Recombinant Mouse Ick protein, His & T7-tagged
| Cat.No. : | Ick-7868M |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Mouse Ick aa. (Met1~Phe284 (Accession # Q9JKV2)) fused with N-terminal His & T7 tag was produced in E. coli cells. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Mouse |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His&T7 |
| Protein Length : | Met1~Phe284 |
| Form : | Freeze-dried powder |
| Molecular Mass : | Predicted Molecular Mass: 36.9kDa. |
| Endotoxin : | <1.0EU per 1ug (determined by the LAL method) |
| Purity : | >90% |
| Characteristic : | The isoelectric point is 9.3. |
| Applications : | SDS-PAGE; WB; ELISA; IP. |
| Stability : | The thermal stability is described by the loss rate of the target protein. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. (Referring from China Biological Products Standard, which was calculated by the Arrhenius equation.) The loss of this protein is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition. |
| Storage : | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months. |
| Storage Buffer : | Supplied as lyophilized form in PBS, pH7.4, containing 5% trehalose, 0.01% sarcosyl. |
| Reconstitution : | Reconstitute in sterile PBS, pH7.2-pH7.4. |
| Gene Name | Ick intestinal cell kinase [ Mus musculus (house mouse) ] |
| Official Symbol | Ick |
| Synonyms | Ick; intestinal cell kinase; Mrk; AI848300; 2210420N10Rik; serine/threonine-protein kinase ICK; MAK-related kinase; mICK |
| Gene ID | 56542 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001163780.1 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001157252.1 |
| UniProt ID | Q9JKV2 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ICK-7867H | Recombinant Human ICK protein, His & T7-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ICK-28676TH | Recombinant Human ICK | +Inquiry |
| Ick-7869R | Recombinant Rat Ick protein, His & T7-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ICK-1026H | Recombinant Human Intestinal Cell (MAK-like) Kinase, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ICK-4404M | Recombinant Mouse ICK Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ICK-833HCL | Recombinant Human ICK cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Bolick DT, et al. PLoS One. 2014
Intestinal health is vulnerable to nutritional deficiencies and stress, which can compromise its structure and immune defenses, increasing the risk of diseases. The precise mechanisms of how the intestine reacts to malnutrition are not fully known. This study identifies intestinal cell kinase (ICK) as a key player in the intestinal response to protein deficiency. In a mouse model, they found that ICK levels rise during protein deprivation, activating cell proliferation and survival pathways like Wnt/β-catenin, mTOR, MAPK, and PKB/Akt, and enhancing stem cell markers. In vitro, ICK upregulation in response to serum starvation in HCT-8 cells was reversible, and its knockdown hindered proliferation and β-catenin signaling, inducing apoptosis.
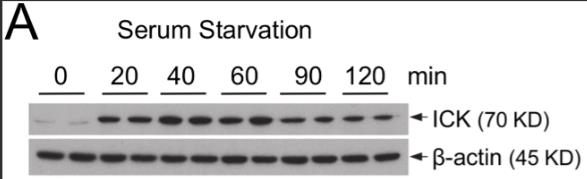
Fig1. Equal amount of total proteins from cell extracts were Western blotted against ICK and β-actin antibodies as indicated.
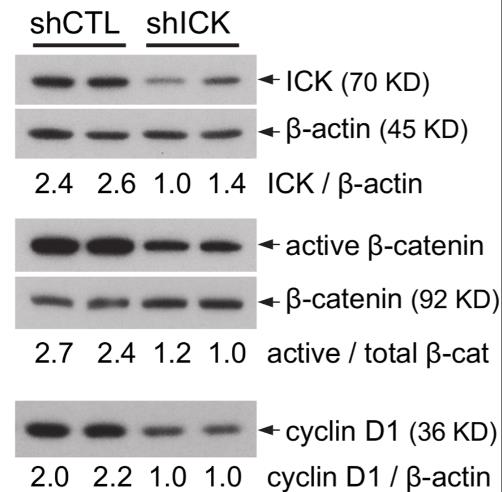
Fig2. Equal amount of total proteins from cell extracts was used on Western blot.
Case 2: Chen T, et al. PLoS One. 2013
ICK/MRK, MAK, and MOK are closely related protein kinases with unclear biological roles and regulatory mechanisms. Despite similarities in their catalytic domains, their C-terminal non-catalytic domains vary, suggesting potential functional diversity. This study explores their expression patterns in the intestine, revealing distinct spatio-temporal distributions and developmental expression dynamics. Notably, ICK expression increases in human colon cancer and mouse intestinal adenomas, while MOK expression decreases in adenomas, highlighting potential roles in intestinal health and disease.
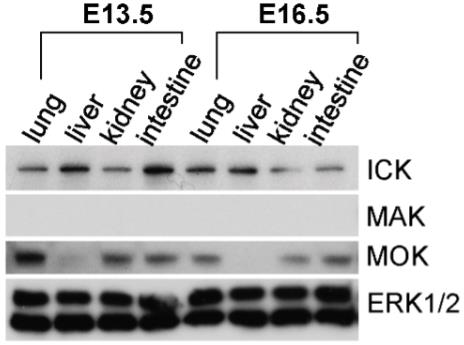
Fig1. Expression of ICK/MAK/MOK proteins in embryonic mouse tissues.
