CREBBP
-
Official Full Name
CREB binding protein -
Overview
This gene is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in the transcriptional coactivation of many different transcription factors. First isolated as a nuclear protein that binds to cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), this gene is now known to play critical roles in embryonic development, growth control, and homeostasis by coupling chromatin remodeling to transcription factor recognition. The protein encoded by this gene has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity and also acts as a scaffold to stabilize additional protein interactions with the transcription complex. This protein acetylates both histone and non-histone proteins. This protein shares regions of very high sequence similarity with protein p300 in its bromodomain, cysteine-histidine-rich regions, and histone acetyltransferase domain. Mutations in this gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RTS). Chromosomal translocations involving this gene have been associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. This gene is ubiquitously expressed and is involved in the transcriptional coactivation of many different transcription factors First isolated as a nuclear protein that binds to cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), this gene is now known to play -
Synonyms
CREBBP;CREB binding protein;CBP;RSTS;KAT3A;CREB-binding protein;EC 2.3.1.48;CREBB;OTTHUMP00000159801;Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome;RTS
Recombinant Proteins
- Monkey
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Dog
- Rhesus macaque
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Sf21 Insect Cell
- Sf9 Insect Cell
- E. coli
- Wheat Germ
- Sf9 insect cell
- HEK293T
- His
- GST
- N-His&C-FLAG
- N-His-Flag
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
Background
What is CREBBP protein?
CREBBP gene (CREB binding protein) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16p13. The protein encoded by this gene has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity and also acts as a scaffold to stabilize additional protein interactions with the transcription complex. This protein acetylates both histone and non-histone proteins. This protein shares regions of very high sequence similarity with protein p300 in its bromodomain, cysteine-histidine-rich regions, and histone acetyltransferase domain. The CREBBP protein is consisted of 2442 amino acids and CREBBP molecular weight is approximately 265.4 kDa.
What is the function of CREBBP protein?
CREBBP protein (also known as P300/CBP) is a transcriptional coactivator widely expressed in tissues throughout the body. It plays a key role in embryonic development, growth control and homeostasis in vivo. CREBBP protein has intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity, which can regulate gene transcription through acetylation of histone and non-histone proteins. This acetylation changes the structure of chromosomes, making genes available for transcription. The CREBBP protein also acts as a scaffold that stabilizes interactions with other proteins, thereby facilitating the formation of transcription complexes. In addition, CREBBP has important roles in the nervous system, including roles in learning and memory formation, neuroprotection, and certain neurodegenerative diseases.
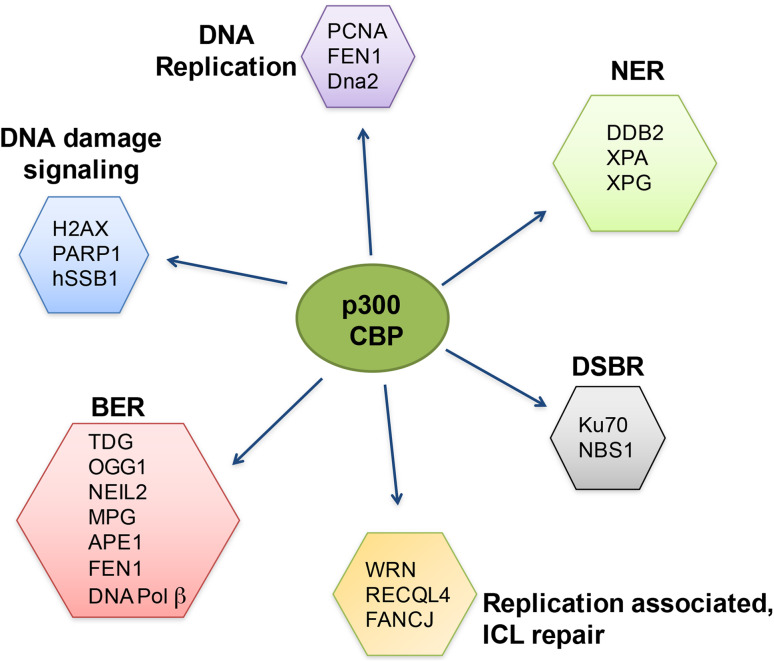
Fig1. Schematic representation of protein substrates of p300 and CBP participating in different aspects of the DNA damage response. (Ilaria Dutto, 2018)
CREBBP related signaling pathway
The CREBBP-related signaling pathway is pivotal in gene transcription regulation, where CREBBP (CREB-Binding Protein) acts as a coactivator. It interacts with the cAMP Response Element Binding (CREB) protein to enhance the transcription of target genes involved in energy metabolism, synaptic plasticity, and cell growth. Upon phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA), CREB binds to CREBBP, facilitating the recruitment of RNA polymerase II and other transcription factors to initiate gene transcription. This pathway is crucial for cellular responses to external stimuli, learning and memory processes, and maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to various diseases, emphasizing its significance in cellular function and disease pathogenesis.
