JAK1
-
Official Full Name
Janus kinase 1 -
Overview
Members of the Janus family of tyrosine kinases (Jak1, Jak2, Jak3, and Tyk2) are activated by ligands binding to a number of associated cytokine receptors. Upon cytokine receptor activation, Jak proteins become autophosphorylated and phosphorylate their a -
Synonyms
JAK1;Janus kinase 1;JAK1B;tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1;JAK1A;JTK3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Yeast
- Insect cells
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- MBP
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- T7
- Non
Background
What is JAK1 protein?
JAK1 gene (Janus kinase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p31. This gene encodes a membrane protein that is a member of a class of protein-tyrosine kinases (PTK) characterized by the presence of a second phosphotransferase-related domain immediately N-terminal to the PTK domain. The encoded kinase phosphorylates STAT proteins (signal transducers and activators of transcription) and plays a key role in interferon-alpha/beta, interferon-gamma, and cytokine signal transduction. This gene plays a crucial role in effecting the expression of genes that mediate inflammation, epithelial remodeling, and metastatic cancer progression. This gene is a key component of the interleukin-6 (IL-6)/JAK1/STAT3 immune and inflammation response and is a therapeutic target for alleviating cytokine storms. The JAK1 protein is consisted of 1154 amino acids and JAK1 molecular weight is approximately 133.3 kDa.
What is the function of JAK1 protein?
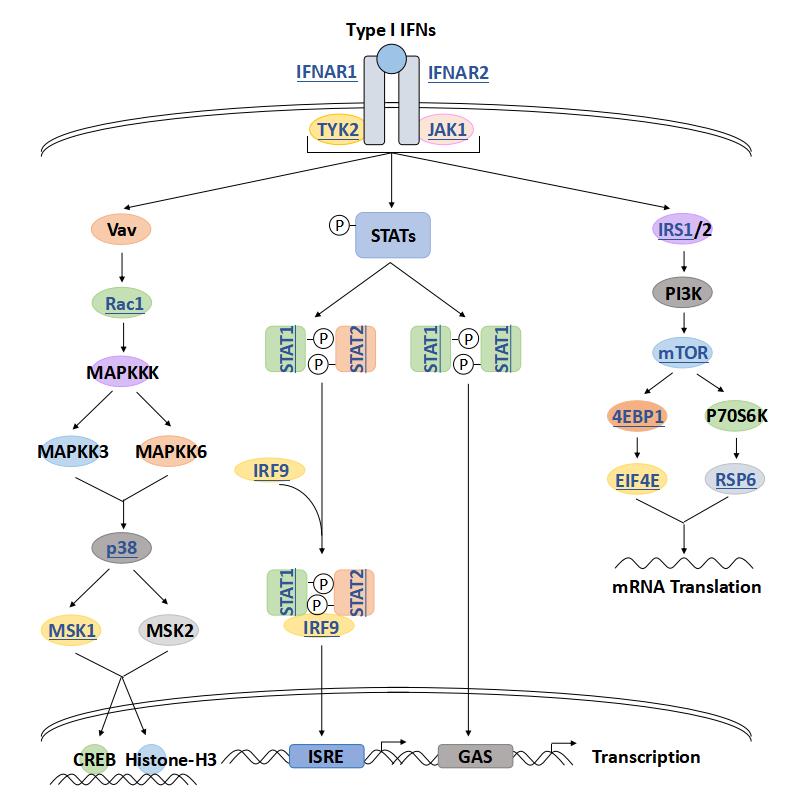
JAK1 phosphorylates STAT proteins, which are then activated, dimerize, and translocate to the nucleus to regulate the expression of specific genes. JAK1 plays a significant role in immune responses, including the development and function of the immune system, particularly in the signaling of interferons (IFNs) and interleukins (ILs). It contributes to the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, and