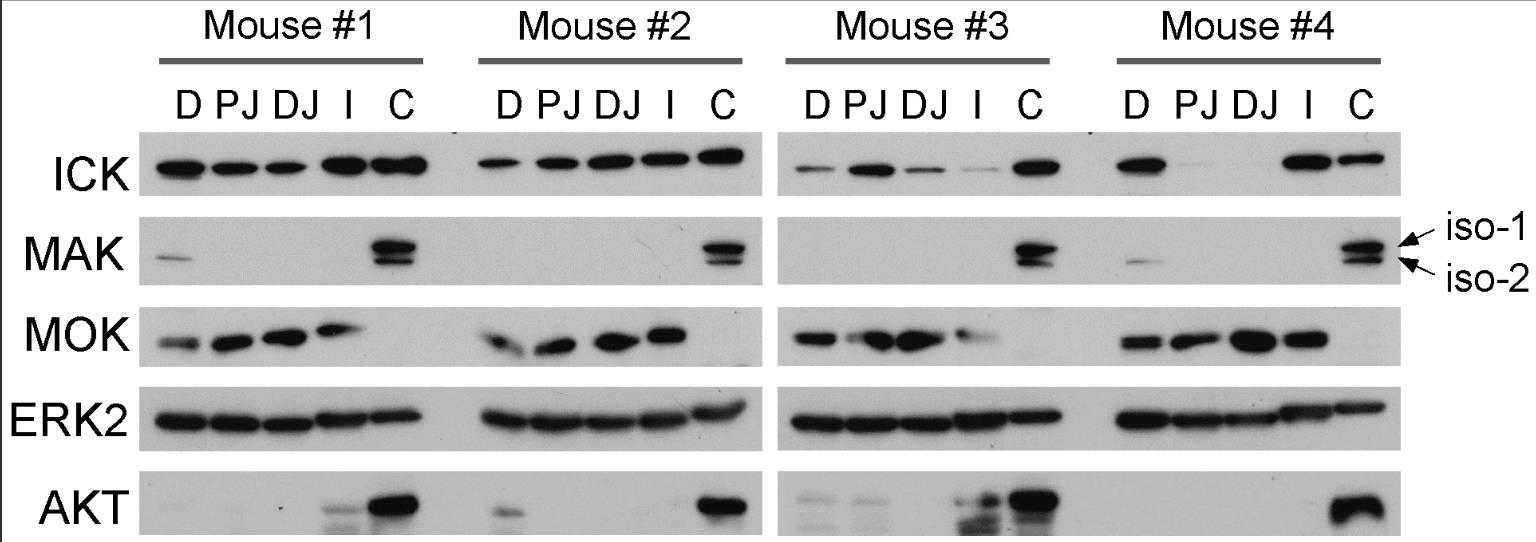
Fig2. Expression of ICK/MAK/MOK proteins along the duodenum-to-colon axis in the intestine.
Recombinant Mouse Ick protein, which refers to the protein encoded by the Ick gene in mice, is a serine/threonine kinase that plays a crucial role in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. The Ick gene is known to be involved in various cellular processes, including the control of the cell cycle and the regulation of gene expression.
In the context of research, recombinant Mouse Ick protein can be utilized in various experimental setups to study its function and the effects of its manipulation. This can involve the use of the protein in cell culture models to understand its role in cell signaling pathways, or in assays to investigate its kinase activity.
The practical applications of recombinant Mouse Ick protein are broad and include drug discovery and development. For instance, if Ick is found to be involved in the pathology of a particular disease, such as a type of cancer, the recombinant protein can be used to screen for potential therapeutic compounds that could modulate its activity. Additionally, understanding the role of Ick in cell division can provide insights into the development of new treatments for conditions characterized by abnormal cell growth.
Moreover, the study of Ick protein may also contribute to the broader understanding of cell cycle regulation, which is fundamental to many areas of biology and medicine. This knowledge can be applied to the development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored to the specific molecular characteristics of an individual's disease.
In summary, recombinant Mouse Ick protein is a valuable tool in the research and potential therapeutic development related to cell cycle control and the treatment of diseases associated with dysregulated cell proliferation.
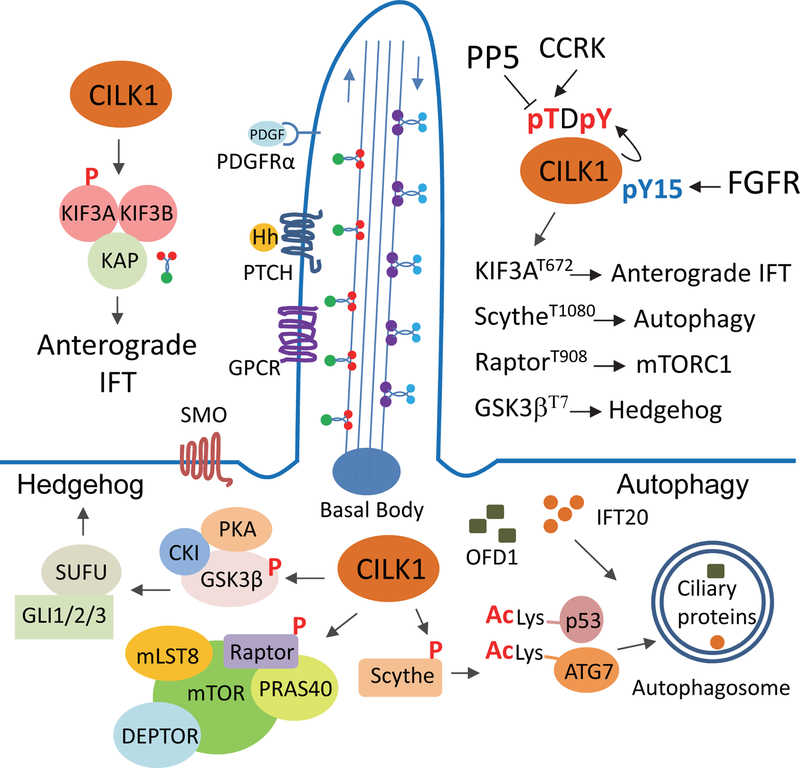
Fig1. A working model for CILK1 signalling. (Zheng Fu, 2019)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All Ick Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Ick Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