CREBBP related diseases
Mutations in the CREBBP gene have been linked to a variety of diseases, notably Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS), a rare disorder characterized by intellectual disability, distinctive facial features, growth retardation, and skeletal abnormalities. There are various types of mutations in the CREBBP gene, including nonsense/missense mutations, deletion mutations, splice site mutations, etc., which may lead to impaired protein function, resulting in disease. In addition, abnormalities in the CREBBP gene are also associated with other diseases such as certain types of cancer and neurological diseases. In neurological diseases, CREBBP plays a role by affecting synaptic plasticity, learning and memory, and its abnormal expression may be associated with postoperative cognitive dysfunction, vascular dementia, epilepsy and other diseases.
Bioapplications of CREBBP
In therapeutic contexts, rhCREBBP holds potential for treating neurological disorders by supporting neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity, crucial for learning and memory. Its role in metabolic regulation suggests applications in managing metabolic diseases through improved glucose homeostasis and energy balance. Additionally, rhCREBBP's involvement in DNA repair mechanisms makes it a candidate for interventions in conditions requiring enhanced genomic stability, such as certain cancers or genetic disorders. These applications leverage its natural functions in transcriptional coactivation and cellular processes, demonstrating the broad utility of manipulating this protein for medical advancements.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhiyuan Qu, 2021
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are increasingly recognized for their roles in diseases like cancer, but their involvement in viral infections is less understood. In this study, researchers identified 11,620 circRNAs in A549 cells, with 411 showing altered expression upon influenza virus infection. A novel intronic circRNA, AIVR, was notably upregulated and its suppression enhanced viral replication. AIVR, primarily cytoplasmic, acts as a miRNA sponge, sequestering a miRNA that targets CREBBP, a key factor in the IFN-β enhanceosome. Overexpressing AIVR increased IFN-β levels, suggesting it promotes an antiviral response by facilitating IFN-β production through miRNA regulation.

Fig1. Western blotting of the protein level of CREBBP in miR-330-3p- and AIVR-overexpressing or -silenced A549 cells.
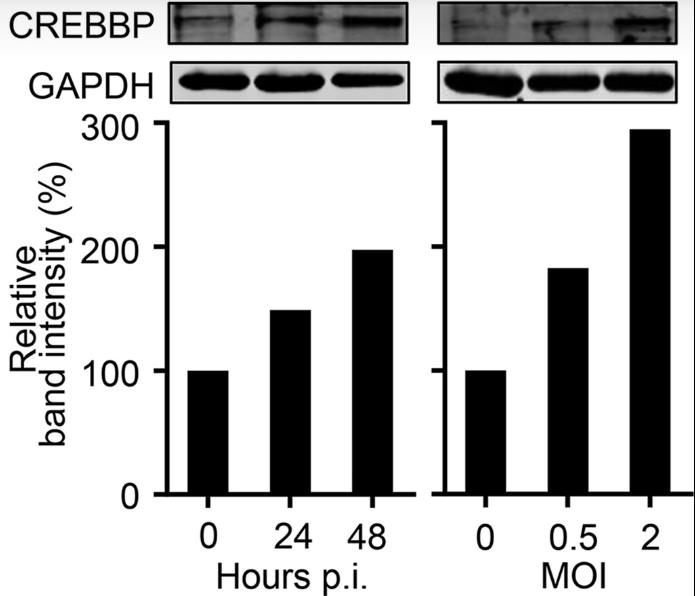
Fig2. Western blotting of the protein level of CREBBP in A549 cells infected with H9N2 virus.