survival through its involvement in cytokine signaling pathways. JAK1 is involved in various developmental processes, including organogenesis and tissue repair. JAK1 is crucial for blood cell production, as it is involved in the signaling pathways of several cytokines important for hematopoietic function.
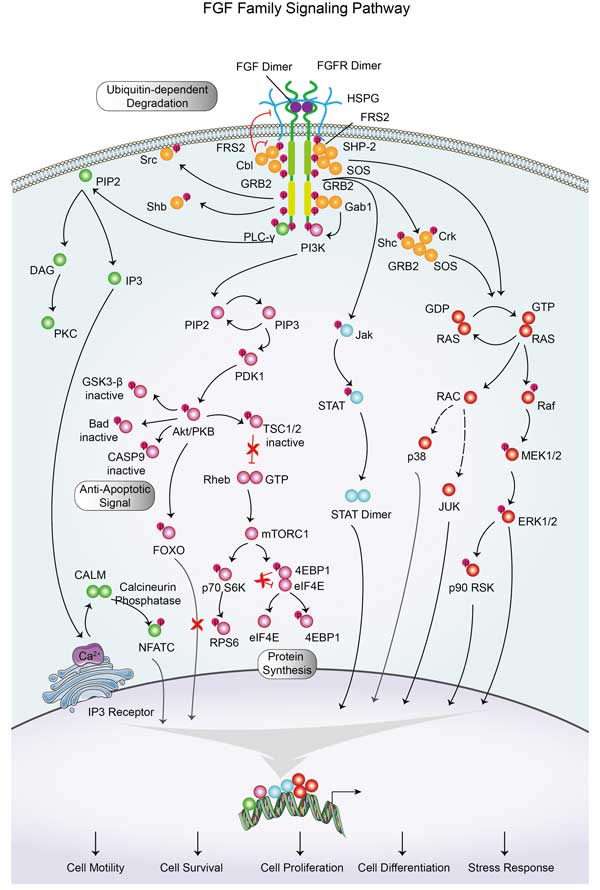
JAK1 Related Signaling Pathway
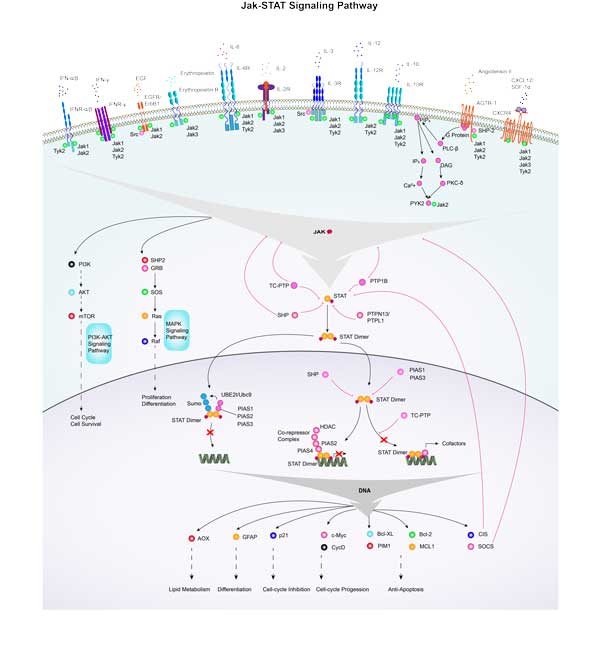
JAK1 plays an important role in the development and function of immune cells, especially in lymphocyte signaling. JAK1 is involved in signaling by binding to specific domains of cytokine receptors via FERM domains and SH2 domains at its amino terminus. JAK1 mediates the transmission of various cytokine signals, such as interferon (IFNs) and interleukin (ILs), which play a key role in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and immune regulation. JAK1 can phosphorylate STAT protein after activation, resulting in the dimerization of STAT protein and migration to the nucleus, regulating the expression of target genes.
JAK1 Related Diseases
Mutations in the JAK1 gene can lead to primary immunodeficiency, such as some types of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), because JAK1 plays a crucial role in the development and function of lymphocytes. Overactivation of JAK1 has been linked to the development of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease, which involve the immune system attacking its own tissues. Sustained activation of JAK1 is associated with the development, progression, and treatment resistance of certain cancers, including blood cancers and solid tumors, and it may promote the proliferation, survival, and metastasis of tumor cells. JAK1's role in regulating the immune response also makes it relevant for allergic diseases, such as asthma, where activation of JAK1 can lead to inflammation and activation of immune cells. In addition, it is also associated with viral infection, chronic inflammation and blood diseases.

