Recombinant Human CST3 protein(Ser27-Ala146), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CST3-3172H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human Cystatin-C (NP_000090.1) (Ser 27-Ala 146) was expressed in HEK293 with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Availability | April 20, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-146 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its ability to inhibit papain cleavage of a fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-FR-AMC. The IC50 value is < 12 nM. |
| Molecular Mass : | The mature recombinant human Cystatin-C consists of 131 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 14.8 kDa. The rh Cystatin-C migrates as approximately 17 kDa band in SDS-PAGE as a result of glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CST3 cystatin C [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CST3 |
| Synonyms | CST3; cystatin C; cystatin C (amyloid angiopathy and cerebral hemorrhage); cystatin-C; cystatin 3; cystatin-3; gamma-trace; post-gamma-globulin; bA218C14.4 (cystatin C); neuroendocrine basic polypeptide; ARMD11; MGC117328; |
| Gene ID | 1471 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000099 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000090 |
| MIM | 604312 |
| UniProt ID | P01034 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CST3-2641H | Active Recombinant Human CST3 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CST3-1847H | Recombinant Human CST3 Protein (Ser27-Ala146) | +Inquiry |
| Cst3-2205M | Active Recombinant Mouse Cst3 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Cst3-4094R | Recombinant Rat Cst3 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CST3-1846H | Recombinant Human CST3 Protein (Ser27-Ala146), C-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| CST3-4309H | Native Human CST3 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CST3-26152TH | Native Human CST3 | +Inquiry |
| CST3-8100H | Native Human Cystatin C (Cystatin 3) | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CST3-2991HCL | Recombinant Human CST3 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CST3-1938RCL | Recombinant Rat CST3 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CST3-2470MCL | Recombinant Mouse CST3 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Jurczak P, et al. Chembiochem. 2024
Human cystatin C (hCC) inhibits cysteine proteinases but can form toxic amyloids in disease. It’s active outside cells and inactive inside, yet how it crosses into cells wasn't clear. This study used HeLa cells and found that hCC enters mainly through endocytosis, and its form—monomer or dimer—doesn't significantly affect this. This insight helps to better understand hCC's roles inside and outside the cell.
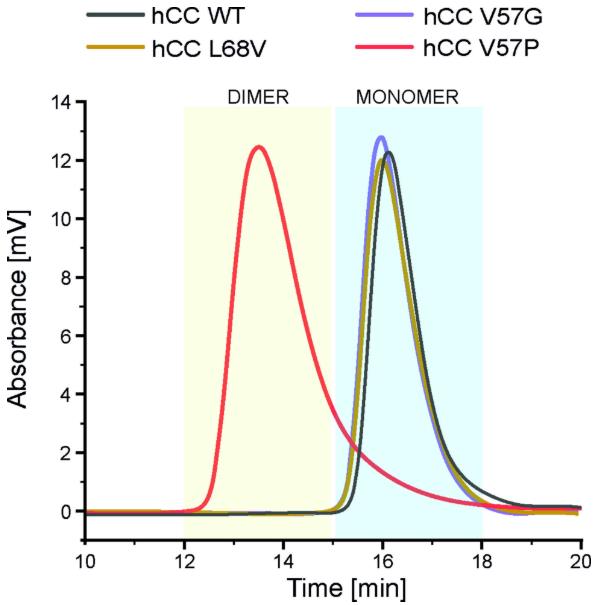
Fig1. Chromatograms representing the oligomeric states of hCC WT (monomer) and its three mutants hCC V57G (monomer), hCC L68V (monomer), and hCC V57P (dimer).
Fig2. Live cell imaging of hCC penetration into HeLa cells.
Case 2: Modenbach JM, et al. Nat Commun. 2025
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is when the pancreas digests itself due to early activation of trypsinogen by CTSB. Normally, CTSL degrades trypsin to prevent this, while CST3 inhibits both CTSB and CTSL. In CST3-deficient mice, CTSB activity increases, worsening AP. When CST3 is cleaved by trypsin, it fails to inhibit CTSB and instead enhances its activity, intensifying the enzyme cascade in AP.
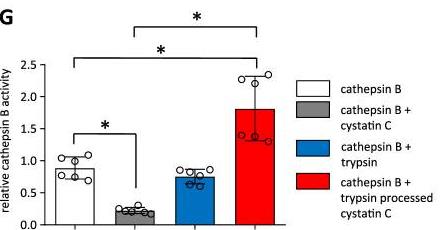
Fig1. Measurement of CTSB activity.
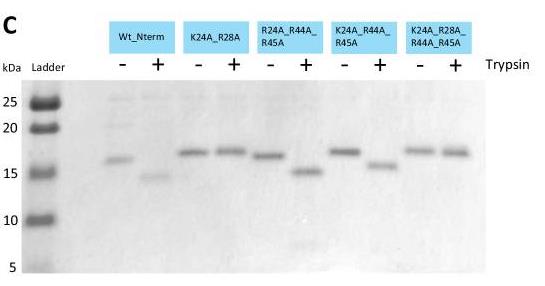
Fig2. SDS-PAGE analysis of cystatin C wild-type and mutants where several possible cleavage sites were substituted with alanine residues.
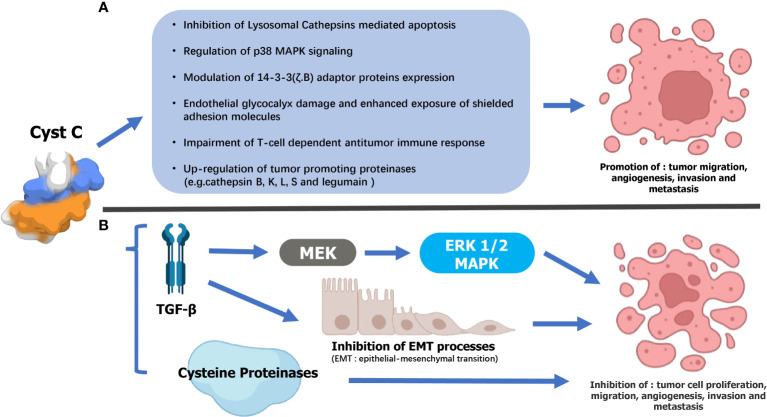
Fig1. Supposed mechanisms underlying the dual opposing effects of Cystatin C (Cyst C) on urogenital malignancy progression. (Li Ding, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CST3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CST3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