Case Study 2: Jesús Duque-Afonso, 2018
Dasatinib, a multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is approved for Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) but faces resistance issues. This research, using shRNA screening and transcriptomic analysis, identified new genes and pathways that could improve dasatinib's effectiveness in pre-BCR+ ALL. Depleting the CBP transcriptional coactivator enhances dasatinib sensitivity by reducing pre-BCR signaling, which is linked to dasatinib responsiveness. Resistance can arise from the upregulation of alternative pathways like WNT, indicating transcriptional adaptability. Compounds that interfere with CBP interactions with CREB KID or β-catenin, in combination with dasatinib, showed promising preclinical results.
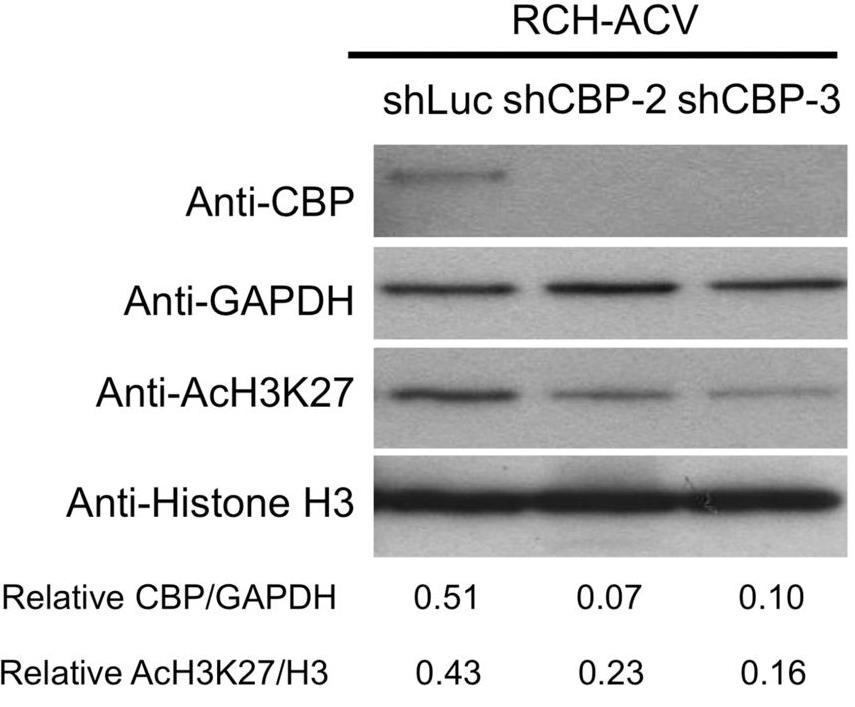
Fig3. Representative Western blot analysis shows CBP levels following knockdown by two different shRNA constructs in RCH-ACV cells.