Fig1. JAK/STAT pathway in myeloproliferative neoplasms. (Alfonso Quintás-Cardama, 2013)
Bioapplications of JAK1
In terms of disease treatment, as a key component of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, JAK1 is a focus for the development of targeted therapeutics for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammation, and certain cancers. JAK1 inhibitors are used to regulate the immune response and reduce the activity of pathological immune cells and inflammation in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. The active status of JAK1 or its mutation may be used as a disease marker for the diagnosis of certain diseases and the monitoring of therapeutic response. In basic research, JAK1 serves as an important tool for studying cell signaling, immune response, and disease mechanisms, contributing to a deeper understanding of related biological processes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nicholas P D Liau, 2018
Interferon gamma (IFNγ) is a potent inflammatory and immune cytokine. IFNγ signals via the interferon gamma receptor (IFNGR), which is constitutively bound to Janus Kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2 via its intracellular domain. These two JAK proteins then initiate the inflammatory signaling cascade. The most potent inhibitor of IFNγ signaling is Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS1). SOCS1 negatively regulates IFNγ signaling pathway (and other pathways) by directly inhibiting JAKs. In this study, purified JAK1 was used for structural and biochemical studies.

Fig1. SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie Blue.

Fig2. A 280 absorbance trace of JAK1 JH1 elution from a Superdex200 16/600 size exclusion chromatography column.
Case Study 2: Yuechao Sun, 2023
The role of METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification has been elucidated in several cancers, but the concrete mechanism underlying its function in colorectal cancer is still obscure. Here, researchers revealed that upregulated methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) in colorectal cancer exerted both methyltransferase activity-dependent and -independent functions in gene regulation. METTL3 deposited m6A on the 3' untranslated region of the JAK1 transcript to promote JAK1 translation relying on YTHDF1 recognition. The increased JAK1 and STAT3 corporately contributed to the activation of the p-STAT3 signaling pathway and further upregulated downstream effectors expressions, including VEGFA and CCND1, which finally resulted in enhanced cancer cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo.

Fig3. METTL3-regulated JAK1 expression is independent of proteasome-mediated protein degradation.

Fig4. Dual-luciferase reporter assays for the wild type or mutant JAK1 3'UTR sequence in cancer cells with or without silenced YTHDF1.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
JAK1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways JAK1 participated on our site, such as ARMS-mediated activation,Antiviral mechanism by IFN-stimulated genes,Axon guidance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with JAK1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Developmental Biology | CTNNA2,RANBP9,NRTN,CCNC,ITSN1,SEMA3AB,PLXNC1,CHL1,MYL9,NR2F2 |
| Antiviral mechanism by IFN-stimulated genes | EIF4EB,IFIT10,IFIT8,HERC5,DPF1,ARIH1,EIF4G2A,NUP35,KPNA4,KPNA5 |
| ARMS-mediated activation | HBEGF,SPRED3,DUSP9,DLG4,EGF,PTPRA,PSMD14,DUSP6,SPTBN2,PHB |
| Downstream signal transduction | FGF18B,AGO2,SPRED3,FRS3,SPRED1,FGFR1B,FGF8B,CRKL,PEA15,IL17RD |
| Axon guidance | EZRA,AP2A1,SEMA4C,RAC3,SCN2B,CRMP1,FES,DUSP10,GFRA2,CNTN6 |
| DAP12 interactions | FRS3,SPTB,FRS2,SIRPB1,SPTBN1,PEBP1,GRAP2B,DUSP2,KLB,RASGRP4 |
| Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | NOD1,USP18,IFIT3,ISG20,CASPB,WDR83,JAK3,TRIM31,NRG3,GBP2 |
| DAP12 signaling | DAB2IPB,GRAP2A,FRS3,TRAT1,FRS2,NRG4,FGFR1B,IL17RD,PTPRA,DUSP10 |
Protein Function
JAK1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,CCR5 chemokine receptor binding,growth hormone receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by JAK1 itself. We selected most functions JAK1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with JAK1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | CASK,RECQL5,CHD1,VCP,PRKAG3,SARS,EPHB3,CBWD1,YRK,SNRKB |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | PRKCD,CSK,EIF2AK2,STK16,TXK,LCK,FYNB,PTK2,TEC,PTK2BB |
| growth hormone receptor binding | GH1,Gh,SOCS2,JAK2,TYK2 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | BECN1,VCL,GPR37,RPA2,LRPPRC,SUMO2,GRIK2,DNM1L,MAP1LC3C,MYOD1 |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | BMX,IGF1R,MAP2K5,YES1,TNK2,ABL1,ABL2,TNK1,SRC,LTK |
| CCR5 chemokine receptor binding | CNIH4,CCL4,CCL3,STAT3,CCL5 |
| protein phosphatase binding | MAPK14,MET,CSF1R,PARD3,TRAF3,GNB2L1,HSF4,ERBB2,CDKN1B,ANAPC7 |
| protein binding | GPRC5A,NEK3,YAF2,FLT3,HERC5,DYNC1LI1,ADAM22,ARL2BP,ALDH7A1,DBNL |
Interacting Protein
JAK1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with JAK1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of JAK1.
IFNAR2;STAM2;ERBB2;Dlg4;P;v_rindsa;HSP90AB1;IL6R;PRKCA;BRCA1;P/V;V
JAK1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Apoptosis Intracellular Kinases
- Intracellular Kinases in the Akt Pathway
- Jak Kinases
- Negative Regulators of the Jak/STAT Pathway
- Intracellular Signaling Molecules in Angiogenesis
- T Follicular Helper (Tfh) Cells
- Th17 Cells
- IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules
- Oncoprotein-Signal Transducers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Cianciulli, A; Dragone, T; et al. IL-10 plays a pivotal role in anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol in activated microglia cells. INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY 24:369-376(2015).
- Kubo, S; Yamaoka, K; et al. The JAK inhibitor, tofacitinib, reduces the T cell stimulatory capacity of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES 73:2192-2198(2014).


.jpg)
.jpg)