FGL1
-
Official Full Name
fibrinogen-like 1 -
Overview
Fibrinogen-like 1 is a member of the fibrinogen family. This protein is homologous to the carboxy terminus of the fibrinogen beta- and gamma- subunits which contains the four conserved cysteines of fibrinogens and fibrinogen related proteins. However, this protein lacks the platelet-binding site, cross-linking region and a thrombin-sensitive site which are necessary for fibrin clot formation. This protein may play a role in the development of hepatocellular carcinomas. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein exist for this gene. -
Synonyms
FGL1;fibrinogen-like 1;fibrinogen-like protein 1;HFREP 1;FGL 1;FGL1_HUMAN;Fibrinogen like 1;Fibrinogen like protein 1;Fibrinogen related protein 1;Hepassocin;Hepatocellular carcinoma related sequence;Hepatocyte derived fibrinogen related protein 1;Hepatocyte-derived fibrinogen-related protein 1;HFREP-1;HFREP1;HP 041;HP-041;HP041;LFIRE 1;LFIRE-1;LFIRE1;Liver fibrinogen related protein 1;Liver fibrinogen-related protein 1;MFIRE 1;MGC108569;MGC12455;MGC37822;OTTHUMP00000122468;OTTHUMP00000224774;OTTHUMP00000224775;OTTHUMP00000224776;OTTHUMP00000224916;hepatocellular carcinoma-related sequence;hepatocyte-derived fibrinogen-related
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cynomolgus
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Cattle
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- N-hFc
- Mammalian Cell
- Insect Cells
- HEK293T
- Baculovirus-Insect Cells
- Human Cell
- Mammalian cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E. coli
- HEK293F
- GST
- Fc
- His&Avi
- Non
- mFc
- N-His-Avi
- His
- His&S
- His&GST
- Myc&DDK
- Fc&Avi
- mIgG2a
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- Fc&Myc
- N-His-GST&C-Myc
Background
What is FGL1 protein?
FGL1 gene (fibrinogen like 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p22. FGL1 is a protein that is secreted primarily by the liver and has been identified as an immune checkpoint ligand. It has been confirmed in multiple studies to be a newly emerging checkpoint ligand of the lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3). FGL1 is involved in various physiological and pathological conditions, including the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), and immune responses. It is also implicated in the immune evasion of cancer cells and has been associated with poor prognosis and resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy in cancer patients. The FGL1 protein is consisted of 312 amino acids and FGL1 molecular weight is approximately 36.4 kDa.
What is the function of FGL1 protein?
FGL1 has been identified as a major ligand of the immune checkpoint receptor LAG-3 (Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3) on activated T cells. It functions as an immune suppressive molecule by binding to LAG-3, which can inhibit antigen-specific T cell activation. FGL1 is highly produced by human cancer cells, and its elevated levels in the plasma of cancer patients are associated with poor prognosis and resistance to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. FGL1 is related to cell proliferation and metabolism. In the context of HCC, FGL1 has been found to be modified by acetylation, targeting it for proteasomal degradation.
FGL1 Related Signaling Pathway
FGL1 is a ligand for LAG3 (Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3), an immune checkpoint receptor expressed on activated T cells and dendritic cells. FGL1 influences cell proliferation and metabolism by regulating the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. This pathway plays a key role in the growth and survival of tumor cells. In some types of cancer, FGL1 has been found to promote tumor immune escape through the Notch signaling pathway, suggesting that FGL1 may modulate immune responses in the tumor microenvironment through multiple mechanisms. FGL1 expression can be regulated by the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which plays an important role in cytokine-mediated cellular responses, including immune cell activation and cytokine production. FGL1 may be related to Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGFβ) signaling pathway, which plays a role in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and may also be related to the radiation sensitivity of tumor cells.
FGL1 Related Diseases
FGL1 protein (Fibrinogen like protein 1) is associated with a variety of diseases, especially closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. FGL1 is upregulated in a variety of tumors, and its high levels in patient plasma are associated with poor prognosis and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. For example, in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), FGL1 expression is associated with tumor immune escape and treatment resistance. In addition, FGL1 has been implicated in the early diagnosis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Upregulation of FGL1 is also associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT), proliferation, apoptosis, and drug resistance. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), FGL1 expression levels are associated with patient survival.