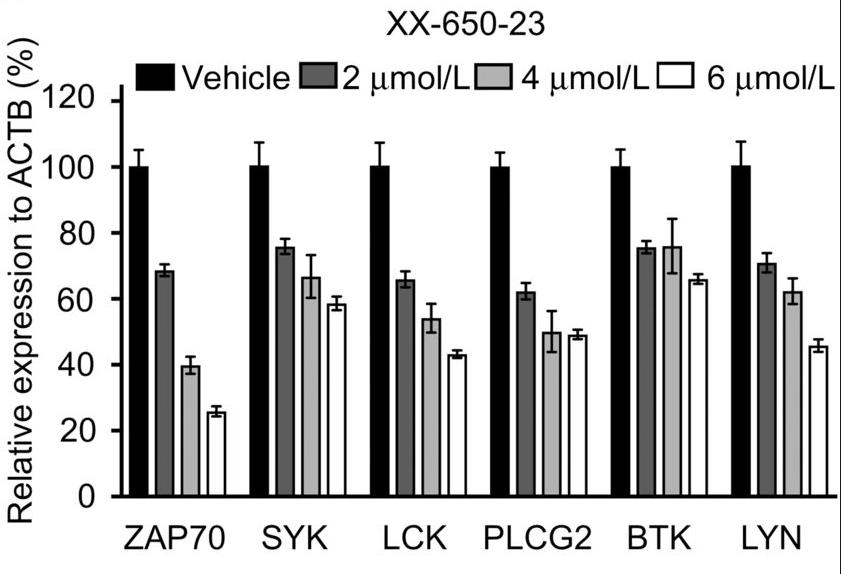
Fig4. Relative expression of pre-BCR–associated genes by qRT-PCR after pharmacologic inhibition of CBP in RCH-ACV cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CREBBP-2815H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CREBBP-1852H)
Involved Pathway
CREBBP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CREBBP participated on our site, such as Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP),Adherens junction,Androgen receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CREBBP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) | IL1B2,AHCYL1,CLEC4D,TAB1,CLEC6A,CASP8L1,ITPR2,UBE2V1,CLEC4A,MALT1 |
| Androgen receptor signaling pathway | KAT5,DAXX,ETV5A,CCDC102A,KAT7,DSTN,RUNX2A,RNF14,GNB2L1,POU2F1B |
| Adherens junction | INSRA,FGFR1A,SMAD3,PVRL3B,RHOAB,PTPRJ,WASF3,AASS,ACTG1,TCF7 |
| Angiogenesis | TIMP2 |
| C-MYB transcription factor network | CDKN1B,CEBPB,CBX4,MYOD1,CSF1R,TRIM28,PPID,SMARCA2,TOM1,ELANE |
| Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) | CYP51A1,MTF1,NFYBB,PMVK,NCOA2,SREBF2,DHCR7,NFYBA,HELZ2,NFYAL |
| Attenuation phase | HSBP1,HSBP1B,PTGES3,HSBP1A |
| BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian gene expression | CRY2,CARM1,NCOA2,NRIP1,HELZ2,DBP,CRY1,NAMPT |
Protein Function
CREBBP has several biochemical functions, for example, MRF binding,RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding,RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CREBBP itself. We selected most functions CREBBP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CREBBP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | MIXL1,KLF1,DMRT3A,DMRT1,DMRTC1B,DMRT2B,CXXC1,UHRF1,SP3,DMRTC1C2 |
| damaged DNA binding | POLI,NEIL3,HMGB1,POLD1,XPC,POLB,XRCC5,ERCC4,REV1,PNKP |
| SMAD binding | SKOR1A,MEF2A,STUB1,TOB1,SOD3,TGFBR1,DAB2,SNW1,SKIA,HMGA2 |
| RNA polymerase II transcription coactivator activity | SOX12,PITX2,SMARCA2,ANKRD1,MED12,PSIP1,SOX4,CITED1,MEF2A,NEUROD1 |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific binding | TRP53,GATA1,MAFBB,CREB3L3,STAG2,OSR2,MAFF,CSRNP3,HSF2,ELF5 |
| contributes_to transcription coactivator activity | EP300,PHF2,ARID5B |
| MRF binding | TSC22D3,KDM1A,BHLHE40 |
| transcriptional repressor activity, RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | MINA,AHRRA,EOMES,AHRR,ELP2,PITX2,MLIP,BHLHE40,T,AHRRB |
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | ZFPM2,XBP1,GSC,GATA3,GATA5,TOX2,GATA2A,MEF2A,TBX20,GATA4 |
Interacting Protein
CREBBP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CREBBP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CREBBP.
TP53;e1a_ade12;IRF3;RELA
Resources
Research Area
Notch FamilyHistone Acetyltransferases and Associated Proteins
Epigenetics and EMT
p53 Pathway
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lindskog, C; Kuhlwilm, M; et al. Analysis of Candidate Genes for Lineage-Specific Expression Changes in Humans and Primates. JOURNAL OF PROTEOME RESEARCH 13:3596-3606(2014).


