GTF2H5 |
| Base excision repair | POLD3,MPG,UNGA,TDG.1,MUTYH,NTHL1,NEIL2,POLE,nth,TDG |
| Cell cycle | NEK6,ERCC6L,TUBGCP3,E2F4,MIS18A,CDKN1B,TUBG2,CDKN2A,CDC27,MCM5 |
| Mismatch repair | RFC4,RFC3,POLD1,MSH6,RPA3,MLH3,EXO1,RPA1,MSH2,MLH1 |
| DNA Replication | GINS4,RNASEH2B,GINS1,CDT1,GINS3,POLE3,GMNN,RNASEH2C,RFC1,MCM3 |
Protein Function
PCNA has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA polymerase binding,DNA polymerase processivity factor activity,MutLalpha complex binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PCNA itself. We selected most functions PCNA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PCNA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| damaged DNA binding | DCLRE1C,FANCG,RUVBL2,RAD23AB,CREBBP,XRCC6,EP300,XRCC5,RAD52,CRY2 |
| estrogen receptor binding | TAF10,FOXL2,LEF1,ARRB1,STRN,TMEM38A,DDX54,CTNNB1,MMS19,MED1 |
| DNA polymerase processivity factor activity | TEFM |
| identical protein binding | ATXN10,CEACAM16,SRPX2,SH3GLB1,RB1,PLIN5,GPSM2,SH3BP4,PARK2,C1QTNF6 |
| chromatin binding | KLF14,NOC2L,DNMT3A,SMARCC1,CEBPB,ZEB1,HDAC4,DLX2,TRIM24,MEOX1 |
| histone acetyltransferase binding | EID1,NR4A3,CEBPB,GLI3,MTF1,TRIP4,CITED2,SIRT2,TRIM68,ETS1 |
| DNA polymerase binding | SMARCA4,LONP1,RAD51,FANCD2,CDK2AP1,HMGB1,ACD,FANCI |
| MutLalpha complex binding | TREX1 |
| receptor tyrosine kinase binding | PTPN1,NRG1,FNTA,SHC4,PTPN2,PLCG1,GNB2L1,TRP53,PIK3R2,LRP4 |
Interacting Protein
PCNA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PCNA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PCNA.
CDKN1A;FEN1
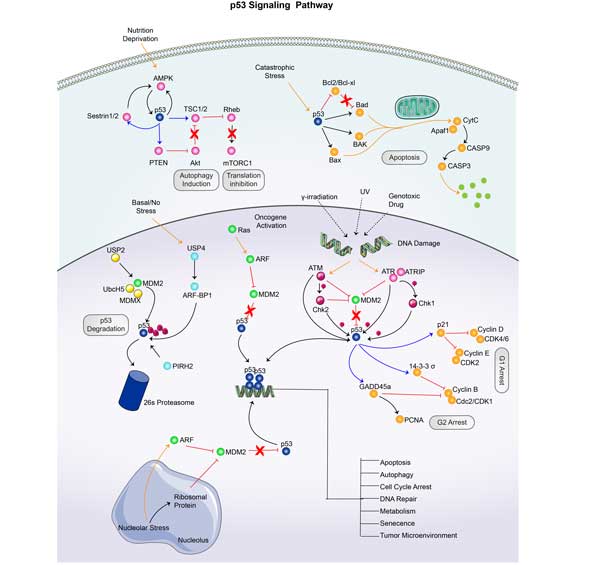
PCNA Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Abdel-Latif, M; Sakran, T; et al. Immunomodulatory effect of diethylcarbamazine citrate plus filarial excretory-secretory product on rat hepatocarcinogenesis. INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY 24:173-181(2015).
- Park, JB; Lee, JS; et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured at high cell density express brain-derived neurotrophic factor and exert neuroprotective effects in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease. GENES & GENOMICS 37:213-221(2015).