Fig1. Characterization of tumor cells regulated by FGL1. (Wenjing Qian, 2021)
Bioapplications of FGL1
The application of FGL1 protein is mainly concentrated in the field of medical research and tumor immunotherapy. Because FGL1 is upregulated in a variety of tumors, it is considered a potential biomarker and therapeutic target. In tumor immunotherapy, FGL1 interacts with immune checkpoint receptors such as LAG-3, and targeted therapy against FGL1 may help overcome tumor resistance to existing immunotherapy. In addition, the expression pattern of FGL1 in liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma also suggests its potential application in disease diagnosis and treatment. For example, inhibition of the SIRT2-FGL1 regulatory axis or the combination of IL-6 and FGL1 antibody therapy can enhance the anti-tumor immune response and improve the efficacy of tumor immunotherapy. At the same time, the introduction of FGL1 antibody and ELISA reagents is helpful to carry out various studies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jia-Jun Li, 2023
Colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with liver metastases usually obtain less benefit from immunotherapy, and the underlying mechanisms remain understudied. Here, researchers identify that fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1), secreted from cancer cells and hepatocytes, facilitates the progression of CRC in an intraportal injection model by reducing the infiltration of T cells. Mechanistically, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) activate NF-κB by secreting TNFα/IL-1β in the liver microenvironment and transcriptionally upregulate OTU deubiquitinase 1 (OTUD1) expression, which enhances FGL1 stability via deubiquitination. Disrupting the TAM-OTUD1-FGL1 axis inhibits metastatic tumor progression and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. Clinically, high plasma FGL1 levels predict poor outcomes and reduced ICB therapy benefits. Benzethonium chloride, an FDA-approved antiseptics, curbs FGL1 secretion, thereby inhibiting liver metastatic tumor growth.
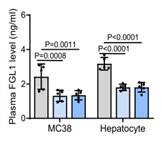
Fig1. ELISA detection of plasma FGL1 levels.

Fig2. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between HA-Ub and Flag-FGL1.
Case Study 2: Changjie Yang, 2023
The key role of tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells in the immune regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been investigated and reported, but the regulatory mechanism of tumor microenvironment on TRM cells is still unclear. Fibrinogen-like protein 1 (FGL1) is a classical ligand of LAG-3 and can promote T cell exhaustion in tumors. Here, researchers excavated the effect of FGL1-LAG3 regulatory axis on TRM cells in HCC. They investigated the suppressive effect of FGL1 on CD8+ TRM cells both in in vitro induction model and in vivo orthotopic HCC mouse model. The results showed increased FGL1 expression in HCC may result in CD8+ TRM cell exhaustion, causing tumor immune escape.

Fig3. FGL1 (100 nM) was added to the cultures, and the percentage of CD8+ TRM cells was detected after activation.
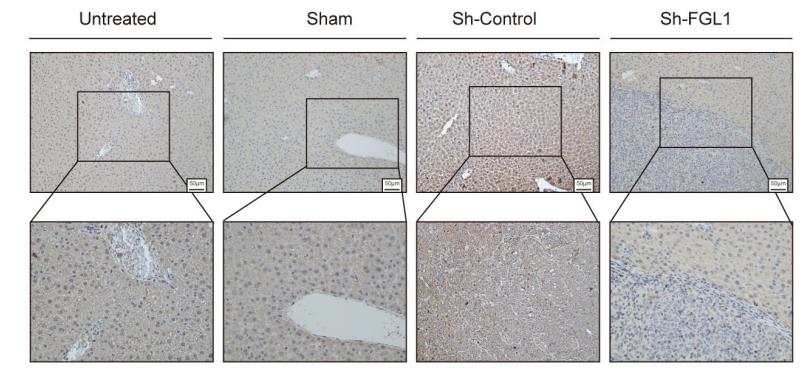
Fig4. Representative IHC staining of FGL1 in the livers of mice.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FGL1-8243H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FGL1-4152H)
Involved Pathway
FGL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FGL1 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FGL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
FGL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FGL1 itself. We selected most functions FGL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FGL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
FGL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FGL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FGL1.
BCL2L11;q9wmx2-pro_0000037550
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


